Top 35+ Most Asked Cyber Security Interview Questions and AnswersFollowing is a list of most frequently asked Cyber Security interview questions and answers. 1) What is Cyber Security? / What do you know about Cyber Security?Cyber Security is a practice of protecting internet-connected systems such as hardware, software, programs, computers, servers, mobile devices, electronic systems, networks, and data from malicious digital attacks. The main purpose of cyber security is to protect against cyberattacks like accessing, changing, or destroying sensitive information from your computer system. The cyber attackers are mainly aimed at accessing, changing, or destroying sensitive information, extorting money from users, or interrupting normal business processes. Cyber Security is also known as computer security, information technology (IT) security, cybersecurity etc. It is used to measure the combat threats against networked systems and applications, whether those threats originate from inside or outside of an organization. We can divide the term cyber security into two parts: cyber and security. Cyber refers to the technology that includes systems, networks, programs, and data of an internet-connected system. The word security specifies the protection of the systems, networks, applications, and information. 2) What is Cyber Crime? Give some examples of Cyber Crime.Cyber Crime is just like regular crime but happens on the Internet. Following are some examples of Cyber Crime:
3) Why is Cyber Crime increasing day by day every year?Cyber Crime is increasing day by day every year because of the following reasons:
4) What is the main goal of Cyber Security?The main objective of cyber security is to protect data from cyber-attacks. It follows a principle called CIA trio. It is a security sector that provides a triangle of three connected principles. The CIA model is used to help organizations to develop policies for their information security architecture. There are three main components Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability of this CIA model. One or more of these principles is broken when it finds a security breach. This model provides a security paradigm to guide individuals through many aspects of IT security. 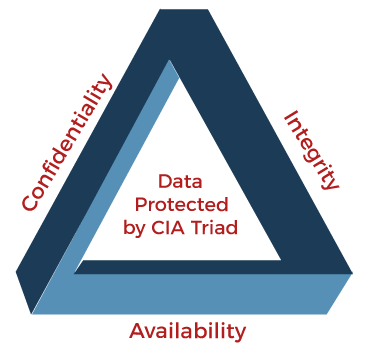
Let's see these three security aspects in detail: Confidentiality: Confidentiality is used to provide privacy to prevent unauthorized access to data. It ensures that the data is only accessible to those who are authorized to use it and restricts access to others. It restricts vital information to be exposed to the wrong hands. A good example of Confidentiality is Data encryption which is used to keep information private. Integrity: The Integrity principle is used to assure that the data is genuine, correct, and safe from unwanted threat actors or unintentional user alteration. It also specifies that the source of information must be genuine. If any changes are made, precautions should be taken to protect sensitive data from corruption or loss and recover from such an incident quickly. Availability: The Availability principle ensures that the information is constantly available and accessible to those who have access to it. It also ensures that any types of system failures or cyber-attacks do not obstruct these accesses. 5) What are the main advantages of cyber security?Following is a list of main advantages of cyber security:
6) What is the difference between IDS and IPS?A list of differences between IDS and IPS:
7) What are the key elements of Cyber Security?Following is the list of key elements of Cyber Security:
8) What is Cryptography?Cryptography is a technique or practice used to protect information from third parties called adversaries. It is a method of protecting information and communications through codes so that only those for whom the information is intended can read and process the data. In Cryptography, we also study several techniques for secure communication, mainly to protect the sensitive data from third parties that the data is not intended for. 9) What is the difference between a threat, vulnerability and risk?Generally, people think that threat, vulnerability and risk are the same, but there are some crucial differences between them: Threat: A threat can be any form of hazard capable of destroying or stealing data, disrupting operations, or cause harm in general. Some examples of threats are Malware, phishing, data breaches, and even unethical employees etc. Any type of threat may be harmful for the organization, so; it is essential to understand threats for developing effective mitigation and making informed cyber security decisions. Vulnerability: Vulnerability is a possible problem or a flaw in hardware, software, personnel, or procedures that can harm the organization. Threat actors can use these vulnerabilities to achieve their objectives. Some examples of vulnerabilities are given below:
To cope up with vulnerabilities, we have a method called Vulnerability management. It is the process of identifying, reporting and repairing vulnerabilities. Risk: Risk is a combination of threat and vulnerability. When we combine the probability of a threat and the consequence of vulnerability, it is called a risk. Risk is the likelihood of a threat agent successfully exploiting vulnerability. A formula to calculate risk: To control and manage the risk, we use a method called Risk management. It is a process of identifying all potential hazards, analyzing their impact, and determining the best course of action. This is an always running procedure used to examine the new threats and vulnerabilities regularly. By using this method, we can avoid or minimize risks. We can also accept or passed them to a third party according to the response chosen. 10) What is the difference between Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption in Cyber security?A list of differences between Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption in Cyber security:
11) What do you understand by CIA triad?CIA is an acronym that stands for Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. It is commonly known as the CIA triad. CIA is a model that specifies the guide policies for Information Security. It is one of the most popular models used by organizations.
12) What is the difference between Encryption and Hashing? / How is Encryption different from Hashing?Encryption and Hashing are techniques used to convert readable data into an unreadable data format, but they have some key differences. Differences between Encryption and Hashing
13) What is the difference between IDS and IPS?IDS stands for Intrusion Detection System. It is used to detect intrusions, and it warns administrators to be careful while preventing the intrusion. IPS stands for Intrusion Prevention System, and it facilitates the system to find the intrusion and prevent it. 14) What are some common Hashing functions/algorithms?Following is the list of some common and most used hashing functions/algorithms: Message-Digest Algorithm (MD5) Message-Digest Algorithm or MD5 is the latest and advanced form of MD4. It was introduced after finding severe security issues in MD4. MD5 is used to generate 128-bit outputs for a variable length of inputs. MD5 is the advanced version and the successor to MD4. It covers a lot of security threats but fails to provide full data security services. It is one of the most widely used algorithms, but the main issue with using MD5 is its vulnerability and collisions. Secure Hashing Algorithm (SHA) Secure Hashing Algorithm, or SHA, was developed by the National Security Agency. Later it was updated repeatedly to improve the security flaws in the old genre. Its latest and advanced version is SHA-2 that many firms are using for cryptographic purposes. Tiger Cipher Algorithm Tiger cypher algorithm is a faster and more efficient algorithm compared to Message Digest (MD5) and Secure Hashing Algorithm. It is mostly used in new generation computers and has a 192-bit hashing system. Its latest and advanced version is the Tiger2 algorithm which is more powerful than the Tiger algorithm. RIPMEND Algorithm Hans Dobbertin designed RIPMEND cryptographic hashing algorithm. It is created using the EU project RIPE framework and has a 164-bit digest. WHIRLPOOL Algorithm Vincent Rijmenand Paul Barreto designed the WHIRLPOOL algorithm. It accepts any messages of a length less than 2256 bits and returns a 512-bit message digest. Its first version was whirlpool-0, the second version was named Whirlpool-T, and the latest and most advanced version is Whirlpool. 15) What is the main purpose of Hashing?Hashing is required when we have to compare a huge amount of data. We can create different hash values for different data, and we can compare hashes too. Following is a list of some most important usage of Hashing:
16) What is a Firewall? What is the usage of it?A Firewall can be defined as a network security system set on the boundaries of the system/network and is used to monitor and control the network traffic. The main usage of Firewalls is to protect the system/network from viruses, worms, malware, threats etc. Firewalls can also be used to prevent remote access and content filtering. 17) What do you understand by VA (Vulnerability Assessment) and PT (Penetration Testing)?As the name specifies, VA or Vulnerability Assessment is the process of finding vulnerabilities or flaws on the target. In this process, the organization already knows that their system/network has flaws or weaknesses and wants to find these flaws and prioritize fixing them. PT or Penetration Testing is the process of deep searching and finding vulnerabilities on the target. In this process, the organizations set up all the possible security measures they could think of and test if there is any other way their system/network can be hacked. 18) What do you understand by Black Hat Hackers, White Hat Hackers and Grey Hat Hackers?Black Hat Hackers: Black Hat Hackers are the most critical types of hackers. They attempt to obtain unauthorized access to a system to disrupt its operations or steal sensitive and important data. Black Hat Hackers are also known as crackers. Black Hat Hacking is always illegal due to its malicious aim. The main purpose of Black Hat Hacking is to steal company data, violate privacy, cause system damage, block network connections, etc. White Hat Hackers: White Hat Hackers are used to accessing the system for penetration testing and vulnerability assessments. They never intend to harm the system; rather, than strive to uncover holes in a computer or network system. White Hat Hackers are also referred to as Ethical Hackers. Hacking done by White Hat Hackers is called Ethical hacking. It is not a crime, and it is considered one of the most difficult professions in the IT business. Many businesses hire ethical hackers to do penetration tests and vulnerability assessments. Grey Hat Hackers: Grey Hat Hackers are a combination of Black Hat Hackers and White Hat Hackers. They use elements of both black and white hat hacking techniques. They are supposed to act without malice, but for the sake of amusement, they can exploit the security flaw in a computer system or network without the permission or knowledge of the owner. The main goal of Grey Hat Hackers is to draw the owners' attention to the security flaw or hole in the network in the hope of receiving gratitude or a reward. 19) What is Traceroute in Cyber Security?In Cyber Security, a traceroute is used to show the packet path by listing all the points that the packet passes through. Traceroute is mainly used when the packet does not reach the destination. With the help of a traceroute, we can check where the connection breaks or stops to identify the failure. 20) What is a VPN? What is its use in Cyber Security?VPN is an acronym that stands for Virtual Private Network. It creates a safe encrypted tunnel across the internet by connecting a VPN server to a VPN client. Suppose a user has a VPN client installed on their machine. The VPN client then creates an encrypted tunnel to the VPN server, and the user can securely send or receive information over the internet. 21) What do you understand by Brute Force Attack? How can you prevent it?Brute Force Attack is a method of finding the right credentials by repetitively trying all the permutations and combinations of possible credentials. Brute Force Attacks are automated in most cases where the tool/software automatically tries to log in with a list of possible credentials. Following is a list of some ways to prevent Brute Force Attacks:
22) What do you understand by Port Scanning?Port scanning is the technique administrators, and hackers use to identify the open ports and services available on a host. Hackers use this technique to find information that can be helpful to find flaws and exploit vulnerabilities, and administrators use this technique to verify the security policies of the network. Following is a list of some most common Port Scanning Techniques:
23) What is the difference between the Host Intrusion Detection System (HIDS) and Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS)?As we know, HIDS and NIDS are both Intrusion Detection Systems and work for the same purpose, i.e., to detect intrusions. Difference between HIDS and NIDS:
24) What are the different types of Cyber Security?Every organization has some assets that are made up of a variety of different systems. These systems must have a strong Cyber Security aspect to make the organization work well. According to the devices used in Cyber Security, it can be divided into the following types:
25) What do you understand by Unicasting, Multicasting, and Broadcasting? What is the difference between them?Unicasting, Multicasting, and Broadcasting are the three methods used to transmit data over a network.
26) What are the steps used to set up a firewall?Following is a list of different steps used to set up a firewall:
27) What is Patch management in Cyber security? How often should we perform Patch management?In Cyber security, patch management is a process to keep the software on computers and network devices up to date and make them capable of resisting low-level cyber attacks. It is used in any software which is prone to technical vulnerabilities. We should perform patch management as soon as it is released. For example, when a patch is released for Windows, it should be applied to all machines as soon as possible. Same in network devices, we should apply patch management as soon as it is released. We should follow proper patch management for better security. 28) Which are the best Patch management tools or software? Why are they used?Patch management tools or software are used to ensure that the components of a company's software and IT infrastructure are up to date. The patch management tools work by tracking updates of various software and middleware solutions, and then they alert users to make necessary updates or execute updates automatically. Following is a list of the top 10 best patch management software or tools:
29) What is the full form of SSL? Why is it used?The full form of SSL is Secure Sockets Layer. This is a technology used to create encrypted connections between a web server and a web browser. SSL is used to protect the information in online transactions and digital payments to maintain data privacy. 30) What do you understand by a botnet?A botnet can be defined as a collection of infected internet-connected devices, such as servers, PCs, and mobile phones. These devices are infected with malware and controlled by it. The primary motive of a botnet is to steal data, send spam, launch distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, etc. It can also provide the user access to the device and its connection. 31) What is data leakage in the context of Cyber security?In the context of Cyber security, data leakage is an unauthorized transfer of data to the outside of the secure network. Data leakage can occur via email, optical media, laptops, and USB keys etc. 32) What do you understand by honeypots?Honeypots are the possible attack targets set up to see how different attackers attempt to exploit a network. Private firms and governments use this concept to evaluate their vulnerabilities, widely used in academic settings. 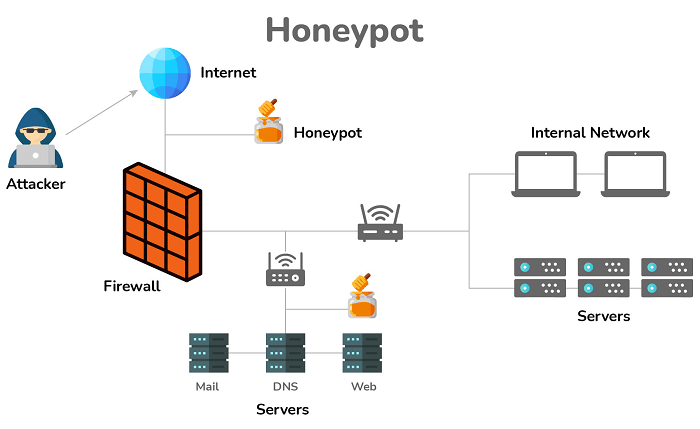
33) What do you understand by Shoulder Surfing?Shoulder surfing is a form of physical assault used by fraudsters by physically peering at people's screens to cheat while they type sensitive information in a semi-public area. 34) What are the most common types of cyber security attacks?The most common types of cyber security attacks are:
35) What do you understand by the MITM attack?The MITM attack stands for Man-in-the-Middle attack. As the name specifies, it is a type of attack where a third person pr an attacker intercepts communication between two persons. The primary intention of MITM is to access confidential information. 36) What is an XSS attack, and how can you prevent it?The full form of XSS attack is a Cross-Site Scripting attack. It is a cyberattack that makes hackers able to inject malicious client-side scripts into web pages. The XSS attacks are mainly used to hijack sessions, steal cookies, modify DOM, remote code execution, crash the server, etc. We can use the following practices to prevent XSS attacks:
37) What is the difference between stored XSS and reflected XSS?Difference between stored XSS attacks and reflected XSS attacks:
|
You may also like:
- Java Interview Questions
- SQL Interview Questions
- Python Interview Questions
- JavaScript Interview Questions
- Angular Interview Questions
- Selenium Interview Questions
- Spring Boot Interview Questions
- HR Interview Questions
- C Programming Interview Questions
- C++ Interview Questions
- Data Structure Interview Questions
- DBMS Interview Questions
- HTML Interview Questions
- IAS Interview Questions
- Manual Testing Interview Questions
- OOPs Interview Questions
- .Net Interview Questions
- C# Interview Questions
- ReactJS Interview Questions
- Networking Interview Questions
- PHP Interview Questions
- CSS Interview Questions
- Node.js Interview Questions
- Spring Interview Questions
- Hibernate Interview Questions
- AWS Interview Questions
- Accounting Interview Questions







