C++ Algorithm transform()C++ Algorithm transform() function is used in two different ways: 1.unary operation:- This method performs unary operation op on the elements in range [first1, last1] and stores the result in range starting from result. This transform() applies a function to each element of a range: 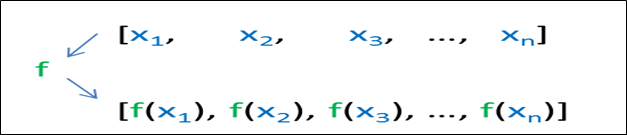
2.Binary operation:- This method performs binary operation binary_op on the elements in range [first1, last1] with the elements in the range starting with iterator first2 and stores the result in range starting from result. This transform() takes two 2 ranges and applies a function that takes 2 parameters, on each couple of elements from the input ranges: 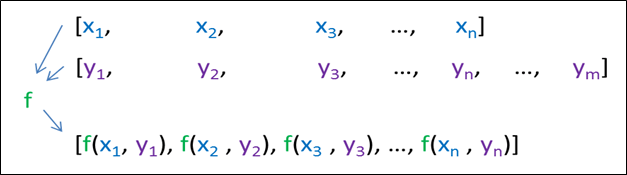
Syntaxunary operation(1) Binary operation(2) Parameterfirst1: An input iterator pointing the position of the first element of the first range to be operated on. last1: An iterator pointing the position one past the final element of the first range to be operated on. first2: Input iterator pointing to the first element in the second range to be operated on. result: An output iterator to the initial position of the range where the operation results are stored. op: Unary function applied to each element of the range. binary_op: Binary function that two elements passed as its arguments. Return valuetransform() returns an iterator pointing to the end of the transformed range. ComplexityComplexity is linear in the distance between first1 and last1. Data racesThe objects in the range [first1, last1) are accessed where each object is accessed exactly once. The object in the range beginning at result is modified. Exception safetyThrows an exception if any of the function calls the assignments or the operations on iterators throws an exception. Please note that invalid parameters cause an undefined behavior. Example 1Let's see the simple example to demonstrate the use of transform(): Output: 6 2 8 Example 2Let's see another simple example: Output: aaa b cccc Example 3Let's see another simple example: Output: Transform operation b[i] a[i] c[i] 1 ^ 1 = 1 2 ^ 2 = 4 3 ^ 1 = 3 1 ^ 2 = 1 2 ^ 1 = 2 3 ^ 2 = 9 1 ^ 1 = 1 2 ^ 2 = 4 3 ^ 1 = 3 1 ^ 2 = 1 The above example illustrates the transform() algorithm. The program creates two vectors and transforms the third vector by inserting a value equal to an element from first vector raise to the power of element in second vector. The function power is passed as a predicate to the function transform(). Example 4Let's see another simple example: Output: foo contains: 21 41 61 81 101
Next TopicC++ Algorithm
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










