Interface in JavaAn interface in Java is a blueprint of a class. It has static constants and abstract methods. The interface in Java is a mechanism to achieve abstraction. There can be only abstract methods in the Java interface, not method body. It is used to achieve abstraction and multiple inheritance in Java. In other words, you can say that interfaces can have abstract methods and variables. It cannot have a method body. Java Interface also represents the IS-A relationship. It cannot be instantiated just like the abstract class. Since Java 8, we can have default and static methods in an interface. Since Java 9, we can have private methods in an interface. Why use Java interface?There are mainly three reasons to use interface. They are given below.

How to declare an interface?An interface is declared by using the interface keyword. It provides total abstraction; means all the methods in an interface are declared with the empty body, and all the fields are public, static and final by default. A class that implements an interface must implement all the methods declared in the interface. Syntax:Java 8 Interface ImprovementSince Java 8, interface can have default and static methods which is discussed later. Internal addition by the compilerThe Java compiler adds public and abstract keywords before the interface method. Moreover, it adds public, static and final keywords before data members.In other words, Interface fields are public, static and final by default, and the methods are public and abstract. 
The relationship between classes and interfacesAs shown in the figure given below, a class extends another class, an interface extends another interface, but a class implements an interface. 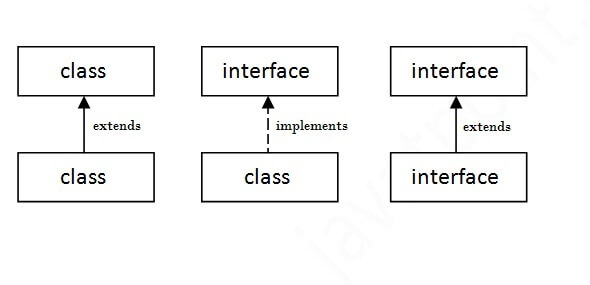
Java Interface ExampleIn this example, the Printable interface has only one method, and its implementation is provided in the A6 class. Output: Hello Java Interface Example: DrawableIn this example, the Drawable interface has only one method. Its implementation is provided by Rectangle and Circle classes. In a real scenario, an interface is defined by someone else, but its implementation is provided by different implementation providers. Moreover, it is used by someone else. The implementation part is hidden by the user who uses the interface. File: TestInterface1.java Output: drawing circle Java Interface Example: BankLet's see another example of java interface which provides the implementation of Bank interface. File: TestInterface2.java Output: ROI: 9.15 Multiple inheritance in Java by interfaceIf a class implements multiple interfaces, or an interface extends multiple interfaces, it is known as multiple inheritance. 
Output:Hello
Welcome
Q) Multiple inheritance is not supported through class in java, but it is possible by an interface, why?As we have explained in the inheritance chapter, multiple inheritance is not supported in the case of class because of ambiguity. However, it is supported in case of an interface because there is no ambiguity. It is because its implementation is provided by the implementation class. For example: Output: Hello As you can see in the above example, Printable and Showable interface have same methods but its implementation is provided by class TestTnterface1, so there is no ambiguity. Interface inheritanceA class implements an interface, but one interface extends another interface. Output: Hello Welcome Java 8 Default Method in InterfaceSince Java 8, we can have method body in interface. But we need to make it default method. Let's see an example: File: TestInterfaceDefault.java Output: drawing rectangle default method Java 8 Static Method in InterfaceSince Java 8, we can have static method in interface. Let's see an example: File: TestInterfaceStatic.java Output: drawing rectangle 27 Q) What is marker or tagged interface?An interface which has no member is known as a marker or tagged interface, for example, Serializable, Cloneable, Remote, etc. They are used to provide some essential information to the JVM so that JVM may perform some useful operation. Nested Interface in JavaNote: An interface can have another interface which is known as a nested interface. We will learn it in detail in the nested classes chapter. For example: |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










