BatteryA battery is a charging device used to power devices such as mobile phones, electric geysers, flashlights, electric vehicles, etc. The battery has two terminals called cathode and anode. The cathode is the positive terminal, while the anode is the negative terminal. The electrons possess a negative charge. Hence, the negative terminal of the battery is the source of electrons. When we connect the external circuitry to the battery's terminals, the electrons flow from the negative to the positive terminal. The reaction occurs, and the battery's chemical energy is delivered to the connected circuitry as the electric current. The battery comes in various designs and shapes. Some small battery cells are used in watches or as a remote cell. Thin cells are used in wristwatches or mobile phone chargers. The vehicles consist of large lithium acid batteries, while some large rooms like batteries are used for computer data centers. Here, we will discuss the following topics:
History of BatteryLet's discuss the invention of the battery in detail. Consider the below points:
Working of a BatteryLet's discuss the working of the battery in detail. Principle of BatteryThe battery process is to convert the chemical energy present in the cell to electrical energy, which is delivered to the circuitry for its operation. A battery comprises of one or various electrochemical cells. Each cell in a battery includes an electrolyte and two (positive and negative) charged electrodes. The dry cells have electrolytes in the form of a paste, while wet cells have electrolytes in the liquid form. Let's discuss the components in detail. 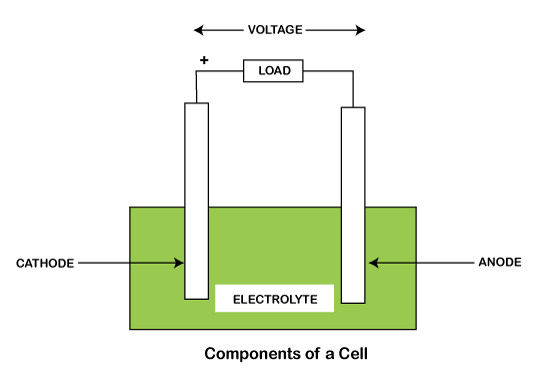
Electrodes The battery has two electrodes called anode and cathode. The anode is named the battery's negative terminal, while the cathode is named the battery's positive terminal. The quality, design, and quantity define the speed and density of a battery. Hence, it is the most important component of a battery. If we connect a wire to these two terminals, the current will flow through the wire. Electrolyte The electrolyte is an electrically conducting solution in which electrodes are submerged. It can be in the form of acids, bases, soluble salts, etc. that promote the movement of ions. Let's discuss the working of a battery. It will help us to understand the concept and the flow of electricity. WorkingThe battery consists of three parts named as a cathode, anode, and an electrolyte, as discussed above. The chemical composition is a battery causes the potential difference between the two electrodes, which results in the flow of electrons. The electrons try to maintain the difference. The electrons attract towards the place that has fewer electrons. It causes the electrons to flow from the anode to the cathode. When the external circuitry is connected to the terminals of the battery, the electrons flow towards that circuitry. It further generates electricity. When the circuit is incomplete, the chemical composition stops the flow of electrons. The more usage causes more loss of electrons. Hence, batteries have a limited amount of power. Similarly, when an external charge is applied to the recharging batteries, it reverses the chemical composition. The electrons are restored and gather loss power again. Example 1: Torch or FlashlightLet's consider an example of a torch. The torch is also known as a flashlight, which is used in every household. It is a type of portable device that can work for long hours. The structure of the torch is shown below: 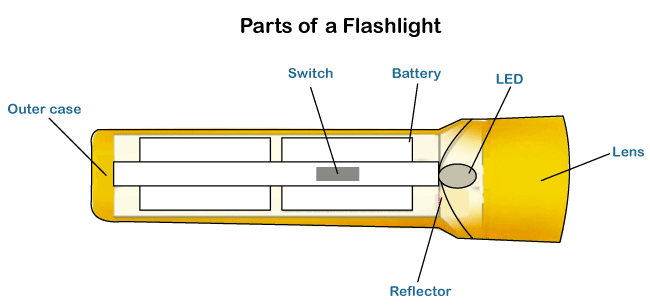
It clearly shows the arrangement of battery cells in the torch. Here, we will discuss the torch's operation and the role of battery cells in the torch. This source of light has also replaced the use of lamps. The light source (popularly LED) in a flashlight is mounted in a lens with the reflector. The battery, light source, and lens are covered with a case. The role of the reflector is to redirect the light ray into a steady beam. The contact strips are used to connect the positive and negative terminal of a battery. The terminals of the battery are made such that it will not work with the opposite polarity. Hence, we can easily insert the battery with the correct polarity. The principle of the flashlight is also used in the front of head helmets that provide light to the miners, without holding in the hands. Apparatus in a torch: The apparatus of a torch or flashlight includes an outer case, primary batteries, switch, lens, reflector, lamp with the tungsten filament, and LED. Working: When we power ON the switch, the contact strips to complete the connection. The contact strips are connected to the two ends of a switch. It permits the current to flow in the circuitry of a flashlight. The LED or tungsten filament of the bulb starts producing visible light. The reflector creates a direct beam that emits from a flashlight. A lens is used as a protective guard for the bulb or LED. When we power OFF the switch, the contact strips come to its original position, i.e., away from a switch's terminals. Today, the flashlight comes in various sizes. The size is appropriate that we can easily carry it anywhere. Types of BatteryThere are two types of batteries, primary and secondary. It is also defined as a primary and secondary cell. The electrochemical composition of a battery determines that the reaction is reversible or not. If the reaction is reversible, it means that the battery can be easily charged. Such composition is the main reason that defines the primary and secondary battery. Let's discuss the types of batteries in detail. Primary BatteryThe primary battery is called the temporary battery or disposable battery. Primary batteries are generally portable. The chemical reaction in such batteries cannot be restored. Hence, primary batteries are not rechargeable. For example, zinc-carbon cells, alkaline batteries, dry cells, lithium-metal batteries, etc. Secondary BatteryThe secondary battery is often called the rechargeable battery. Using an electric current, we can recharge these batteries multiple times. The composition of secondary batteries is such that it can be restored when current is applied. For example, lithium-acid batteries used in vehicles, such as cars, trucks, etc. The lithium-ion batteries are primarily used in various electronic devices, such as mobile phones or personal computers. Let's discuss some differences between primary and secondary battery.
Energy DensityIt determines how energy can be stored in a given small mass calculated per unit volume. Among different types of batteries, the lithium-ion battery has the highest energy density. It means that it can store a large amount of energy. Note: We should not be confused between energy density and power density. Both are different terms.Categories of cell or batteryThere are two categories of cells, called "dry cell" and "wet cell". Both of the cells can be primary or secondary. Dry CellThe electrolyte present in the dry cell is immobilized in the form of a paste, where a small amount of moisture is enough to permit the flow of current in the cell. Carl Gassner, a German Scientist, developed the dry cell in the year 1886. It has a high energy density and low internal resistance. It is portable because it contains no fluid. Dry cells can also operate in any orientation without any leakage. Examples include alkaline batteries, silver oxide batteries, and zinc-carbon batteries. Wet CellThe electrolyte of the wet cells is in the form of liquid. In laboratories, wet cells are commonly prepared in the beakers to demonstrate their working. Wet cells required proper handling due to the presence of liquid in it. It is a type of rechargeable battery. The electrolyte of the battery is liquid, which is acidic in nature, such as sulfuric acid. The examples include the lead-acid battery. The wet batteries are commonly found in cell phone towers, electric utilities, etc. The uses of different types of battery are shown in the below image: 
Lithium BatteriesLithium batteries are used in most of the applications in daily life. Lithium batteries have various advantages, such as lightweight, long lifetime, and high energy density, making it a great choice. Let's discuss some of the most common types of lithium batteries. Lithium metal batteriesThe name lithium refers to the material, which is present as the anode of a battery. Hence, they are known as lithium-metal batteries. These batteries come in the category of primary batteries. Lithium-ion batteriesThe lithium-ion batteries are named for the active materials present in it. Here, we will discuss some of the types of lithium-ion batteries. Every type has a different chemical composition.
StorageWhenever we want to store a battery, remove it from the device and store it in a cool and dry place. Do not try to freeze any type of battery. We know that battery storage causes a loss of charge. So, we should always check the specific gravity and voltage of a battery before using it. The battery whose state of charge falls below 70 percent requires charging. Now, let' discuss the type of batteries and duration for which it can be stored.
Chemical Composition of BatteriesMany chemical reactions work inside a battery when we use a flashlight, remote controllers, vehicles, etc. The basic idea is similar in all types of battery. The electricity is produced when a chemical reaction occurs between the electrolyte and its two electrodes (cathode and anode). Batteries are made up of the material, such as nickel, cadmium, mercury, lead, lithium, and alkaline. The ions move from the electrolyte towards the anode. A compound is formed at the anode, which releases electrons. It means that the oxidation reaction takes place at the anode. Similarly, a compound is formed at cathode when released electrons combine with it. It means that a reduction reaction takes place at the cathode. The concept is simple: anode releases electrons by taking ions from the electrolyte, and the cathode absorbs these electrons. The transport of electrons from anode to cathode causes electricity. The presence of chemical composition in a battery determines the life of a battery. As soon as it depletes, the battery starts losing energy. For example, Lead-acid battery: It consists of a metallic lead or lead dioxide as the material for two electrodes and sulfuric acid solution as the material of electrolyte. It is a type of rechargeable battery. Recharging a batterySome batteries, such as a primary battery, cannot be used more than once. But, some batteries like secondary batteries are generally rechargeable and can be used repetitive times. Discharging of a BatteryThe electrons flow from anode to cathode. It releases ions (positive or negative) into the electrolyte that gives energy to the circuitry in the form of electricity. The energy gets depleted and prevents the electrolyte from continuing the reaction. Hence, a battery starts discharging. Charging of a BatterySome of the batteries are created such that the reaction involved in the process can be reversed. The electrodes of these batteries are created from the material that can reverse its chemical composition when the batteries are supplied with external energy. It means that the external energy supplied to the battery reveres the chemical process that causes the discharging of that battery. The ions return to the cathode and anode of a battery. The battery gets charged and can be used again. Fast charging batteries are in great demand today, ranging from mobile devices to vehicles. These batteries quickly absorb the charge. Some of the fast charging batteries are Lithium-ion batteries, Graphene batteries, and Carbon-ion batteries. Battery made with toxic materialsSome of the batteries used in industries, etc., are made up of toxic materials, such as mercury, lead, etc. These materials are considered the E-waste (electronic waste) and require disposal to prevent damage to the environment. The leakage caused by toxic batteries can pollute the water and soil, which may harm the earth's wildlife. Most of the manufacturers are trying to avoid toxic materials. Some authorities have also joined the manufactures to create awareness about the recycling schemes. These schemes spread information to send the used batteries for recycling rather than going to landfill. The batteries are recycled in such a way that toxic chemicals do not enter the environment. Solar charging batteriesThe solar charging batteries consist of a charge controller that takes energy from the solar and convert it into the required voltage suitable for charging. The actual solar power output of such batteries is reduced during the shadows, overcast sky, raining, etc. It is because the solar panel requires direct solar energy to produce output as energy. The solar are arranged in series at a stationary place and is connected to a battery bank to store energy. In an off-peak state, it is recommended to use the stored energy from the solar panel.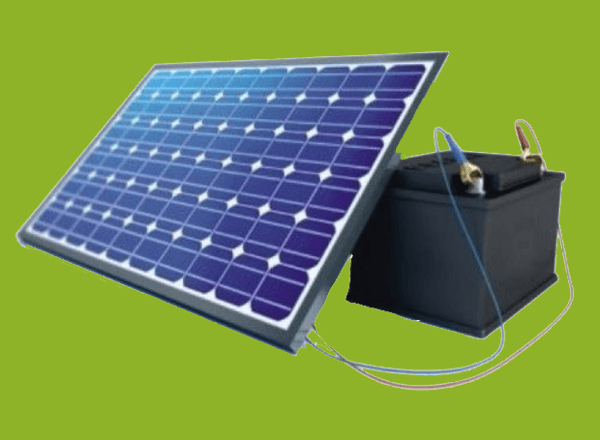 
Small solar batteries are portable that are used in devices, such as mobile phones, iPods, etc. Big solar batteries are generally placed at a fixed location, generally in public places, such as parks, streets, etc. Today, various types of solar chargers with improved efficiency. Wind turbine charging batteries are also available. It also consists of a charge controller that takes energy from a wind turbine and converts it into the required voltage suitable for charging. Self-charging batteriesSelf-charging batteries do not require charging. The cell such batteries can work for a long time without losing any energy. It also leads to enhanced power output. The concept behind the self-charging capability is the combination of negative resistance with negative capacitance. One of the materials in a battery will change its composition to form a capacitor that can store a large amount of charge. The self-charging batteries are currently applicable for low-frequency applications, such as digital converters, blinking lights, etc. Environmental friendly BatteriesWe should always opt for environment friendly, recyclable, and rechargeable batteries before purchasing it. The battery that is non-hazardous and can be recycled is Nickel Metal Hydride (NiMH), etc. The batteries that are hazardous and can also be recycled are Nickel Cadmium (NiCd), lead acid batteries, button cell batteries, etc. But, some of the battery cells that cannot be recycled are AAA, AA, D, and C.
Next TopicMOSFET
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









