Deadlock in JavaDeadlock in Java is a part of multithreading. Deadlock can occur in a situation when a thread is waiting for an object lock, that is acquired by another thread and second thread is waiting for an object lock that is acquired by first thread. Since, both threads are waiting for each other to release the lock, the condition is called deadlock. 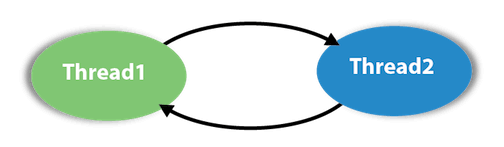
Example of Deadlock in JavaTestDeadlockExample1.java Output:
Thread 1: locked resource 1
Thread 2: locked resource 2
More Complicated DeadlocksA deadlock may also include more than two threads. The reason is that it can be difficult to detect a deadlock. Here is an example in which four threads have deadlocked: Thread 1 locks A, waits for B Thread 2 locks B, waits for C Thread 3 locks C, waits for D Thread 4 locks D, waits for A Thread 1 waits for thread 2, thread 2 waits for thread 3, thread 3 waits for thread 4, and thread 4 waits for thread 1. How to avoid deadlock?A solution for a problem is found at its roots. In deadlock it is the pattern of accessing the resources A and B, is the main issue. To solve the issue we will have to simply re-order the statements where the code is accessing shared resources. DeadlockSolved.java Output: In block 1 In block 2 In the above code, class DeadlockSolved solves the deadlock kind of situation. It will help in avoiding deadlocks, and if encountered, in resolving them. How to Avoid Deadlock in Java?Deadlocks cannot be completely resolved. But we can avoid them by following basic rules mentioned below:
Next TopicInter Thread Communication Example
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










