Collections in JavaThe Collection in Java is a framework that provides an architecture to store and manipulate the group of objects. Java Collections can achieve all the operations that you perform on a data such as searching, sorting, insertion, manipulation, and deletion. Java Collection means a single unit of objects. Java Collection framework provides many interfaces (Set, List, Queue, Deque) and classes (ArrayList, Vector, LinkedList, PriorityQueue, HashSet, LinkedHashSet, TreeSet). What is Collection in JavaA Collection represents a single unit of objects, i.e., a group. What is a framework in Java
What is Collection frameworkThe Collection framework represents a unified architecture for storing and manipulating a group of objects. It has:
Hierarchy of Collection FrameworkLet us see the hierarchy of Collection framework. The java.util package contains all the classes and interfaces for the Collection framework. 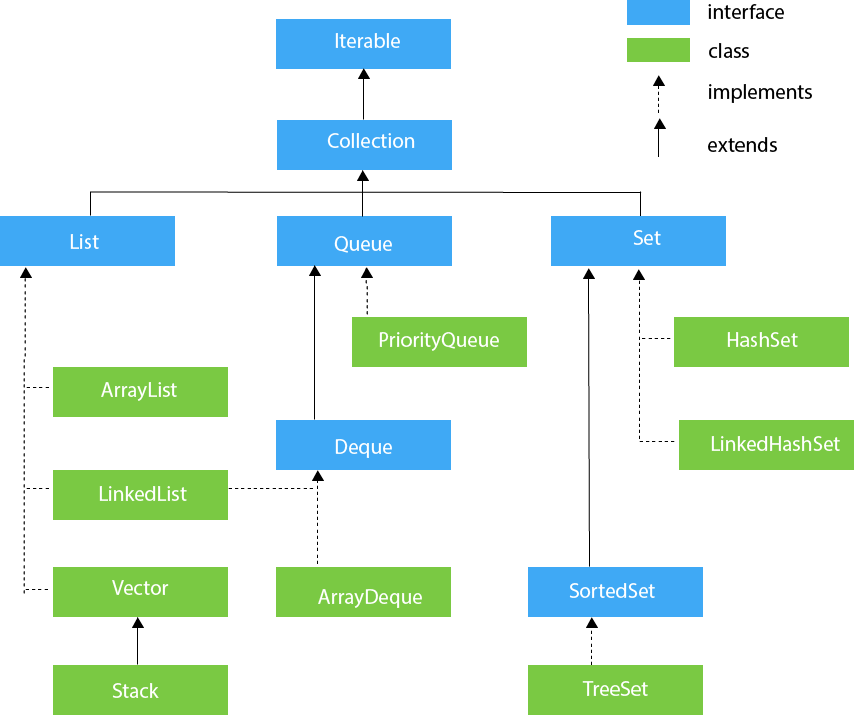
Methods of Collection interfaceThere are many methods declared in the Collection interface. They are as follows:
Iterator interface
Methods of Iterator interfaceThere are only three methods in the Iterator interface. They are:
Iterable InterfaceThe Iterable interface is the root interface for all the collection classes. The Collection interface extends the Iterable interface and therefore all the subclasses of Collection interface also implement the Iterable interface. It contains only one abstract method. i.e., It returns the iterator over the elements of type T. Collection InterfaceThe Collection interface is the interface which is implemented by all the classes in the collection framework. It declares the methods that every collection will have. In other words, we can say that the Collection interface builds the foundation on which the collection framework depends. Some of the methods of Collection interface are Boolean add ( Object obj), Boolean addAll ( Collection c), void clear(), etc. which are implemented by all the subclasses of Collection interface. List InterfaceList interface is the child interface of Collection interface. It inhibits a list type data structure in which we can store the ordered collection of objects. It can have duplicate values. List interface is implemented by the classes ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector, and Stack. To instantiate the List interface, we must use : There are various methods in List interface that can be used to insert, delete, and access the elements from the list. The classes that implement the List interface are given below. ArrayListThe ArrayList class implements the List interface. It uses a dynamic array to store the duplicate element of different data types. The ArrayList class maintains the insertion order and is non-synchronized. The elements stored in the ArrayList class can be randomly accessed. Consider the following example. Output: Ravi Vijay Ravi Ajay LinkedListLinkedList implements the Collection interface. It uses a doubly linked list internally to store the elements. It can store the duplicate elements. It maintains the insertion order and is not synchronized. In LinkedList, the manipulation is fast because no shifting is required. Consider the following example. Output: Ravi Vijay Ravi Ajay VectorVector uses a dynamic array to store the data elements. It is similar to ArrayList. However, It is synchronized and contains many methods that are not the part of Collection framework. Consider the following example. Output: Ayush Amit Ashish Garima StackThe stack is the subclass of Vector. It implements the last-in-first-out data structure, i.e., Stack. The stack contains all of the methods of Vector class and also provides its methods like boolean push(), boolean peek(), boolean push(object o), which defines its properties. Consider the following example. Output: Ayush Garvit Amit Ashish Queue InterfaceQueue interface maintains the first-in-first-out order. It can be defined as an ordered list that is used to hold the elements which are about to be processed. There are various classes like PriorityQueue, Deque, and ArrayDeque which implements the Queue interface. Queue interface can be instantiated as: There are various classes that implement the Queue interface, some of them are given below. PriorityQueueThe PriorityQueue class implements the Queue interface. It holds the elements or objects which are to be processed by their priorities. PriorityQueue doesn't allow null values to be stored in the queue. Consider the following example. Output: head:Amit Sharma head:Amit Sharma iterating the queue elements: Amit Sharma Raj JaiShankar Vijay Raj after removing two elements: Raj Vijay Raj Deque InterfaceDeque interface extends the Queue interface. In Deque, we can remove and add the elements from both the side. Deque stands for a double-ended queue which enables us to perform the operations at both the ends. Deque can be instantiated as: ArrayDequeArrayDeque class implements the Deque interface. It facilitates us to use the Deque. Unlike queue, we can add or delete the elements from both the ends. ArrayDeque is faster than ArrayList and Stack and has no capacity restrictions. Consider the following example. Output: Gautam Karan Ajay Set InterfaceSet Interface in Java is present in java.util package. It extends the Collection interface. It represents the unordered set of elements which doesn't allow us to store the duplicate items. We can store at most one null value in Set. Set is implemented by HashSet, LinkedHashSet, and TreeSet. Set can be instantiated as: HashSetHashSet class implements Set Interface. It represents the collection that uses a hash table for storage. Hashing is used to store the elements in the HashSet. It contains unique items. Consider the following example. Output: Vijay Ravi Ajay LinkedHashSetLinkedHashSet class represents the LinkedList implementation of Set Interface. It extends the HashSet class and implements Set interface. Like HashSet, It also contains unique elements. It maintains the insertion order and permits null elements. Consider the following example. Output: Ravi Vijay Ajay SortedSet InterfaceSortedSet is the alternate of Set interface that provides a total ordering on its elements. The elements of the SortedSet are arranged in the increasing (ascending) order. The SortedSet provides the additional methods that inhibit the natural ordering of the elements. The SortedSet can be instantiated as: TreeSetJava TreeSet class implements the Set interface that uses a tree for storage. Like HashSet, TreeSet also contains unique elements. However, the access and retrieval time of TreeSet is quite fast. The elements in TreeSet stored in ascending order. Consider the following example: Output: Ajay Ravi Vijay
Next TopicJava ArrayList
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









