Management Information SystemIs Information Critical?The information we have is different from what we want, the information we want is further from the information we need, and the information we need is unavailable. Information is a resource
Why do We Need Information?To ensure effective and efficient decisions and lead the organization's prosperity. What is MIS?MIS refers to Management Information System. It is a computer-based system that gives administrators the resources to effectively organize, assess, and manage their departments. The three sub-components are: Management, Information, and System A system prioritizes a moderate level of integration and a global perspective. Information stressing processed data in the context in which end users use it, and management focuses on using such information systems for managerial decision-making. Concept of MISThe data will be given to MIS, and there are processing logic, computers, human beings, and database in MIS. These are the factors compromising MIS. So, the data is given to the systems, and humans process the data; databases also process the data, and the computers will reduce the processing time. The information is generated from that data. As far as decision-making is concerned, intelligence is working, and then the designs are being made. So, intelligence is the basis of judgment and intuition, and accordingly, with the help of skill and experience, some design is being made, and choices are being generated. By selecting the best options and the decision is implemented. Hence the implementation process goes on. Whenever a few decisions are being applied, the performance is generated, the performance is evaluated, and feedback monitoring is done. Furthermore, the data is brought from it, and that data is given for the processing logic, computers, human beings, and databases. From that, information is collected, and more decisions are taken, and this is what we call the concept of MIS. What is the Role of MIS?MIS is a tool for simplifying different management complexities to increase business and manage complexities. The companies are growing at a large scale, and to simplify those things or the company's working processes, many departments are getting connected to marketing and related operations. Operations are connected to human resources, and human beings are connected to financial management. These people are getting associated with the quality control and research department, and all these departments need to work together in such a manner the complexity is being increased. MIS is a magic tool; if we use it, we can improve our business, and providing the information to the right person at the right place is very important. We are increasing the business complexities of the technological revolution taking place day by day. People have started using laptops, smartphones, and different kinds of operating systems are growing. Research and development are going on, and when new technologies come into the market, which is far more beneficial than the previous technology. There is also an explosion of data, like millions of videos uploaded on YouTube. Millions of transactions will occur by segregating and analyzing the data to information; reports are being created with the help of MIS. So that is why MIS is a very useful tool for business people. Increased Management ComplexitiesThere is also an increase in management complexities by management science technologies, decision-making, and the onset of computers. Decisions need to be taken perfectly, and previously, management was simple, and nowadays, it has become a complex process. Functional uses of MISThe practical use of MIS is to enhance the quality of our operations, what a company does, and the quality of services offered by the company. MIS is also used to increase efficiency and to increase transparency, and also increase speed in decision-making. Strategic Uses of MIS
Noteworthy Turn of Events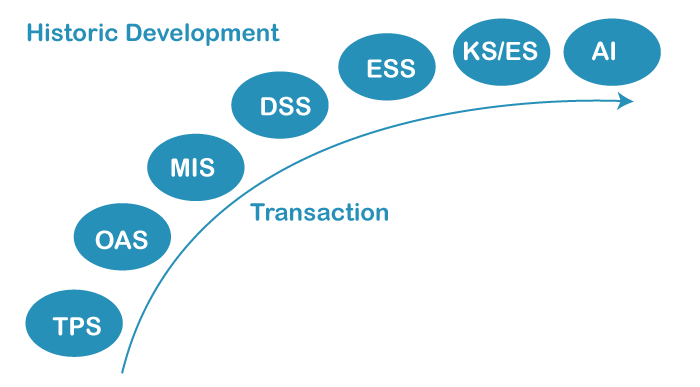
The idea of MIS has changed considerably throughout the long term. During the 50s and 60s, the administration saw the capability of PCs to deal with a lot of information quickly and precisely. Electronic Information Handling (EDP) offices comprised the divisions engaged with such exercises. The focal point of EDP was Record-Keeping, like bookkeeping and finance information. During the 70s, there was a recognizable shift from information to data. The attention was on something other than information but rather on investigating authoritative information. There was a shift in perspective. Such an idea came to be commonly known as "The executive's Data Framework." During the 70s, the top administration depended on the staff of EDP and MIS to supply vital data. The 80s saw the PC (PC) upheaval. The PC and the work area representation changed the image. The greatest result for such direct use was the "imagine a scenario in which" examination capacity. So this prompted the rise of Choice Emotionally supportive networks (DSS). The data and choice-hungry supervisors of the 80s saw enormous likely in the master frameworks because of tremendous development in the Computerized reasoning region. Joined with the DSS reasoning, the master frameworks could supply a prevalent administrative data support class known as Information Based Frameworks (KBS). The EDP designated the functional degree of the executives. Endeavors were made to give data to top administration, known as Leader Data Framework (EIS). The above outline is the flowchart of the authentic improvement of MIS. During the 1950s, the Value-based Handling Framework (TPS) kept the exchanges in the frameworks, and the work was finished on handling exchanges. During the 1960s, the Workplace Computerization Framework (OAS) occurred, and workplaces were robotized with the assistance of recording exchanges. A short time later, during the 1970s, the Administration Data Framework (MIS) existed. With the assistance of this MIS, choices were handily taken, which is why the Choice emotionally supportive network appeared. By applying the apparatus and telling the abilities of the DSS, the Leader Emotionally supportive network (ESS) they have appeared. It will uphold the leaders on what choices we want to take, whether they were right, and their impact on choices was determined in the ESS. Subsequently, Master Frameworks (ES) started, directing high-level chiefs to settle on master choices. To wrap things up, Man-made brainpower (computer-based intelligence) appeared, which programs Robots to work falsely, and innovation has changed, and it is the time of the 21st hundred years.
Attributes of the Executive's Data Framework
Hierarchical Frameworks and MISThere are dependably three layers in the organization. The top layer is high-level administration, which is the President, MD, or the directorate of the organization, who is liable for raising assets for the organization and pursuing hard decisions. With fewer individuals, key choices are assumed to control the high-level administration. In any case, they are huge green individuals who will influence center-level and functional-level administration. 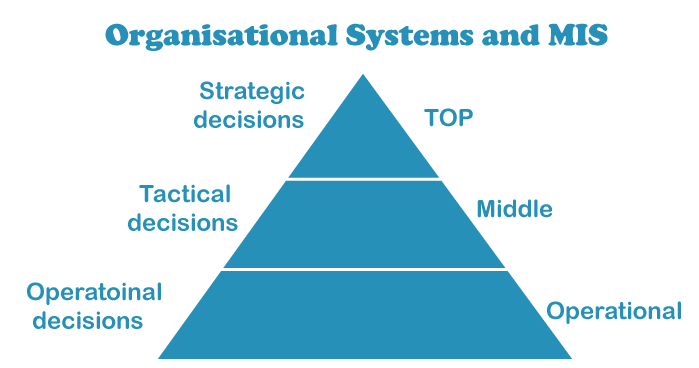
In center-level administration, supervisors will work and be liable for the regular working of the organization, and they manage specialized choices. In functional level administration, it takes the functional choices. Here low-level specialists will work for the day-to-day compensation and ordinary positions, individuals make the item here, and workers will work in this layer. The low-level administration will require help to see what center-level administration is, and center-level administration needs help understanding what high-level administration is. The high-level administration can see the center and low-level administration, and the center-level administration can see the low-level administration. The fundamental objective of MIS is to give the ideal data with impeccable timing at the right level. 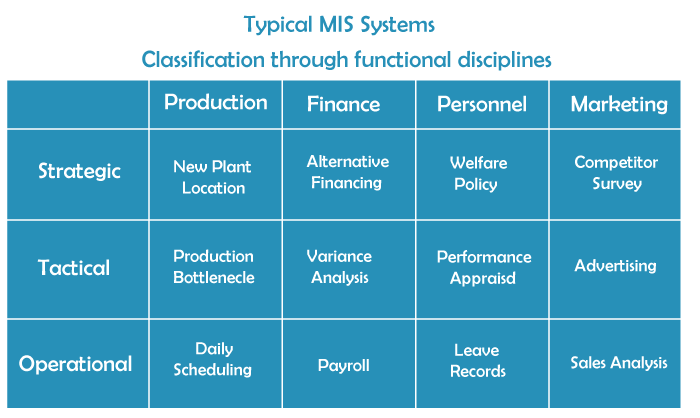
Functional level Data assortment spread exactness and practicality are significant at the functional level. The strategic and key level At this level, the significance of the watchword is assessed. At long last, productivity at the functional level and viability at the strategic and vital levels happen. The authoritative frameworks and MIS worried about planning hierarchical level and construction into the plan of any MIS are vital to effective execution. The innovation part Data Innovation (IT) has changed how associations capability and complete their exercises. On a very basic level, PCs have changed MIS from a theoretical idea to a powerful framework that gives proficiency and straightforwardness in the association. 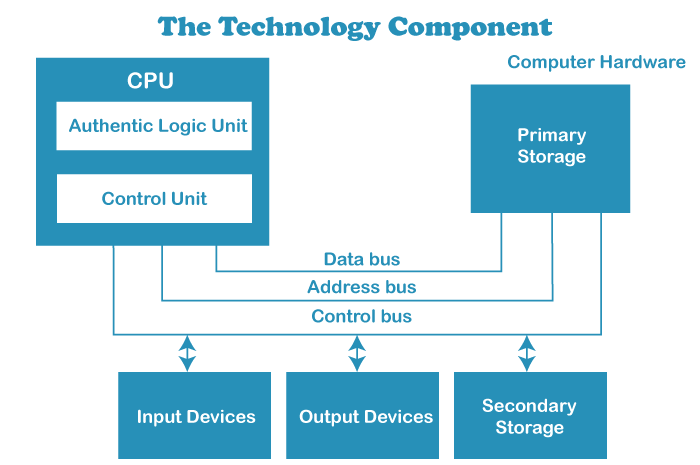
Information base innovation The focal archive of hierarchical information is at the core of an association's data frameworks. The information implies crude realities or subtleties. The data set is a common assortment of sensibly related information. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










