Java TreeMap class
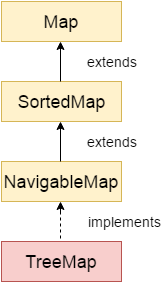
Java TreeMap class is a red-black tree based implementation. It provides an efficient means of storing key-value pairs in sorted order.
The important points about Java TreeMap class are:
- Java TreeMap contains values based on the key. It implements the NavigableMap interface and extends AbstractMap class.
- Java TreeMap contains only unique elements.
- Java TreeMap cannot have a null key but can have multiple null values.
- Java TreeMap is non synchronized.
- Java TreeMap maintains ascending order.
TreeMap class declaration
Let's see the declaration for java.util.TreeMap class.
TreeMap class Parameters
Let's see the Parameters for java.util.TreeMap class.
- K: It is the type of keys maintained by this map.
- V: It is the type of mapped values.
Constructors of Java TreeMap class
| Constructor | Description |
|---|
| TreeMap() | It is used to construct an empty tree map that will be sorted using the natural order of its key. |
| TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) | It is used to construct an empty tree-based map that will be sorted using the comparator comp. |
| TreeMap(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m) | It is used to initialize a treemap with the entries from m, which will be sorted using the natural order of the keys. |
| TreeMap(SortedMap<K,? extends V> m) | It is used to initialize a treemap with the entries from the SortedMap sm, which will be sorted in the same order as sm. |
Methods of Java TreeMap class
| Method | Description |
|---|
| Map.Entry<K,V> ceilingEntry(K key) | It returns the key-value pair having the least key, greater than or equal to the specified key, or null if there is no such key. |
| K ceilingKey(K key) | It returns the least key, greater than the specified key or null if there is no such key. |
| void clear() | It removes all the key-value pairs from a map. |
| Object clone() | It returns a shallow copy of TreeMap instance. |
| Comparator<? super K> comparator() | It returns the comparator that arranges the key in order, or null if the map uses the natural ordering. |
| NavigableSet<K> descendingKeySet() | It returns a reverse order NavigableSet view of the keys contained in the map. |
| NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMap() | It returns the specified key-value pairs in descending order. |
| Map.Entry firstEntry() | It returns the key-value pair having the least key. |
| Map.Entry<K,V> floorEntry(K key) | It returns the greatest key, less than or equal to the specified key, or null if there is no such key. |
| void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K,? super V> action) | It performs the given action for each entry in the map until all entries have been processed or the action throws an exception. |
| SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey) | It returns the key-value pairs whose keys are strictly less than toKey. |
| NavigableMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive) | It returns the key-value pairs whose keys are less than (or equal to if inclusive is true) toKey. |
| Map.Entry<K,V> higherEntry(K key) | It returns the least key strictly greater than the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| K higherKey(K key) | It is used to return true if this map contains a mapping for the specified key. |
| Set keySet() | It returns the collection of keys exist in the map. |
| Map.Entry<K,V> lastEntry() | It returns the key-value pair having the greatest key, or null if there is no such key. |
| Map.Entry<K,V> lowerEntry(K key) | It returns a key-value mapping associated with the greatest key strictly less than the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| K lowerKey(K key) | It returns the greatest key strictly less than the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet() | It returns a NavigableSet view of the keys contained in this map. |
| Map.Entry<K,V> pollFirstEntry() | It removes and returns a key-value mapping associated with the least key in this map, or null if the map is empty. |
| Map.Entry<K,V> pollLastEntry() | It removes and returns a key-value mapping associated with the greatest key in this map, or null if the map is empty. |
| V put(K key, V value) | It inserts the specified value with the specified key in the map. |
| void putAll(Map<? extends K,? extends V> map) | It is used to copy all the key-value pair from one map to another map. |
| V replace(K key, V value) | It replaces the specified value for a specified key. |
| boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) | It replaces the old value with the new value for a specified key. |
| void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> function) | It replaces each entry's value with the result of invoking the given function on that entry until all entries have been processed or the function throws an exception. |
| NavigableMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive, K toKey, boolean toInclusive) | It returns key-value pairs whose keys range from fromKey to toKey. |
| SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) | It returns key-value pairs whose keys range from fromKey, inclusive, to toKey, exclusive. |
| SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey) | It returns key-value pairs whose keys are greater than or equal to fromKey. |
| NavigableMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive) | It returns key-value pairs whose keys are greater than (or equal to, if inclusive is true) fromKey. |
| boolean containsKey(Object key) | It returns true if the map contains a mapping for the specified key. |
| boolean containsValue(Object value) | It returns true if the map maps one or more keys to the specified value. |
| K firstKey() | It is used to return the first (lowest) key currently in this sorted map. |
| V get(Object key) | It is used to return the value to which the map maps the specified key. |
| K lastKey() | It is used to return the last (highest) key currently in the sorted map. |
| V remove(Object key) | It removes the key-value pair of the specified key from the map. |
| Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() | It returns a set view of the mappings contained in the map. |
| int size() | It returns the number of key-value pairs exists in the hashtable. |
| Collection values() | It returns a collection view of the values contained in the map. |
Java TreeMap Example
Output:100 Amit
101 Vijay
102 Ravi
103 Rahul
Java TreeMap Example: remove()
Output:
Before invoking remove() method
100 Amit
101 Vijay
102 Ravi
103 Rahul
After invoking remove() method
100 Amit
101 Vijay
103 Rahul
Java TreeMap Example: NavigableMap
descendingMap: {103=Rahul, 102=Ravi, 101=Vijay, 100=Amit}
headMap: {100=Amit, 101=Vijay, 102=Ravi}
tailMap: {102=Ravi, 103=Rahul}
subMap: {101=Vijay, 102=Ravi}
Java TreeMap Example: SortedMap
headMap: {100=Amit, 101=Vijay}
tailMap: {102=Ravi, 103=Rahul}
subMap: {100=Amit, 101=Vijay}
What is difference between HashMap and TreeMap?
| HashMap | TreeMap |
|---|
| 1) HashMap can contain one null key. | TreeMap cannot contain any null key. |
| 2) HashMap maintains no order. | TreeMap maintains ascending order. |
Java TreeMap Example: Book
Output:
1 Details:
101 Let us C Yashwant Kanetkar BPB 8
2 Details:
102 Data Communications & Networking Forouzan Mc Graw Hill 4
3 Details:
103 Operating System Galvin Wiley 6
|

 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now









