What is BCM?Tragedies cannot be planned for, but can mitigate them. Whether it's floods and fires, crucial personnel collisions, server collisions, malware, ransomware assaults, or even financial crises, you need a strategy for strength, resilience, and recovery. Although it is frequently referred to as "common decency," it is really about taking accountability and carrying business continuity sincerely. Business continuity management (BCM) is described as a foundation's sophisticated preparation and planning for sustaining business operations or rapidly restarting after a catastrophe. It also entails identifying associated consequences such as flood, fire, or cyber-attacks. Business executives devise methods to promote and anticipate specific disasters before they occur. The plans are then checked to ensure that they operate, and the phase is reviewed regularly to make sure that it is updated. BC (Business continuity) is described as a foundation's opportunity to sustain delivering goods or services at appropriate predetermined stages in the aftermath of a disruptive event. BCM Framework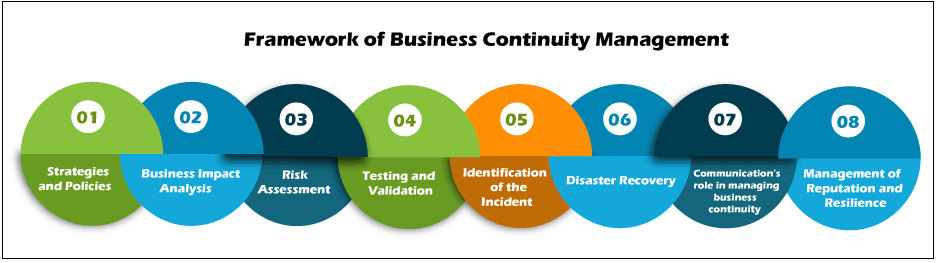
The business continuity management framework includes the following phases. They are discussed below-
Continuity management entail more than just responding to a natural catastrophe or a malware infection. It all starts with the processes and regulations created, evaluated, and implemented when an issue arises. The policy establishes the project's context, key stakeholders, and management style. It must formulate why business continuity is required, and leadership is essential during this step. Realizing who is in charge of creating and updating a business continuity management guideline is one element. The other objective is to establish the company in charge of execution. Leadership brings order to what can be a turbulent situation for everyone involved. The range is also essential; It describes what is the group's definition of business continuity. Duties and responsibilities must also be allocated during this process. These may be apparent duties about job components or role expectations depending on the type of disturbance observed. Strategy, leadership, context, and responsibilities must all be widely communicated and endorsed in all instances.
The impact evaluation is an archiving document that outlines the data held by your corporation, where it is processed, how it is obtained, and how it is obtained. It defines which information is the most crucial and how much leisure time is justifiable if that information or software is inaccessible. While businesses strive for 100 percent throughput, this is not always feasible even with duplicated systems and storage abilities. It is also the stage at which you must evaluate your recovery period aim, which is the maximum time needed to restore apps to as functioning economy in a severe service interruption.
Risk manifests itself in a variety of ways. A Business Value Evaluation as well as a Hazard and Vulnerability Assessment should be carried out. Attacks might include bad people, internal teams, competitors, market trends, internal and overseas policy situations, and natural phenomena. Creating a risk evaluation that recognizes possible threats to the organization is a crucial part of the strategy. The risk assessment determines the wide range of events that may impact the organization. The first task is to select possible threats, which can have far-reaching consequences. It includes the following:
Regulated businesses must evaluate the consequences of negligence, resulting in significant monetary fines and penalties, higher financing criticism, and the deterioration of stance, accreditation, or legitimacy. Each risk must be outlined and explained in detail. The company must then assess each risk's probability and each one's possible effects in the next phase. When it comes to strategy evaluation, possibility and capability are necessary procedures.
Consequences and their consequences must be monitored regularly, quantified, and evaluated. Once remediation plans are developed, they should be assessed to ensure that they work properly and coherently.
Determining what constitutes an event is critical in business continuity. In policy papers, activities should be specifically outlined, as should what or who can cause an event to happen. These inciting motives should result in the implementation of the business continuity plan as described and the group's mobilization.
What exactly is the distinction between business continuity and disaster recovery? The latter is the overriding strategies that direct activities and set policy. When an accident happens, disaster recovery takes place. The implementation of groups and decisions in disaster response is referred to as disaster recovery. It is the result of the actions done to identify and prevent dangers. In contrast to broad organizing, incident management is concerned with specific incident reactions. Due to an incident, one of the most critical tasks is to compare notes and evaluate the reaction, and then revise plans as needed.
Communication is a critical component of business continuity management. One element is crisis interaction, which ensures consistent procedures in place for interacting with clients, workers, senior executives, and investors. During and after an event, continuous communication structures are helpful. Emailing must be compatible, precise, and delivered by a specific enterprise voice. Numerous communication surfaces are involved in crisis management, such as the development of tools to indicate progress, critical requirements, and concerns. Various stakeholders may use different modes connections, but they should all be premised on similar information sources.
The dangers of not creating a business continuity plan are substantial. The lack of preparation suggests that the firm is ill-prepared to deal with pressing problems. These consequences can catch a business off guard and lead to a slew of other issues, such as:
Types of Business continuity management (BCM)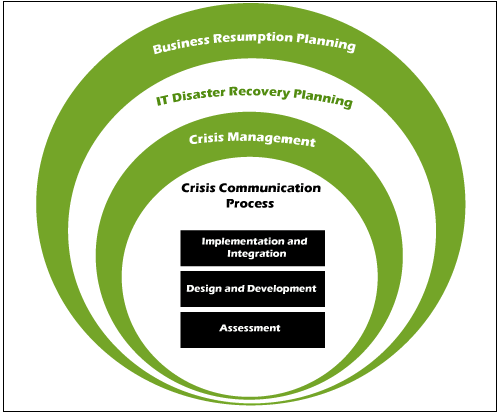
Business continuity is defined further by Business Continuity Management as the implementation of systems, proposals, and decisions that provide security or alternate solution operating modes for those operations or business systems that, if disrupted, would otherwise result in a severely damaging or usually dangerous failure to the business. Here, we discussed four following kind of Business continuity management are given below- 1. Crisis management planThe crisis management plan establishes the critical communications networks required to ensure workplace safety, supports data, direction and guidance, and organizes intense. 2. Disaster recovery planThe term "disaster recovery plan" generally includes the plans to reestablish crucial IT (information technology) services and applications that support crucial business processes. 3. Business resumption planThe business resumption plans are tailored to each important company feature and outline the practical actions to facilitate the procedure. Creating and Documenting a Business Continuity PlanOnce a company has determined its business development continuity orientation, it is essential to arrange and report those alternatives into a "living" strategy. This ensures that the strategy can be retained as the company evolves. The outcome should be business continuity information that has been adequately dispersed and includes all of the information necessary to restore rapidly from a disruption. Emergency plans, restoration groups, and event proposals will also need to be manufactured and publicized during this step. 
Advantages of BCMThe key benefits of business continuity management are mentioned below-
Disadvantages of BCMThe drawbacks of business continuity management are-
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









