Introduction to sap PP (Production Planning)What is Production Planning?Production Planning is the method of aligning demand with manufacturing resources to establish production and supply plans for finished goods and parts. SAP PP is an important module. For example, it tracks and records the process the expected and real costs of the manufacturing process. It is fully compatible with SAP's other modules: SD, MM, QM, and FICO & PM. Organization structure in SAP PPIn the system, manufacturing plant locations and storage inside the plants should be accessible in every live production planning module. Importance in Production Planning of plant and storage locations-
Master Data is SAP PPIn general, master data is immutable for any enterprise and, depending on the necessity, is very rarely altered. In the Production Preparation module, there are five master details to be preserved. 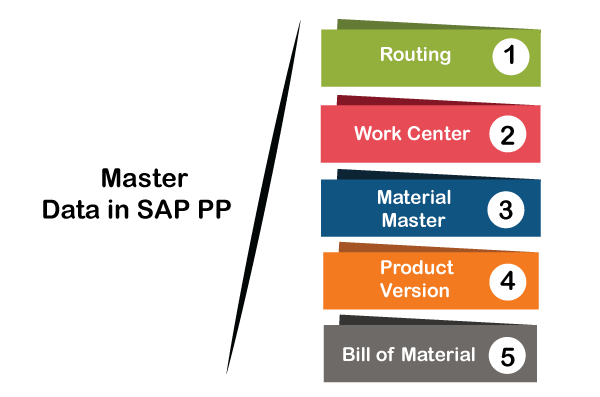
1. Material masterThe commodity master includes details on all the goods procured, manufactured, processed and distributed by a corporation. It is a number that uniquely distinguishes a record of the material master, and thus a material. Materials are grouped together with the same basic characteristics and assigned to a category of materials such as finished materials, raw materials, etc. It is used for the purposes below:
2. Bill of Material (BOM)The material bill is a complete, formally organized list of the components and the quantity needed for creating or assembling the product. BOMs are used in the planning and costing of material specifications. You can build up to 99 alternate BOMs for a single commodity as well. For goods with variants, you can build Super BOM, which has all possible components used to manufacture various types of variants. The suitable component is selected based on the characteristics chosen in the order of sale. For example, all types of frames (with different colors and sizes) can be used in the Product Cycle, and the desired frame is selected by order of production on the basis of the color and size chosen in the order of sale. 3. Work CenterA Work Center is a system or collection of machines in which manufacturing processes are performed. Job center are included in the worklist events (Routings). It provides the details for:
4. RoutingRouting is nothing but a series of procedures done at the Job Site. It specifies the system time, work time, etc., for the execution of operations. It is also used for the scheduling of operations and the routine estimation of the cost of the object. 5. Production versionThe production version is a mixture of BOM and production Routing info. It is a connection between BOM & Routing, which defines the manufacturing phase. There can be many production versions to produce the product according to various manufacturing processes. Production Planning CycleProduction Planning and Control consists of 2 obvious preparing and execution procedures. PlanningGenerally, development planning is carried out using a budgeted revenue schedule. According to the production cycle periods, preparation is based on the Sales Schedule to fulfill the sales demands. In the type of expected independent need, demand for the commodity is entered by demand management (PIR). This demand management data becomes the input to Commodity Requirement Preparation (MRP). Using the master data such as Bill of Material (BOM) and usable existing plant stocks, MRP tests for the supply of various raw materials required for manufacturing at different times. In supply shortages, procurement specifications are produced for commercially procured products and expected orders are created for in-house assembled materials. These purchase requisitions and planned orders will initiate the procurement cycle and the production cycle. Since MRP works with infinite capabilities, to avoid any capacity bottlenecks, capacity leveling must be done. ExecutionThese planned orders are translated to production orders and scheduled as per the production timings using master data such as routings. Production orders are issued on the shop floor by the Production Supervisor, and material availability checks can also be performed to check whether any missing components are present. Output is carried out on the basis of routing activities where master data is identified against each routing activity, such as the Work Center. If the product has been completed, the order confirmations are carried out, and products for material use and receipt of goods are put against the order. The order is then given the status of Delivered (DLV), and the material is received at the desired place of storage. To quantify volume variances by the managing team, the production order typically has to be set to legally finished status at the end of the month before order resolution. 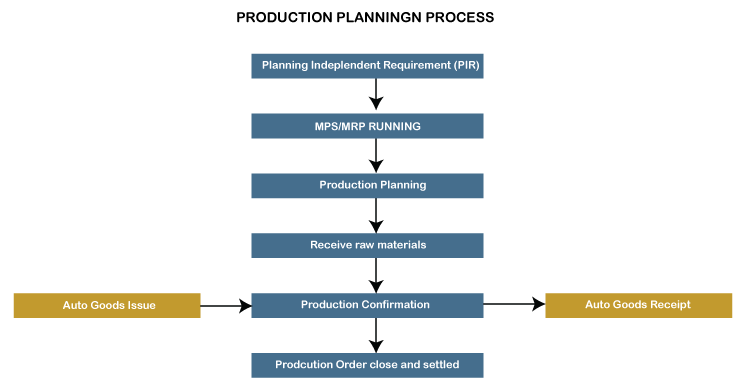
Demand ManagementDemand Management's role is to forecast amounts of demand and distribution dates for finished goods and essential assemblies. PIR (planned autonomous requirements) and consumer requirements are used in Market Management. Planning methods for a commodity must be established. It reflects the methods of development for planning and output. We have two ways to do this. Make to Stock: The manufacturing of goods without orders for sale, i.e. storage, is carried out independently of orders. Make to Order: This technique refers to the manufacturing of material for a particular individual order or line object. Material Requirement Planning (MRP)MRP identifies any shortages and produces the appropriate procurement components. It calculates net requirements and generates planned orders for in-house manufactured materials, and requires raw materials for purchase. It schedules lead time and calculates planned orders for production dates. It blasts the BOM and produces tender proposals at each stage of the BOM. Capacity Planning & LevelingCapacity Preparation is used to assess overloads of work center capacity and shift orders to avoid any bottlenecks. MRP creates capacity requirements on the Work Center and because MRP operates with unlimited capacity without taking into account any capacity limitations and schedules all on the work center. It is needed to level the capability at the work center. The capability may be balanced at each work center via a planning table to create a restricted production schedule. Production OrdersThe output of the MRP would be "Planned Orders," which need to be converted to production orders for further implementation of the process. The Production Order is a signature receipt feature that is not influenced by the MRP run than the Planned Orders.
Production Order ConfirmationWhen products are physically assembled on the factory floor, the order for production must be checked. During confirmation, components can be consumed automatically by means of a back flushing system, and products can be collected automatically using a Control Key in routing service. However, manual issue and receipt of products may be done separately from confirmation instead of the movement of automotive goods. Any failure to move goods due to a component supply shortage can be reprocessed manually. Activity costs, such as equipment, labor, etc., will also be changed on a real basis in the manufacturing order during validation. After final confirmation and final delivery of the objects, the order shall be granted the status of CNF (Confirmed) and DLV (Delivered). If the confirmation is incorrectly posted, we can cancel the confirmation and post it with the correct data again. Production Order CloseThe order should be technically completed after the production order has been or we do not wish to further carry out the order. It is deleted from the stock/requirement list after the order has been granted TECO status and is no longer considered in the process of planning the material requirement. All dependent reservations will also be deleted from the system. Next, let's look at every SAP PP process and learn how to run the SAP PP module.
Next TopicHard Drive for Gaming
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









