Amazon Relational Database Service(Amazon RDS)Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) makes it easy to set up, operate and scale relational databases in the cloud. It provides cost-efficient and resizable capabilities while automating time-consuming administration tasks such as hardware provisioning, database setup, patching, and backup. It frees you up to focus on your applications so that you can provide them with the fast performance, high availability, security and compatibility they need. Amazon RDS is available on multiple database instance types - optimized for memory, performance or I/O - and gives you six familiar database engines to choose from, including Amazon Aurora, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, Oracle Database and SQL Server Huh. You can use the AWS Database Migration Service to migrate easily or replicate your existing databases to Amazon RDS. What is Amazon RDS?Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) is a managed SQL database service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). Amazon RDS supports an array of database engines to store and organize data. It also helps in relational database management tasks like data migration, backup, recovery and patching. Amazon RDS facilitates the deployment and maintenance of relational databases in the cloud. Cloud administrators use Amazon RDS to set up, operate, manage, and scale relational instances of cloud databases. Amazon RDS itself is not a database; It is a service used to manage relational databases. How does Amazon RDS work?Databases store large amounts of data that applications can draw upon to help them perform various tasks. A relational database uses tables to store data and is called relational because it organizes data points with defined relationships. Administrators control Amazon RDS with the AWS Management Console, Amazon RDS API calls, or the AWS command-line interface. They use these interfaces to deploy database instances to which users can apply specific settings. Amazon provides several instance types with different resources, such as CPU, memory, storage options, and networking capability. Each type comes in a variety of sizes to suit the needs of different workloads. RDS users can use AWS Identity and Access Management to define and set permissions to access RDS databases. Amazon RDS FeaturesAmazon RDS features include the following: Replication. RDS uses the replication feature to create read replicas, and these are read-only copies of the database instances that the application uses without changing the original production database. Administrators can also enable automatic failover across multiple availability zones through RDS multi-edge deployment and synchronous data replication. 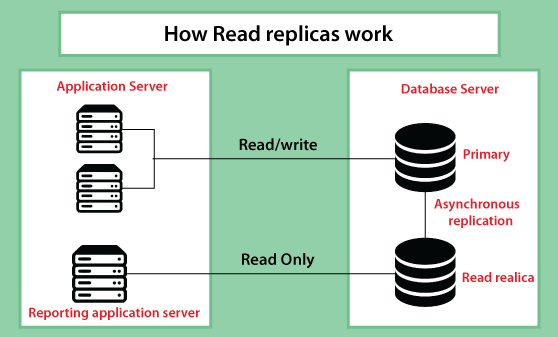
RDS provides three types of storage:A general-purpose solid-state drive (SSD). Amazon recommends this storage as the default choice. Provisioned input-output operations per second (IOPS). SSD storage for I/O-intensive workloads. Magnetic. A lower-cost option. Monitoring. The Amazon CloudWatch service enables managed monitoring, and it lets users view capacity and I/O metrics. Patching. RDS provides patches for whichever database engine the user chooses. Backups. Another feature is failure detection and recovery. RDS provides managed instance backups with transaction logs to enable point-in-time recovery. Users pick a retention period and restore databases to any time during that period. They also can manually take snapshots of instances that remain until they are manually deleted. 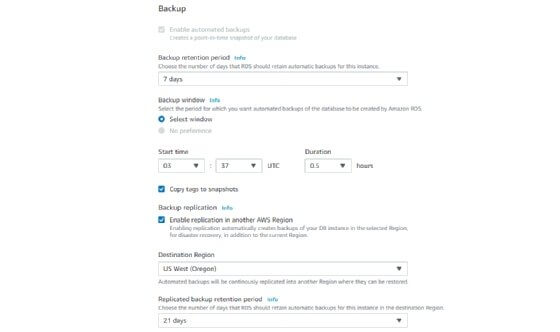
RDS lets users specify the time and duration of the backup processes. They also can choose how long to retain backups and snapshots.
What are the benefits and drawbacks of Amazon RDS?There are several pros and cons to using Amazon RDS.
Reading replicas routes read-heavy traffic away from the main database instance, reducing the workload on that one instance. RDS splits up compute and storage so admins can scale them independently. DrawbacksSome downsides of using Amazon RDS include the following: Lack of root access. Because it is a managed service, users do not have root access to the server running RDS. RDS restricts access for certain procedures to those with advanced privileges. Downtime. Systems must go offline for some patching and scaling procedures, and the timing of these processes varies. With scaling, compute resources need a few minutes of downtime on average. Amazon RDS database instancesA database administrator can create, configure, manage and delete an Amazon RDS instance, along with the resources it uses. An Amazon RDS instance is a cloud database environment. Admins can also spin up many databases or schemas; how many depends on the database used. Amazon RDS limits each customer to a total of 40 database instances per account, and AWS imposes further limitations for Oracle and SQL Server instances. With those database instances, a user generally can only have up to 10. Amazon RDS database enginesAn AWS customer can spin up to six types of database engines within Amazon RDS:
Amazon RDS adds support for major and minor versions of database engines over time. It is designed to allow admins to specify an engine version when they create a database instance. In most cases, Amazon RDS can support developer code, applications, and tools already in use with existing databases. AWS provides other database services, including the following:
Amazon RDS use casesAmazon RDS' scalability, security and availability make it useful for a variety of applications. Some possible uses include the following:
Business-to-business reporting company Enlyft said 6,096 companies were using Amazon RDS in 2021, including The American Red Cross, Penguin Random House and Zendesk. Amazon also reported in 2021 that Airbnb, Intuit and the U.S. The Department of Veterans Affairs is among the organizations that use RDS to support their data workloads. Featured RDS PartnersApp Associates Apps Associate is an AWS partner and Oracle specialist in migrating enterprise workloads to the cloud, freeing customers to focus on high-value initiatives. Join our webinar to learn how Apps Associate helps customers move to Amazon Aurora. Rackspace Rackspace is an AWS partner that can help you implement modern application development best practices with Amazon Aurora to help you keep pace with customers and business needs. Read the eBook to learn how Rackspace helped TotalTracks automate processes and meet growing demand. Use casesWeb and mobile applications Web and mobile applications built to operate at very large scales require databases with high throughput, massive storage scalability, and high availability. Amazon RDS meets the needs of such highly demanding applications with room for future growth. Since Amazon RDS has no licensing constraints, it fits the variable usage patterns of these applications perfectly. Airbnb Airbnb chose Amazon RDS because it simplifies most of the time-consuming administrative tasks typically associated with databases. Airbnb uses Multi-Availability Zone (Multi-AZ) deployment to automate its database replication further and increase data durability. Airbnb was able to complete its entire database migration to Amazon RDS with only 15 minutes of downtime. eCommerce application Amazon RDS provides small and large eCommerce businesses with a flexible, secure, highly scalable and low-cost database solution for online sales and retailing. Amazon RDS provides a managed database that helps eCommerce companies meet PCI compliance and focuses on creating high-quality customer experiences without worrying about managing the underlying database. Instacart Instacart turned to Amazon RDS for its new same-day grocery delivery service to avoid the complexities of building a new production database from scratch. The company can now add millions of new items to its database each month, and its engineering team can focus on developing new features and improving the overall customer experience. Mobile and Online games Mobile and online games require a database platform with high throughput and availability. Amazon RDS manages the database infrastructure, so game developers don't have to worry about provisioning, scaling, or monitoring database servers. Amazon RDS provides a familiar database engine that can rapidly increase capacity to meet user demand. Amazon Aurora and Amazon Aurora Serverless vs Amazon RDSAmazon Aurora is a database engine created by Amazon. RDS is a service used to manage database engines and instances, including the Amazon Aurora database. Amazon Aurora Serverless can also be used to manage instances of Amazon Aurora. Its automation features relieve developers from having to launch servers and manually manage database capacity. With RDS, servers must be manually scaled, which can result in significant downtime. The automatic scaling capability of Aurora Serverless enables rapid deployment with little or no downtime. One downside of Aurora Serverless is that it only works with Amazon Aurora, MySQL, and PostgreSQL. RDS is compatible with six database engines. Amazon RDS is suitable for more predictable applications because capacity adjustment takes longer in RDS than in Aurora Serverless. The takeawayAmazon RDS helps organizations handle relational database management tasks such as migration, backup, recovery and patching. Some of the main features of Amazon RDS are replication, high-performance storage, and failure detection. One of the biggest benefits of Amazon RDS is its ease of use, and it lets administrators manage multiple database instances without having to learn other database management tools. These features allow RDS to help organizations cut costs from time-consuming database administration tasks and manage the hidden costs of using high-performance storage in AWS. What is the future of Amazon RDS on VMware?Amazon RDS on VMware provides Amazon's relational database service for on-premises VMware infrastructure and points to the potential future of hybrid cloud services. Many people used to see VMware and AWS as bitter enemies, but that changed when they announced VMware Cloud on AWS in 2017. The announcement of Amazon RDS on VMware at VMworld 2018 indicated an evolving relationship between the two companies that could point to potential. For greater collaboration between cloud vendors and on-premises infrastructure. The investment required to move everything to the cloud has proved too expensive for many organizations, so as realistic expectations are set, more and more cloud vendors will try to integrate the features and benefits of the cloud with their on-premises infrastructure. Amazon RDS aims to make it easy to set up, run and develop relational databases. RDS provides a flexible and easy way to do previously tedious tasks like patching, capacity management and database tuning. Because this is an Amazon service, it only offers on-demand pricing for what you use or pay for reserved, dedicated capacity. Until recently, Amazon limited this service to Amazon Cloud. Amazon RDS on VMware is in Technical Preview, so all the details about how the platform works are currently unavailable. If it's anything like the native Amazon RDS, you'll be able to create and manage databases from half a dozen popular database types, including Oracle and Microsoft SQL Server. Amazon RDS for VMware will enable the affordable, high-availability hybrid deployment, simple database disaster recovery for AWS, and read-only clones of on-premises data in AWS. This partnership could help Amazon customers easily migrate traditional database deployment from their sites and AWS, even sites with difficult licensing requirements. It can also help VMware customers see the benefits of the AWS management stack for databases in traditional infrastructure. Amazon RDS Vs. VMwareAmazon has focused on moving workloads to the public cloud; Even VMware Cloud on AWS has focused on moving older workloads off-premises. Amazon RDS on VMware is different. With this release, Amazon is following Microsoft to provide public cloud services within the confines of the data centre. Let's say Amazon continues to add its services to the data centre and continues to do the same with Microsoft Azure Stack. In that case, customers can see several major cloud benefits without the enormous effort of moving workloads to the public cloud. As much as the industry has talked about hybrid cloud, most customers haven't implemented it. It takes a major investment for customers to achieve the flexibility, ease of consumption, agility and scale of the public cloud. Instead of making that investment, organizations often just put the time and effort into moving particular workloads to the cloud. As cloud providers look to expand the public cloud into a private data centre, customers can get the best of both worlds and have a true hybrid cloud model. The ability to run Amazon services inside your data centre is all but Amazon admitting that the public cloud isn't the only way forward. Combine that with the fact that you can now run a traditional VMware on-premises infrastructure inside Amazon's public cloud, and you can see that the two companies have decided to have public, private, and hybrid clouds that all coexist.
Next Topic#
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









