Types of ChequeBank accounts are one of the people's essential needs, and a cheque is an important document used in the banking system. Most people, as well as companies, use this document for their day to day transactions. However, certain rules, regulations and protocols have to be followed with different types of cheques. Therefore, we should know about different types of cheques to write and issue them accordingly. In this article, we are discussing different types of cheques with their definitions. Before discussing the different cheque types, let us first understand the definition of a cheque and its characteristics: What is Cheque?A cheque refers to a piece of paper or a document issued by an individual/enterprise to the bank, directing them to pay the mentioned sum of money to a person or organization whose name is written on it. Cheques are a common form of the negotiable instrument. However, to issue a cheque, one must have a savings or current bank account. A cheque without a name, date, or sign is considered invalid. Note: In the banking context, a negotiable instrument is a document that guarantees its bearer to pay a specified amount of money written in digits and words, based on demand or by the date written on it.Parties involved with a ChequeThere are generally three parties who participate in a cheque transaction, such as: Drawer or Maker: A drawer refers to a person who is a customer of a bank (bank account holder) and issues a cheque to someone (individual or organization). Drawee: A drawee refers to a bank where a cheque is withdrawn. A cheque can be withdrawn only at a related bank. Payee: The payee refers to an individual or an organization to whom a cheque is issued. The amount mentioned on the cheque is paid to the payee. In some cases, there can be two other parties involved with a transaction made by cheque: Endorser: If a party (payee) transfers its rights to taking payments to another party, he/she is referred to as an endorser. Endorsee: The party to whom the rights are transferred is referred to as an endorsee. Types of ChequeThere are different types of cheques based on the type of issuer and drawee. The following are the most common types of cheques:
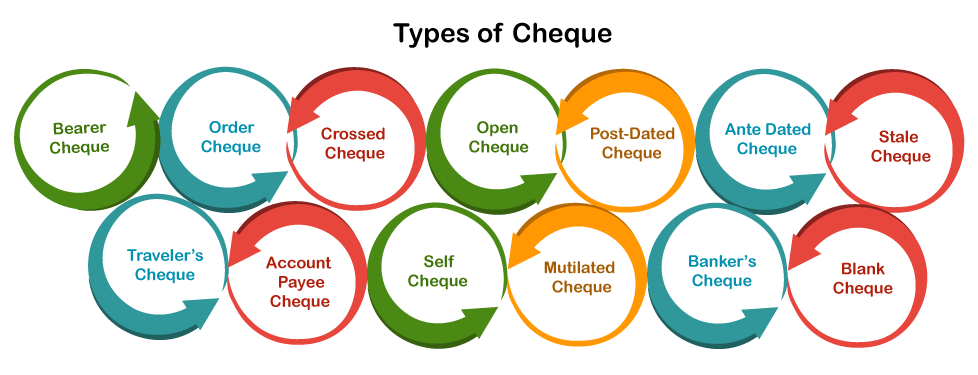
Let us discuss each type in details: What is a Bearer Cheque?A bearer cheque refers to a type of cheque that can be withdrawn or encashed by the person bearing the cheque. In simple words, whoever is carrying this type of cheque is eligible to withdraw the amount mentioned on it. A bearer cheque usually gives the person a right to encash the cheque without any identity verification. It makes these types of cheques endorsable. Besides, we can only use a bearer cheque for cash withdrawal. Bearer cheques are not considered safe because once they are misplaced or given to the wrong hands, it can lead to the loss of money specified on it. These types of cheques can be identified by the words 'or bearer' written on them. What is an Order Cheque?Order cheque refers to a type of cheque in which the printed words 'or bearer' are crossed or canceled. More specifically, this type of cheque can only be withdrawn by the person whose name is written on the cheque. No other has the authority to encash these cheques. Moreover, the bank first verifies the person's identity before releasing the payment to ensure the designated person's payment issuance. We cannot endorse order cheques. Besides, we can only identify such cheques by checking the words 'or bearer', which should be in canceled form. What is a Crossed Cheque?When a drawer makes double parallel lines on the bearer cheque's top left corner, it is called a crossed cheque. Doing so ensures the transfer of money to the authorized person only. This means that no matter what, the bank will only transfer a certain amount from the drawer's bank account to the payee's bank account. However, these cheques can be submitted by any third party or individual at the bank. In case of a crossed cheque, no cash withdrawal is allowed. Besides, these cheques can only be withdrawn at the drawee's bank. What is an Open Cheque?An open cheque is a type of cheque that is not crossed. In particular, the word 'OPEN' printed on a cheque should not be canceled or crossed. That is why these cheques are also known as an uncrossed cheque. Like a bearer cheque, an open cheque can also be withdrawn by the person who is bearing or carrying it. These cheques are eligible to be encashed from any bank and any branch without any identity verification. Besides, we can endorse these cheques accordingly. This means that open cheques can be transferred to any other party by the original payee, making him a new payee. To do this, the issuer must write another party's name on a cheque and put his signature on both the front and back sides of the cheque. Otherwise, the bank may deny the payment, making a cheque invalid or suspicious. Furthermore, Bank may also ask for a new payee's signature on the cheque's backside while issuing the money. What is Post Dated Cheque?A post-dated cheque is a type of cheque that is issued with the future date on it. Although we can submit these types of cheques to the bank at any time after their issuance, they will only be processed only according to the date mentioned on them. Moreover, these type of cheques remains valid for three months from the date written on them. It is important to note that we can also submit post-dated cheques to the bank after the date specified on them. This means that these cheques stand valid past the mentioned date, but not before. What is Ante Dated Cheque?Ante dated cheques are the opposite of post-dated cheques. In other words, when a drawer issues a cheque by mentioning a date before the current date, it is called an ante-dated cheque. We can submit these cheques to the bank immediately after getting them, and the bank will transfer the specified sum from the drawer's account to the payee account. However, the date mentioned on a cheque should not exceed three months. What is a Stale Cheque?A stale cheque refers to a type of cheque that has exceeded the validity date. In simple words, if a cheque has been completed three months after the date mentioned on it, then this type of cheque is called a stale cheque. A stale cheque cannot be withdrawn because any ordinary cheque remains valid only three months after the date written on it. What is a Traveler's Cheque?Foreigners mainly use traveler's cheques. This means that these cheques can be used when a drawer travels abroad and wants to avoid carrying hard cash. Travelers' cheques are issued by the bank and withdrawn in other countries to obtain specific currency. These cheques do not expire and can therefore be used in future visits and trips while traveling abroad. What is an Account Payee Cheque?Account payee cheques are the same as the crossed cheque, but there will be no third party involvement. The amount specified on a cheque is directly transferred from the drawer's account to the payee account. These cheques can be identified by the two parallel lines drawn on the cheque's left top corner and the words 'A/C PAYEE' written between the lines. An account payee cheque's main benefit is eliminating the risk of money being encashed by an unauthorized person. The difference between a crossed cheque and an account payee cheque is that a crossed cheque can be endorsed to other parties, while an account-payee cheque cannot be endorsed. What is a Self Cheque?When we want to withdraw money from our bank account using a cheque, we can write 'SELF' in a column asking for a payee's name. In this case, we (as a drawer) are issuing a cheque to ourselves (as a payee). This type of cheque is called a self cheque and can only be withdrawn at the related bank. What is a Mutilated Cheque?A mutilated cheque refers to a cheque that is torn. In simple words, when a cheque is submitted in a torn condition, it is referred to as a mutilated cheque. In case a cheque is torn apart into two or more pieces or the information written on it is torn, the bank has the right to reject the cheque claiming it as an invalid cheque. However, such cheques may be processed if the drawer confirms their validation. The bank will still make the final decision. Besides, if a cheque has torn issues in corners only and the information written on it is completely intact, the bank shall process it further for the withdrawal. What is a Banker's Cheque?As the name suggests, a banker's cheque is a cheque issued by the bank on behalf of the account holder to transfer a certain amount to any other party within the same city. These cheques are only issued after debiting the specified sum of money from the person's account (drawer). Banker's cheques are also referred to as non-negotiable instruments because banks have no reason to dishonor these cheques. Like other cheques, these cheques are also valid for only three months from the date of issuance. However, they can be revalidated under some specific circumstances. What is a Blank Cheque?A blank cheque is a type of cheque in which no other details or fields are filled except a drawer's signature. In this type of cheque, all the fields are left empty. Characteristics of a ChequeSome of the common characteristics of a cheque are listed below:
Next TopicTypes of Triangles
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









