Exception Handling in JSPThe exception is normally an object that is thrown at runtime. Exception Handling is the process to handle the runtime errors. There may occur exception any time in your web application. So handling exceptions is a safer side for the web developer. In JSP, there are two ways to perform exception handling:
Example of exception handling in jsp by the elements of page directiveIn this case, you must define and create a page to handle the exceptions, as in the error.jsp page. The pages where may occur exception, define the errorPage attribute of page directive, as in the process.jsp page. There are 3 files:
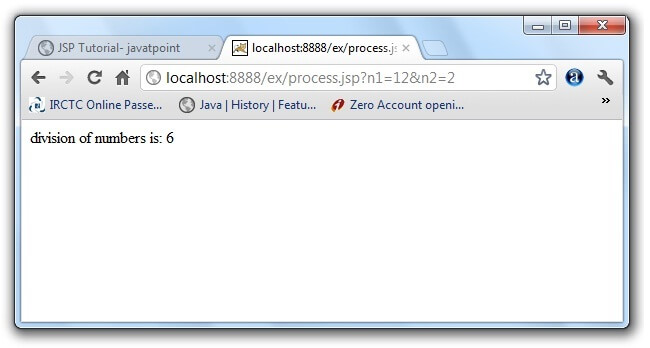
index.jspprocess.jsperror.jspOutput of this example: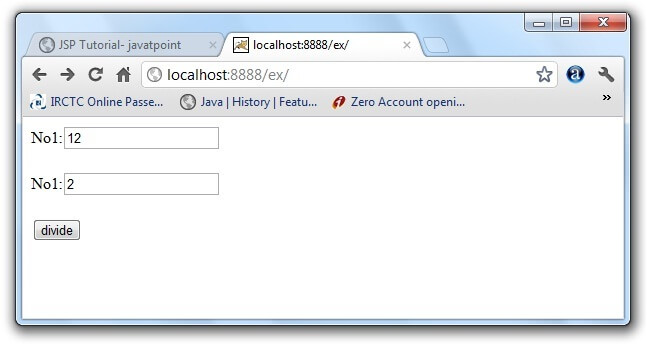
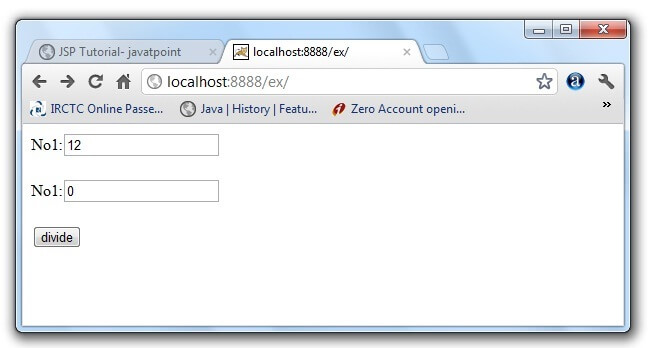
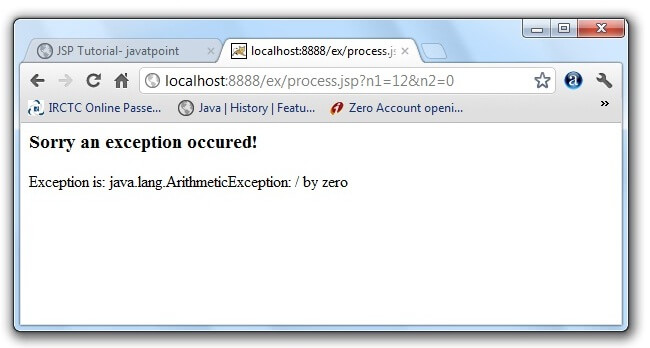
Example of exception handling in jsp by specifying the error-page element in web.xml fileThis approach is better because you don't need to specify the errorPage attribute in each jsp page. Specifying the single entry in the web.xml file will handle the exception. In this case, either specify exception-type or error-code with the location element. If you want to handle all the exception, you will have to specify the java.lang.Exception in the exception-type element. Let's see the simple example: There are 4 files:
1) web.xml file if you want to handle any exceptionThis approach is better if you want to handle any exception. If you know any specific error code and you want to handle that exception, specify the error-code element instead of exception-type as given below: 1) web.xml file if you want to handle the exception for a specific error code2) index.jsp file is same as in the above example3) process.jsp
4) error.jsp file is same as in the above example
Next TopicJsp Action Tags Forward Action
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









