What is Colocation?A colo or colocation facility can be defined as a facility of the data center where a business could rent a place for servers or other computing hardware. A colo typically gives physical security, bandwidth, power, cooling, and building while the customer gives storage and servers. Often, space within the facility is leased by room, cage, cabinet, or rack. Various colos have boosted their offering by including managed services, which helps in improving their initiatives of customer's business. There are many reasons a business may select a colo over creating its data center. However, the primary driver is the Capital Expenditure (Capex) associated with updating, maintaining, and building a big computing facility. Often, colos were used via private organizations for DR (Disaster Recovery) in the past. Today, colo is especially famous with various cloud service providers. Colocation may be an optimal solution for a few organizations, but there could be some down sites to this technique. The distance can be converted into increased movement costs if the equipment would be handled manually. The colo customers see themselves secured into a long-term commitment, which may prevent them from renegotiating rates if prices fall. It is essential for an enterprise to closely determine the SLAs (service-level agreements) of their colo. Hence, it may not be wondered by any hidden charge. Features of ColocationAll colocation providers have their approach to implement things. So, the features change from a single colocation hosting enterprise to the other. Some aspects are common between colocation providers relatively. Commonly, colocation provides some of the features which are as follows:
Colocation AdvantagesEnterprises can capitalize on various profits by taking colocation service advantages. Some of the important advantages are below:
Facilities and buildingThere are differences among data centers and office buildings. A few of these differences are relevant to the path where a data center was created, while others include more to perform with the operational efficiency of the data center. A data center of colocation will typically offer its tenants along with the SLA ensuring the unique amount of availability. However, the data center may guarantee a unique amount of uptime like uptime's five nines. Commonly, the uptime of the data center represented in the context of the four tiers which are listed below:
Commonly, data center express the efficiency by a score called PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness). This score defines how the data center applies power efficiently. Those data centers using a good score of PUE are familiar with the platform and charge lower rates of tenants for power consumption generally. Also, it is important to notice how the data centers were constructed. All the locations in the whole world are vulnerable to at least a single kind of natural disaster. Hence, it is essential to ensure that the data center of the colocation provider was built in a supported form. What are the reasons of colocation data center downtimes?Generally, there are four types of disruptions such as connectivity, disaster, people, and power. 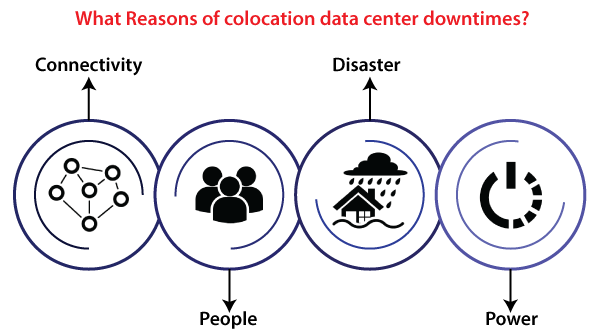
Vendors of ColocationThere are a lot of colocation vendors in the US and across the world. A few of the vendors are boutique vendors that implement only two or one data center. The rest of the vendors are multinational and massive providers of data centers.
Security in ColocationSecurity is important to various cloud providers because good security is necessary to colocation providers as well. The providers of colocation go to the best lengths for ensuring the physical security of the data centers. A few providers of colocation erect fences within the data center same as a way of separating the hardware of their tenant. All the fences have a locking gate. Hence, various tenants can access the hardware of their data center. Security tends to be performed in a form as to need tenants for passing from more than one security checkpoint to be capable to access the hardware of data center. However, a few providers of colocation do not permit the tenants to physically access the facility. Each hardware installation and maintenance is implemented by the staff of the data center from a process called remote hands. Pricing Model of ColocationAll the providers of colocation have their pricing model. A few providers bill the tenants according to the rack space amount that they consume. Some other providers also lease the floor space of the data center using the square foot. This pricing model is not only an aspect that regulates leasing space's overall cost within the colocation facility. A few of the other aspects that affect the overall cost include:
Public Cloud vs. ColocationThere are some major differences between a public cloud provider or a colocation data center, even though these concepts can enable businesses to execute workloads within the remote data center. Several colocation data center facilitates enough space for the physical data center to businesses. These facilities offer network connectivity, cooling, and power. However, it is up to various tenants to give their hardware such as supporting, storage, and server infrastructure. Public cloud providers, besides, apply their hardware. Tenants execute workloads over the hardware of the cloud provider which is inside the cloud data center. The cloud provider bills these tenants for the network, storage, compute, and other types of resources that the workloads have consumed. The public cloud is the preferred choice for enterprises that wish a consumption-based model of pricing. It does not require maintaining or purchasing server hardware. The facilities of colocation are geared to the enterprises that wish to execute the workloads on the hardware but within the remote data center. Configurations of ColocationMost of the data centers of colocation facilitate the selection of a large configurations that could be tailored to the specific needs of a company, mainly depends on how many of the servers they're operating. A few common configurations are discussed below: 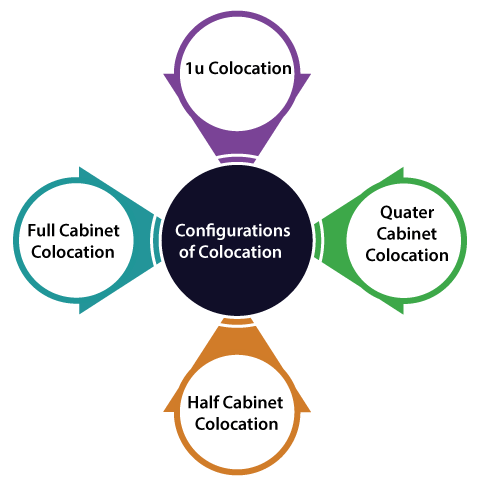
Next TopicResearch Methodology MCQ
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









