Applications of Wireless Communication
Following is a list of applications in wireless communication:
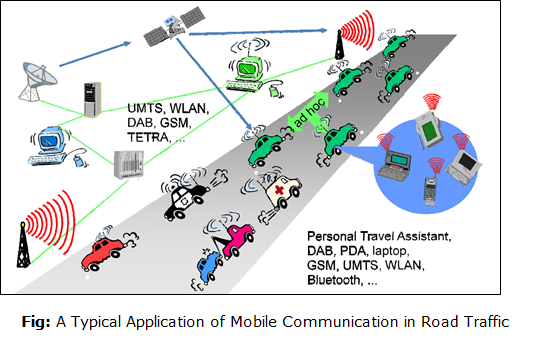
Vehicles
Many wireless communication systems and mobility aware applications are used for following purpose:
- Transmission of music, news, road conditions, weather reports, and other broadcast information are received via digital audio broadcasting (DAB) with 1.5Mbit/s.
- For personal communication, a universal mobile telecommunications system (UMTS) phone might be available offering voice and data connectivity with 384kbit/s.
- For remote areas, satellite communication can be used, while the current position of the car is determined via the GPS (Global Positioning System).
- A local ad-hoc network for the fast exchange of information (information such as distance between two vehicles, traffic information, road conditions) in emergency situations or to help each other keep a safe distance. Local ad-hoc network with vehicles close by to prevent guidance system, accidents, redundancy.
- Vehicle data from buses, trucks, trains and high speed train can be transmitted in advance for maintenance.
- In ad-hoc network, car can comprise personal digital assistants (PDA), laptops, or mobile phones connected with each other using the Bluetooth technology.
Emergency
Following services can be provided during emergencies:
- Video communication: Responders often need to share vital information. The transmission of real time situations of video could be necessary. A typical scenario includes the transmission of live video footage from a disaster area to the nearest fire department, to the police station or to the near NGOs etc.
- Push To Talk (PTT): PTT is a technology which allows half duplex communication between two users where switching from voice reception mode to the transmit mode takes place with the use of a dedicated momentary button. It is similar to walkie-talkie.
- Audio/Voice Communication: This communication service provides full duplex audio channels unlike PTT. Public safety communication requires novel full duplex speech transmission services for emergency response.
- Real Time Text Messaging (RTT): Text messaging (RTT) is an effective and quick solution for sending alerts in case of emergencies. Types of text messaging can be email, SMS and instant message.
Business
Travelling Salesman
- Directly access to customer files stored in a central location.
- Consistent databases for all agents
- Mobile office
- To enable the company to keep track of all the activities of their travelling employees.
In Office
- Wi-Fi wireless technology saves businesses or companies a considerable amount of money on installations costs.
- There is no need to physically setup wires throughout an office building, warehouse or store.
- Bluetooth is also a wireless technology especially used for short range that acts as a complement to Wi-Fi. It is used to transfer data between computers or cellphones.
Transportation Industries
- In transportation industries, GPS technology is used to find efficient routes and tracking vehicles.
Replacement of Wired Network
- Wireless network can also be used to replace wired network. Due to economic reasons it is often impossible to wire remote sensors for weather forecasts, earthquake detection, or to provide environmental information, wireless connections via satellite, can help in this situation.
- Tradeshows need a highly dynamic infrastructure, since cabling takes a long time and frequently proves to be too inflexible.
- Many computers fairs use WLANs as a replacement for cabling.
- Other cases for wireless networks are computers, sensors, or information displays in historical buildings, where excess cabling may destroy valuable walls or floors.
Location dependent service
It is important for an application to know something about the location because the user might need location information for further activities. Several services that might depend on the actual location can be described below:
- Follow-on Services:
- Location aware services: To know about what services (e.g. fax, printer, server, phone, printer etc.) exist in the local environment.
- Privacy: We can set the privacy like who should get knowledge about the location.
- Information Services: We can know about the special offers in the supermarket. Nearest hotel, rooms, cabs etc.
Infotainment: (Entertainment and Education)
- Wireless networks can provide information at any appropriate location.
- Outdoor internet access.
- You may choose a seat for movie, pay via electronic cash, and send this information to a service provider.
- Ad-hoc network is used for multiuser games and entertainment.
Mobile and Wireless devices
Even though many mobile and wireless devices are available, there will be many more devices in the future. There is no precise classification of such devices, by sizes, shape, weight, or computing power. The following list of given examples of mobile and wireless devices graded by increasing performance (CPU, memory, display, input devices, etc.)
Sensor: Wireless device is represented by a sensor transmitting state information. 1 example could be a switch, sensing the office door. If the door is closed, the switch transmits this information to the mobile phone inside the office which will not accept incoming calls without user interaction; the semantics of a closed door is applied to phone calls.
Embedded Controller: Many applications already contain a simple or sometimes more complex controller. Keyboards, mouse, headsets, washing machines, coffee machines, hair dryers and TV sets are just some examples.
Pager: As a very simple receiver, a pager can only display short text messages, has a tiny display, and cannot send any messages.
Personal Digital Assistant: PDAs typically accompany a user and offer simple versions of office software (calendar, notepad, mail). The typically input device is a pen, with built-in character recognition translating handwriting into characters. Web browsers and many other packages are available for these devices.
Pocket computer: The next steps towards full computers are pocket computers offering tiny keyboards, color displays, and simple versions of programs found on desktop computers (text processing, spreadsheets etc.)
Notebook/laptop: Laptops offer more or less the same performance as standard desktop computers; they use the same software - the only technical difference being size, weight, and the ability to run on a battery. If operated mainly via a sensitive display (touch sensitive or electromagnetic), the device are also known as notepads or tablet PCs.
|

 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now









