3D PrinterWhat are printers?A printer is an electronic device that transfers the information and graphics from the computer to paper in the printed form. A printer can be used with mobile phones, personal computers, or laptops. The output document or a file can be in the form of only text information, graphics or images, or the combination of both text and graphics. We need to provide an input command to the printer attached to the device to produce the output. What are 3D printers?3D printers are the hardware devices that produce 3D printing outputs in paper instead of a product. It can also produce a 3D model from ready to print CAD files. It uses less material as compared to other manufacturing processes. The output is generally in the form of a 3D object. 3D printers use a different material, such as stereolithography materials, nylon, photopolymers, etc. that forms the output object. 
The common uses of 3D printers are to produce a prototype, miniature models, etc., for testing or development. The term is generally confused with regular printers. But it is different from the traditional printers. Today, printers are available is wide sizes and prices according to the specific features. Here, we will discuss 3D printers, 3D printing, types of 3D printers, etc. Let's start. Printers are commonly classified as 2D printers and 3D printers. Let's first discuss 3D printers in detail. 3D printers do not require any ink for printing. As discussed, the output of the 3D printers is in the form of a 3D model, prototype, or object. Working on a 3D PrinterWe have discussed 3D printers. But, we must be confused about how the printing process works in a 3D printer. The input of a printer requires a file for printing. Various file formats can be used as an input file for a 3D printer. The input file is generally a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) or STL (Standard Triangle Language) file. It means that the required input file should be a 3D file. We can also use any 3D software to convert a flat file into a 3D file. We can also say that the required file is a blueprint of the object to be formed. The file consists of related information, such as geometry, color compositions, structure, materials, etc. When a file is ready as per the requirements, we can send the file to a 3D printer. The printer uses raw materials, such as resins, thermoplastics, powders, melted solids, etc., to convert that 3D image into a 3D model. The printing process is quick and uses fewer materials than another manufacturing process to produce the same output. Let's discuss the differences between 3D printers and 2D printers. It will help us to understand the process and applications of both printers. 3D Printers vs. 2D Printers3D printers are considered better than 2d printers. It is because 3D printers produce the output as a real 3D object rather than printing on paper. On the other hand, 2D printers are easily accessed by anyone to convert the soft copies into hard copies. It is cheap and affordable. But, 3D printers are mostly used in industries and are not affordable. 
Let's discuss the differences between 3D printers and 2D printers. It is listed in the below table.
3D PrintingMost of the 3D printing files are the output of the CAD modules created in the computer system. 3D printing produces a 3D model from a CAD file or other 3D file systems. The material is used to form a layer by layer structure, which further appears as a 3D model. 3D printing is generally a layering process. It means that the output produced is created layer by layer using a particular material. 3D printing can be performed using different materials, such as thermoplastics, powder, melted metals, etc. Let's discuss the 3D printing technologies. It will help us to clearly understand the materials and the process of different 3D printing technology in various 3D printers. 3D Printing Technology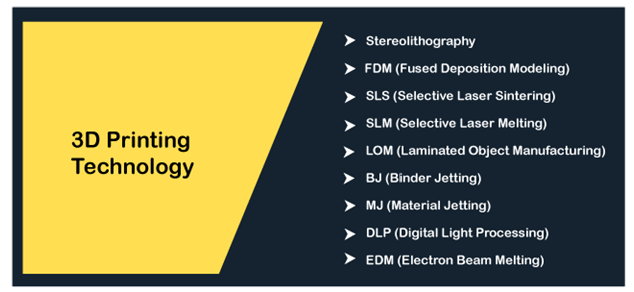
Various 3D printers vary as per the printer cost, quality, speed, etc. The 3D printers depend on the 3D printing quality of various printers. The different types of 3D printers are listed below:
Let's discuss this in detail. StereolithographySLA or Stereolithography 3D printers have various advantages, such as smooth and quality finish, great details, etc. It is the world's first 3D technology used for 3D printing. It was developed around 1986. SLA uses a solid-state laser to cure the part of the product. But, DLP (Digital Light Processing) can take a shorter time to trace the object's cross-section compared to SLA. FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)FDM technology is based on thermal plastic materials for 3D printing. It is generally a spool of filament that is loaded inside a 3D printer. The brands that use FDM for manufacturing 3D objects are Nestle, BMW, etc. It follows the sanding process and finishing process after the printing. Such a printer also can extrude the objects. The extrusion is carried out through the nozzle and the base. Fused Deposition Modeling is popular for creating prototype and concept models. SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)SLS works with a wide variety of materials, such as ceramics, metals, powders, etc. SLS is generally preferred in aerospace manufacturing parts due to its high cost. SLM (Selective Laser Melting)SLM is commonly used in mass production and building prototype. The primary difference between Selective Laser Sintering and Selective Laser Melting is the type of feedstock and the power material usage. Otherwise, both the processes are quite similar. SLS uses a different type of materials, while SLM is a process commonly for metals. LOM (Laminated Object Manufacturing)As the name implies, LOM uses heat and pressure to laminate or fuse plastic and paper parts. The product is further cut using the lasers into the desired shape. It is considered one of the fastest and inexpensive 3D printing processes to create a prototype model. BJ (Binder Jetting)The 3D printing process is a layering process. It means one layer is formed at a time. In the Binder Jetting process, a binder is used to fuse the areas. We can say that the binder acts as a bonding material. The common materials used by the BJ are metals, ceramics, etc. The applications of Binder Jetting include sand casting molds and the fabrication of color prototypes. MJ (Material Jetting)Material Jetting printers work in a similar way to 2D printers. A layer is build using the printhead droplets (like the ink) that are cooled using UV light. The materials used in the droplets are the photosensitive material. It offers high accuracy with a smooth surface finish. DLP (Digital Light Processing)DLP is a similar technology to SLA. It was developed around 1987. DLP is also considered the oldest 3D technology used for 3D printing. It uses modern light sources, such as arc lamps. But, SLA uses an ultraviolet light source. It also prints faster as compared to SLA. EDM (Electron Beam Melting)As the name signifies, it uses an electron beam to fuse parts. The electronic beam originates from an electronic laser. The material used is generally metal rather than thermoplastics. Such a process takes place in a vacuum. It is because electron beams can collide with gas or air particles. EDM builds a layer of powder on the part and applies laser after the power is set. The electronic beam causes the powder to melt that further results in the joining of metal parts. 3D printing is a layering process. It continues till the final object is formed. Types of 3D PrintersHere, we will discuss the types of 3D printers that are based on the 3D technology discussed above.
Advantages of 3D Printers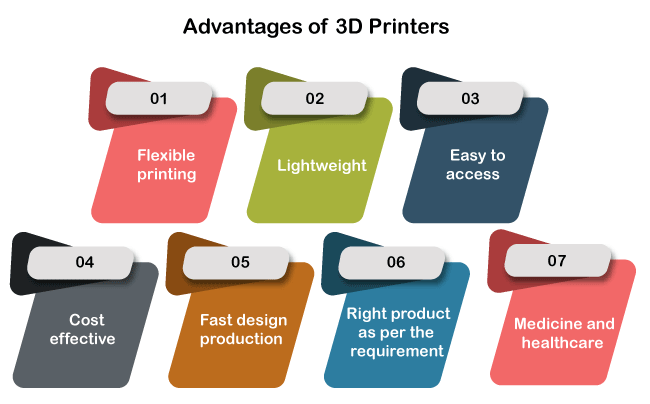
The advantages of 3D printers are listed below:
DisadvantagesThere are also some disadvantages of the 3D printers. Let's discuss some of the most common disadvantages.
Top Manufacturers of 3D Printers in IndiaThe manufacture of 3D printers in India has reduced transportation costs from abroad, such as China. Today, 3D printers are easily available in various designs and features. Let's discuss some of the top manufacturers of 3D printers in India.
Next TopicCardboard
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









