Three properties of metalsWhat are metals?Metals are the material or substances that easily allow the electrons to flow through them. It means that metals are called good conductors of electricity. It is also known for its ability to act as a good conductor of heat. Metals are opaque (not transparent or that does not let the light to pass through) elements that are less dense than other types of elements. A freshly generated metal is lustrous (shining surface) and polished. Metals can also be drawn easily into wires, melted into any shape, or hammered to convert into thin sheets. Metals are used everywhere, ranging from households to large industries. The metals are used in electronic devices, electrical circuits (such as transformers), industrial machines, etc. The scope and use of metals are not limited. Here, we will discuss the properties of metals and some of the common applications of metals. We will also discuss the difference between metals and non-metals. The applications of metals will help us to understand the implementation of the properties of metals. Properties of metals
The three primary properties of metals are conductivity, malleability, and luster. ConductivityConductivity refers to the ability of an element to transfer heat and electricity. It is an essential criterion before selecting metal for use in various applications. Metals present in their purest form are considered as good conductors. The free electrons present in metal are responsible for the conductivity. We can also say that charge inside the metals is free electrons. Let's consider a structure of free electrons, as shown below: 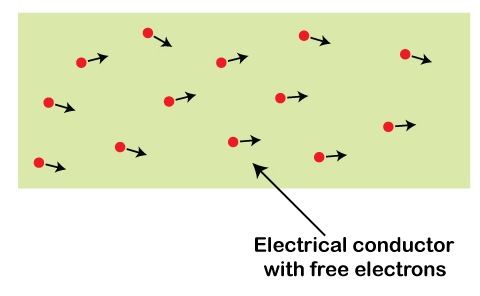
The movement of free electrons determines the electric current in a substance. The easy movement of the free electrons depicts that the metals can easily conduct electric current. In the case of the battery, the charges are both positive and negative that constitute the current. Consider a case of a metal connected with the external voltage source. It is shown below: 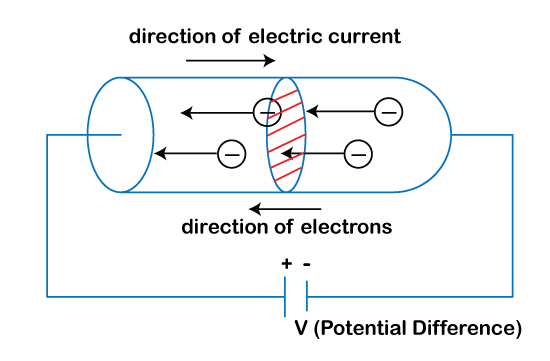
The above diagram clearly depicts the flow of current is in the opposite direction to the flow of electrons. Sometimes, the coating is also added to the metals to increase their conductivity. Silver is the metal known for its highest conductivity but in its pure form. Mercury is the metal known for its lowest conductivity. Let's discuss why?
Thermal conductivityThe metals can easily allow the passage of heat. The common application of metals that depicts their good thermal conductivity is cooking utensils. Copper and aluminum are the metals that have the highest conductivity. The valence electrons of the metals are highly mobile. It means those valence electrons are not bounded to the nucleus. Thus, we can say that metals have high thermal conductivity. MalleabilityMalleability specifies the metals' property to convert it into different shapes and sheets without breaking or cracking. We can apply different operations, such as hammering, etc., on the metals. For example, hot iron can be easily converted into sheets by hammering. The electrons in the metals are held loosely. When any compressive stress is applied to the metal, the electrons move towards the other nucleus. It allows metals to form into different sheets or other shapes. Similarly, the process to convert metals into wires is known as ductility. Generally, if the metal has high malleability, it may also possess high ductility. Metals can also be bend or twisted into various shapes. Metals can also be bend or twisted into various shapes. Let's consider an image that depicts the change in the metallic structure when stress is applied. It is shown below: 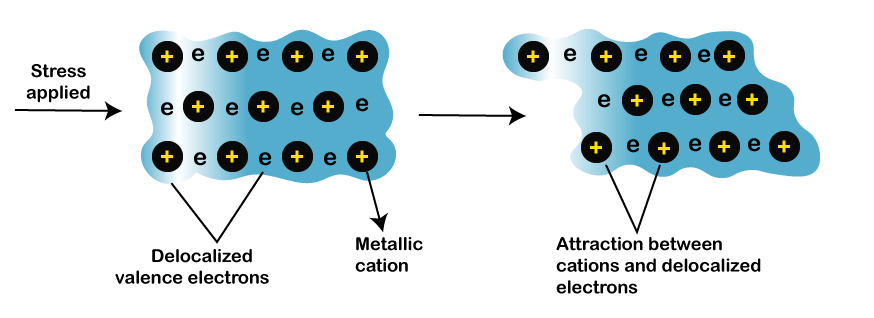
LusterLuster is the property of the metals that makes the appearance of the metal's surface shiny. The fresh manufactured metal piece is generally lustrous and reflects light in different ways. Old metals can also be polished to make a shiny appearance. It is also an identification criterion for various metals. The common lustrous metals include platinum, gold, silver, copper, etc. Due to its shiny surface, such metals are also used in jewelry. The surface finish of these metals can deteriorate over time. Due to this, coating and polishing are preferred. Applications of metalsThe applications of metals are listed below:
The applications are based on the above properties of metals. We can easily relate these properties with their practical use in various parts of the world. Metal vs. Non-metalMetal are the elements that easily allow the conduction of electricity, while non-metals are the elements that do not possess the properties of metals. It means that non-metals have poor conductivity. The non-metals also have their own applications. For example, plastic, etc. The non-metals are not only solid elements but even in the form of liquid and gas, such as oxygen, chlorine, etc. Let's discuss the differences between metals and non-metals. It will help to differentiate the elements that are good and bad conductors.
Next TopicTimestamp to Date
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










