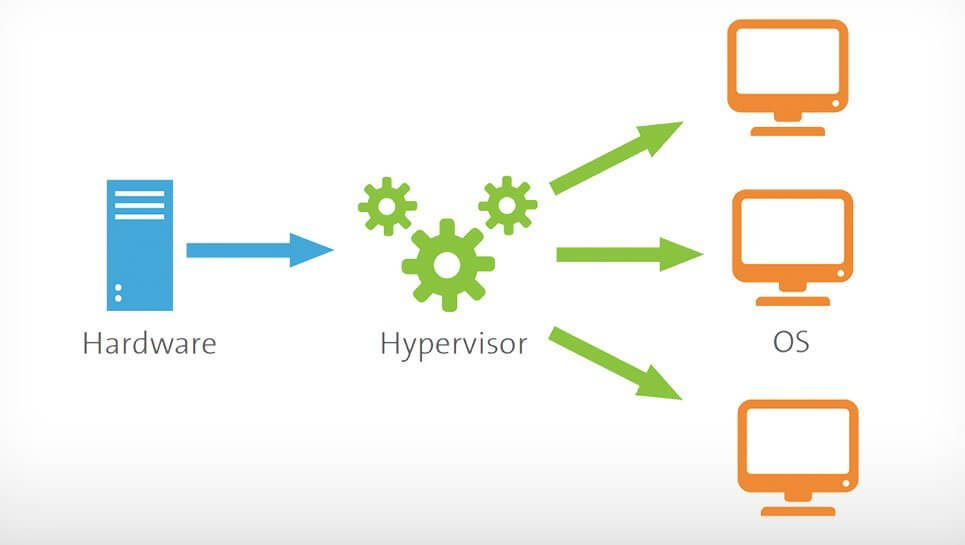
What is a hypervisorA hypervisor, also known as a virtual machine monitor or VMM. The hypervisor is a piece of software that allows us to build and run virtual machines which are abbreviated as VMs. A hypervisor allows a single host computer to support multiple virtual machines (VMs) by sharing resources including memory and processing. What is the use of a hypervisor?Hypervisors allow the use of more of a system's available resources and provide greater IT versatility because the guest VMs are independent of the host hardware which is one of the major benefits of the Hypervisor. In other words, this implies that they can be quickly switched between servers. Since a hypervisor with the help of its special feature, it allows several virtual machines to operate on a single physical server. So, it helps us to reduce:
Kinds of hypervisorsThere are two types of hypervisors: "Type 1" (also known as "bare metal") and "Type 2" (also known as "hosted"). A type 1 hypervisor functions as a light operating system that operates directly on the host's hardware, while a type 2 hypervisor functions as a software layer on top of an operating system, similar to other computer programs. Since they are isolated from the attack-prone operating system, bare-metal hypervisors are extremely stable. Furthermore, they are usually faster and more powerful than hosted hypervisors. For these purposes, the majority of enterprise businesses opt for bare-metal hypervisors for their data center computing requirements. While hosted hypervisors run inside the OS, they can be topped with additional (and different) operating systems. The hosted hypervisors have longer latency than bare-metal hypervisors which is a very major disadvantage of the it. This is due to the fact that contact between the hardware and the hypervisor must go through the OS's extra layer. The Type 1 hypervisorThe native or bare metal hypervisor, the Type 1 hypervisor is known by both names. It replaces the host operating system, and the hypervisor schedules VM services directly to the hardware. The type 1 hypervisor is very much commonly used in the enterprise data center or other server-based environments. It includes KVM, Microsoft Hyper-V, and VMware vSphere. If we are running the updated version of the hypervisor then we must have already got the KVM integrated into the Linux kernel in 2007. The Type 2 hypervisorIt is also known as a hosted hypervisor, The type 2 hypervisor is a software layer or framework that runs on a traditional operating system. It operates by separating the guest and host operating systems. The host operating system schedules VM services, which are then executed on the hardware. Individual users who wish to operate multiple operating systems on a personal computer should use a form 2 hypervisor. This type of hypervisor also includes the virtual machines with it. Hardware acceleration technology improves the processing speed of both bare-metal and hosted hypervisors, allowing them to build and handle virtual resources more quickly. On a single physical computer, all types of hypervisors will operate multiple virtual servers for multiple tenants. Different businesses rent data space on various virtual servers from public cloud service providers. One server can host multiple virtual servers, each of which is running different workloads for different businesses. What is a cloud hypervisor?Hypervisors are a key component of the technology that enables cloud computing since they are a software layer that allows one host device to support several virtual machines at the same time. Hypervisors allow IT to retain control over a cloud environment's infrastructure, processes, and sensitive data while making cloud-based applications accessible to users in a virtual environment. Increased emphasis on creative applications is being driven by digital transformation and increasing consumer expectations. As a result, many businesses are transferring their virtual computers to the cloud. Having to rewrite any existing application for the cloud, on the other hand, will eat up valuable IT resources and create infrastructure silos. A hypervisor also helps in the rapid migration of applications to the cloud as being a part of a virtualization platform. As a result, businesses will take advantage of the cloud's many advantages, such as lower hardware costs, improved accessibility, and increased scalability, for a quicker return on investment. Benefits of hypervisorsUsing a hypervisor to host several virtual machines has many advantages:
As an application requires more computing power, virtualization software allows it to access additional machines without interruption. Container vs hypervisorContainers and hypervisors also help systems run faster and more efficiently. But they both do these things in very different manner that is why are different form each other. The Hypervisors:
Containers:
Containers and hypervisors have various functions. Containers, unlike virtual machines, contain only an app and its associated services. Since they are lighter and more compact than virtual machines, they are often used for rapid and versatile application creation and movement. Security considerations for hypervisorsA virtual machine (VM) creates a separate world from the rest of the device, so whatever runs inside it won't mess with everything else on the host hardware. Since virtual machines are isolated, even though one is compromised, the rest of the system should be unaffected. However, if the hypervisor is compromised, it may trigger issues with all of the VMs that it handles, putting the data in each one at risk. Depending on the type of hypervisor, security protocols and specifications can differ.
Next TopicWhat is data integrity
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









