What is LAMP?LAMP is an open-source Web development platform that uses Linux as the operating system, Apache as the Web server, MySQL as the relational database management system and PHP/Perl/Python as the object-oriented scripting language. Sometimes LAMP is referred to as a LAMP stack because the platform has four layers. Stacks can be built on different operating systems. LAMP is a example of a web service stack, named as an acronym. The LAMP components are largely interchangeable and not limited to the original selection. LAMP is suitable for building dynamic web sites and web applications. Since its creation, the LAMP model has been adapted to another component, though typically consisting of free and open-source software. Developers that use these tools with a Windows operating system instead of Linux are said to be using WAMP, with a Macintosh system MAMP, and with a Solaris system SAMP. Linux, Apache, MySQL and PHP, all of them add something unique to the development of high-performance web applications. Originally popularized from the phrase Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP, the acronym LAMP now refers to a generic software stack model. 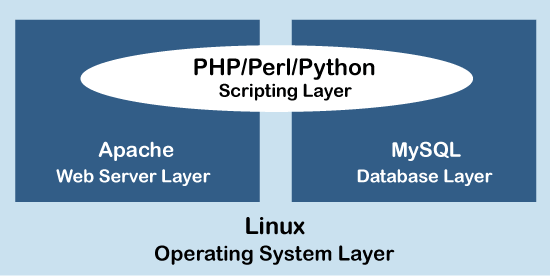
The modularity of a LAMP stack may vary. Still, this particular software combination has become popular because it is sufficient to host a wide variety of website frameworks, such as Joomla, Drupal, and WordPress. The components of the LAMP stack are present in the software repositories of the most Linux distributions. The LAMP bundle can be combined with many other free and open-source software packages, such as the following:
LAMP Stack ComponentsLinux based web servers consist of four software components. These components are arranged in layers supporting one another and make up the software stack. Websites and Web Applications run on top of this underlying stack. The common software components are as follows:
LAMP ArchitectureLAMP has classic layered architecture, with Linux at the lowest level. The next layer is Apache and MySQL, followed by PHP. Although PHP is at the top or presentation layer, the PHP component sits inside Apache. 
The LAMP stack order of execution shows how the elements interoperate. The process starts when the Apache webserver receives requests for web pages from a user's browser. If the request is for a PHP file, Apache passes the request to PHP, which loads the file and executes the code contained in the file. PHP also communicates with MySQL to fetch any data referenced in the code. PHP then uses the code in the file and the data from the database to create the HTML that browsers require to display web pages. The LAMP stack is efficient at handling not only static web pages but also dynamic pages where the content may change each time it is loaded depending on the date, time, user identity and other factors. After running the file code, PHP then passes the resulting data back to the Apache webserver to send to the browser. It can also store this new data in MySQL. And of course, all of these operations are enabled by the Linux operating system running at the base of the stack. FlexibilityAlthough LAMP uses Linux as the OS, we can use the other components with an alternative OS to meet specific needs. For example, there is a WAMP stack, which uses Microsoft Windows. LAMP is open source and non-proprietary so we can avoid lock-in. We have the flexibility to select the right components for specific projects or business requirements. LAMP offers flexibility in other ways as well. Apache is modular in design, and we will find there are existing, customizable modules available for many different extensions. These modules range from support for other languages to authentication capabilities. Another advantage of LAMP is its secure architecture and well-established encryption practices that have been proven in the enterprise. EfficiencyLAMP can help to reduce development time because it is an open-source stack that has been available for more than a decade. We can build on what other people have done in the past and make it own. Work within an Apache module that gets 80% of the way there customize the last 20%, and save considerable time as a result. Advantages of LAMPLAMP has the following advantages, such as:
LAMP Stack AlternativesThere are several variants of the four stack model as well. These variants use alternative software, replacing one or more of the standard components. Open-source alternatives are:
While non-open source alternatives include:
Next TopicTypes of Transmission
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










