Exception Handling in JavaThe Exception Handling in Java is one of the powerful mechanism to handle the runtime errors so that the normal flow of the application can be maintained. In this tutorial, we will learn about Java exceptions, it's types, and the difference between checked and unchecked exceptions. What is Exception in Java?Dictionary Meaning: Exception is an abnormal condition. In Java, an exception is an event that disrupts the normal flow of the program. It is an object which is thrown at runtime. What is Exception Handling?Exception Handling is a mechanism to handle runtime errors such as ClassNotFoundException, IOException, SQLException, RemoteException, etc. Advantage of Exception HandlingThe core advantage of exception handling is to maintain the normal flow of the application. An exception normally disrupts the normal flow of the application; that is why we need to handle exceptions. Let's consider a scenario: Suppose there are 10 statements in a Java program and an exception occurs at statement 5; the rest of the code will not be executed, i.e., statements 6 to 10 will not be executed. However, when we perform exception handling, the rest of the statements will be executed. That is why we use exception handling in Java. Hierarchy of Java Exception classesThe java.lang.Throwable class is the root class of Java Exception hierarchy inherited by two subclasses: Exception and Error. The hierarchy of Java Exception classes is given below: 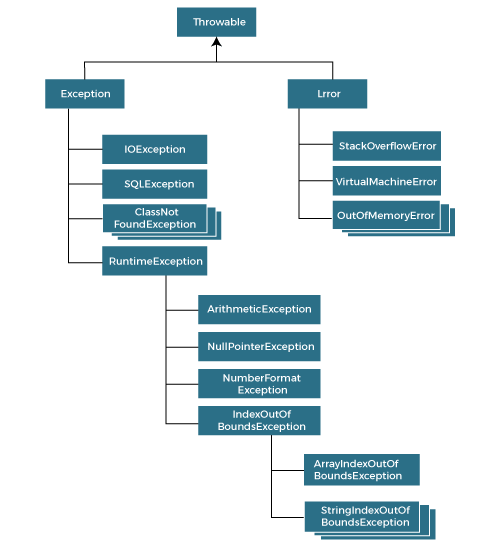
Types of Java ExceptionsThere are mainly two types of exceptions: checked and unchecked. An error is considered as the unchecked exception. However, according to Oracle, there are three types of exceptions namely:
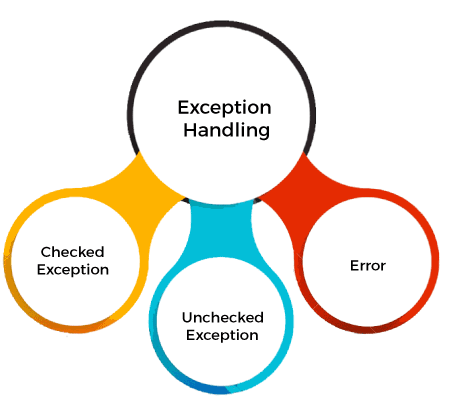
Difference between Checked and Unchecked Exceptions1) Checked ExceptionThe classes that directly inherit the Throwable class except RuntimeException and Error are known as checked exceptions. For example, IOException, SQLException, etc. Checked exceptions are checked at compile-time. 2) Unchecked ExceptionThe classes that inherit the RuntimeException are known as unchecked exceptions. For example, ArithmeticException, NullPointerException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException, etc. Unchecked exceptions are not checked at compile-time, but they are checked at runtime. 3) ErrorError is irrecoverable. Some example of errors are OutOfMemoryError, VirtualMachineError, AssertionError etc. Java Exception KeywordsJava provides five keywords that are used to handle the exception. The following table describes each.
Java Exception Handling ExampleLet's see an example of Java Exception Handling in which we are using a try-catch statement to handle the exception. JavaExceptionExample.java Test it NowOutput: Exception in thread main java.lang.ArithmeticException:/ by zero rest of the code... In the above example, 100/0 raises an ArithmeticException which is handled by a try-catch block. Common Scenarios of Java ExceptionsThere are given some scenarios where unchecked exceptions may occur. They are as follows: 1) A scenario where ArithmeticException occursIf we divide any number by zero, there occurs an ArithmeticException. 2) A scenario where NullPointerException occursIf we have a null value in any variable, performing any operation on the variable throws a NullPointerException. 3) A scenario where NumberFormatException occursIf the formatting of any variable or number is mismatched, it may result into NumberFormatException. Suppose we have a string variable that has characters; converting this variable into digit will cause NumberFormatException. 4) A scenario where ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException occursWhen an array exceeds to it's size, the ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException occurs. there may be other reasons to occur ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException. Consider the following statements. Java Exceptions Index
Next TopicJava Try catch block
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









