Types of EcosystemAn ecosystem is a common term and is widely used in biology and environmental studies. In general, it is known as a system or community that consists of all living organisms and their related non-living components in nature. All such components are directly or indirectly associated with each other to create ecological balance. Therefore, it is necessary to know the different types of ecosystems and what they specifically contain. Before discussing the various ecosystem types, let us first understand the term ecosystem with its definition. What is an Ecosystem?By defining an ecosystem, it refers to a community of living organisms that interact with each other and with non-living components. An ecosystem can be defined as a structural and functional unit of ecology in which different living organisms interact with others and surrounding non-living environments. Ecosystems are changing at a steady rate. This is because there are many human actions that directly or indirectly affect the environment and the ecosystem. Some of such tasks are deforestation, pollution, disease transmission across natural boundaries, transfer of non-native species, depletion of natural habitat through overgrowth, etc. Besides, natural hazards are also responsible for making changes in the ecosystem. These changes include migration of species to a particular area, weather changes, various disasters, or fatal diseases that affect only one species. Structure of the EcosystemAn ecosystem's structure mainly refers to the description of both biotic and abiotic components in their organization's environment. In particular, it involves the distribution of energy in the environment. Furthermore, it includes various climatic conditions prevailing in that specific environment. Both biotic and abiotic components are interconnected and form an open system in which energy is transferred from one particular component to another. 
Biotic (Living Components)Biological components refer to all living organisms in the ecosystem. These components typically include organisms such as animals, plants, humans, and other microorganisms. Based on different nutrition, biological components are classified into the following three categories:
Abiotic (Non-living Components)Abiotic components refer to all non-living elements and compounds in the ecosystem, including climates and climate-components. Furthermore, the abiotic components are the primary sources of energy and nutrients and set the stage for proper ecosystem functioning. The Sun is the primary source of energy for an ecosystem. Other examples of abiotic components are light, humidity, temperature, gas, water, air, minerals, soil, topography, and various habitats. Note: Without abiotic components, no ecosystem can provide for biological components.Types of EcosystemThere are different types of ecosystems based on different climates, habitats, and life forms. This means that ecosystems can typically be divided into hundreds and thousands of smaller systems. However, all such types generally fall into one of the following two categories:
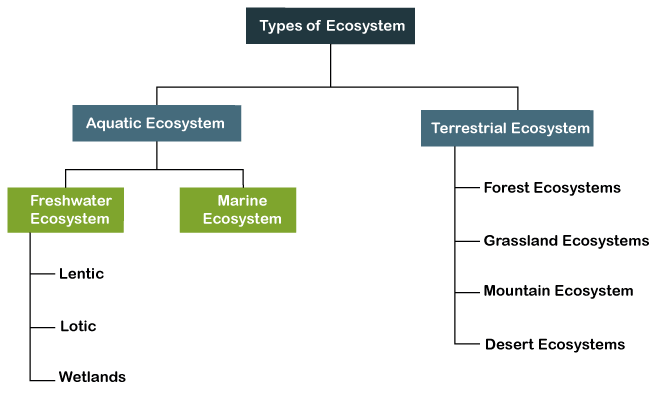
Let us now understand in detail about both the above ecosystems: Aquatic EcosystemAquatic ecosystems refer to all such ecosystems that are primarily located on or inside water bodies. The nature and characteristics of all living and non-living organisms in the aquatic system are determined based on the environment surrounding their ecosystem. Organisms in these ecosystems interact with other organisms in aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. The aquatic ecosystem is mainly sub-divided into the following types: Freshwater EcosystemThe freshwater ecosystem is one of the essential ecosystems for humans and other organisms living on land. This is because this ecosystem is a source of drinking water. Additionally, it also helps in providing the necessary energy and water for transportation, recreation, etc. Freshwater ecosystems mainly include lentic, lotic, and wetlands.
The freshwater ecosystem is the smallest type of ecosystem among the major types of ecosystems. There is usually no salt content in the freshwater ecosystem. Besides, it consists of many insects, small fish, amphibians, and various plant species. Plants help provide oxygen through photosynthesis and also provide food for the organisms living in this ecosystem. Marine EcosystemMarine ecosystems are usually characterized by the presence of salt content. These ecosystems have a higher salt content than the freshwater ecosystem. Moreover, they are known as the largest type of ecosystem on Earth. It usually includes all the oceans and their parts. Besides, marine ecosystems have a distinctive flora and fauna, which support greater biodiversity than freshwater ecosystems. This type of ecosystem is essential for both marine and terrestrial environments. In particular, this ecosystem includes salt marshes, lagoons, coral reefs, estuaries, intertidal zones, mangroves, seafloor, and deep seas. Salt marshes, mangrove forests, and sea-grass meadows are said to be among the most productive ecosystems. Coral reefs are known to provide adequate quantities of food and shelter to most marine inhabitants worldwide. Terrestrial EcosystemTerrestrial ecosystem refers to all such ecosystems which are mainly located on land. Although the presence of water in these ecosystems is measured, they are entirely land-based and exist on land. More specifically, a low and sufficiently needed amount of water is located in terrestrial ecosystems. The low amount of water separates these ecosystems from aquatic ecosystems. Besides, terrestrial ecosystems typically have temperature fluctuations in both seasonal and diurnal climates. It is also a specific factor that makes these ecosystems different from aquatic ecosystems in similar environments. Furthermore, the availability of light is somewhat higher in terrestrial ecosystems than in aquatic ecosystems. The reason for this is that the climate in the land is relatively more transparent than water. Due to entirely different light availability and temperature in terrestrial ecosystems, they have diverse flora and fauna. Terrestrial ecosystems include various ecosystems distributed around different geological zones. Terrestrial ecosystems are mainly classified into the following types: Forest EcosystemsA forest ecosystem is an ecosystem where many organisms live together with the environment's abiotic components. There are much different flora and fauna in this ecosystem. This usually means that the forest ecosystem has a high density of living organisms that live with non-living abiotic elements. The forest ecosystem usually includes various plants, microorganisms, animals, and other species. Forests are significant carbon sinks and participate in controlling and balancing the overall temperature of the Erath. Changes in the forest ecosystem affect the entire ecological balance, and severe changes or destruction of forests can also kill the whole ecosystem. Forests are generally classified into tropical deciduous forests, tropical evergreen forests, temperate deciduous forests, temperate forests, and Taig. Grassland EcosystemsGrassland ecosystems are referred to as those ecosystems where the number of trees is low. These ecosystems mainly consist of grasses, shrubs, and herbs. That means grasses are the primary vegetation in these ecosystems, along with legumes that typically belong to the composite family. Grassland ecosystems are commonly situated in both the tropical and temperate regions globally; however, they have distinct variations. Examples of these ecosystems include the savanna grasslands and temperate grasslands. They are home to various grazing animals, insectivores, and herbivores. Mountain EcosystemsAs the name suggests, the mountain ecosystem is characterized by mountainous regions where the climate is usually cold, and rainfall is low. Due to these climate changes, these ecosystems have a wide variety of habitats where various animal and plant species are found. The high altitude areas of mountainous regions have a cold and harsh climate. This is the reason why only treeless alpine vegetation is found in these ecosystems. Animals found in these ecosystems usually have tick fur coats to protect them from cold climates. Besides, mainly coniferous trees exist on the lower slopes of the mountains. Examples of mountain ecosystems include mountain tops in Arctic regions. They are covered with snow for most of the year. Desert EcosystemsDesert ecosystems exist worldwide and cover about 17 percent of desert areas. These are areas where annual rainfall is usually measured less than 25 mm. Due to fewer trees and land of sand, sunlight intensifies in these ecosystems. This is why these ecosystems have incredibly high temperatures and low availability of water. However, the nights are quite cold. The Desert ecosystem has unique flora and fauna. Plants grow with small amounts of water and conserve water's possible amount in their leaves and stems. For example, the spiny-leafed cactus is a type of desert plant that has the characteristic of storing water using a stem. Similarly, animals are also adopted to the condition of desert ecosystems. Some common animals are camels, reptiles, a diverse range of insects and birds. Functions of EcosystemSome of the most common functions of the ecosystem are listed below:
Next TopicHow to add Like button in HTML and CSS
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









