Temporary Magnets
We have seen a variety of magnets around us in our lives, unlike a bar magnet or a horseshoe magnet. Almost all the magnets that you come across are acritical and possess a magnetic field around them. Though our scientists are constantly trying to knack the augmentation of the magnetic force and why it exists. There are various shapes, types, and forms of a magnet, and each possesses its unique characteristics. In this tutorial, we will cover the definition of a temporary magnet, with detailed information of its existence, its types, the process of creating it, and demagnetize it to provide you a better insight into the topic. What is a temporary magnet?Temporary magnets are a type of magnet that occurs artificially (human-made) in nature. These magnets are created from soft metals. Magnetism can be induced in a magnetic material in the presence of a permanent magnetic field or electronic current, or any other external magnetic field. Those materials are known as Permanent magnets. These magnets lose their magnetic property once you remove the magnetic field. For Example, Paperclips, iron nails, and similar materials act as temporary magnets in the presence of an external magnetic field. In a nutshell, a Temporary Magnet:
What Can Be Considered a Temporary Magnet?Below given are few essential points that would assist you in identifying the properties of a Temporary Magnet:
Types of Temporary Magnets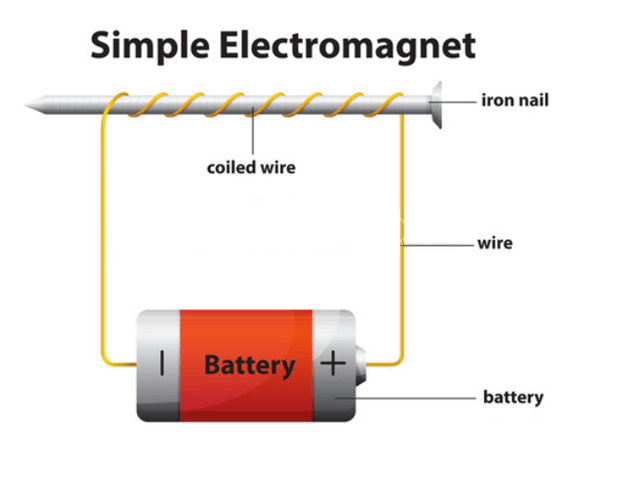
Temporary magnets are created through soft metals and only hold their magnetic properties if any external magnetic field, unlike a permanent magnet or electronic current, is near it. Commonly used temporary magnets involve iron nails and paperclips, pulled or attracted by a strong magnet. Another typical example of a temporary magnet is an electromagnet that preserves the magnetic properties whenever electrical current is passed through it. However, the strength and polarity of Electromagnets may vary depending on the coil wire (made up of iron core) used and various other factors. You have electromagnets all across you, and you even used them in the form of everyday objects such as doorbells, motors, etc. How to Make a Temporary MagnetMagnets are made when all the atoms (specifically electrons) in the object point in the same direction. The common ways to produce a temporary magnet are as follows:
Demagnetize a Temporary MagnetIn nature, magnets are usually formed when all the atoms inside a material align themselves with the north pole for one direction and the south pole in another direction. This is valid in the case of a temporary magnet, and that's how they gain their magnetic property. Whenever the atoms of a temporary object are shaken, for instance, the object is dropped on the ground, it will demagnetize itself. It will gradually revert to its natural non-magnetic phase. Difference between Permanent Magnets & Temporary MagnetsMagnets are usually classified into two broad categories, i.e., permanent magnets and temporary magnets. Though we have already covered the detailed description and characteristics of temporary magnets, the insights regarding permanent magnets are worth considering. To fetch a better understanding of a permanent magnet and a temporary magnet, we will be comparing their features. Please refer to the below table to find the detailed differentiation between a temporary magnet and permanent magnet:
Next TopicData Interpretation Questions
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










