Java Catch Multiple ExceptionsJava Multi-catch blockA try block can be followed by one or more catch blocks. Each catch block must contain a different exception handler. So, if you have to perform different tasks at the occurrence of different exceptions, use java multi-catch block. Points to remember
Flowchart of Multi-catch Block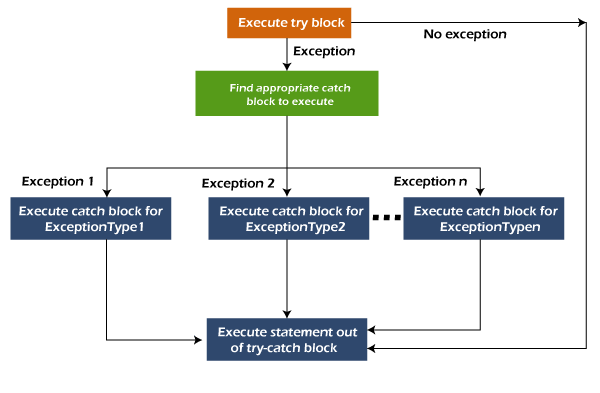
Example 1Let's see a simple example of java multi-catch block. MultipleCatchBlock1.java Test it NowOutput: Arithmetic Exception occurs rest of the code Example 2MultipleCatchBlock2.java Test it NowOutput: ArrayIndexOutOfBounds Exception occurs rest of the code In this example, try block contains two exceptions. But at a time only one exception occurs and its corresponding catch block is executed. MultipleCatchBlock3.java Test it NowOutput: Arithmetic Exception occurs rest of the code Example 4In this example, we generate NullPointerException, but didn't provide the corresponding exception type. In such case, the catch block containing the parent exception class Exception will invoked. MultipleCatchBlock4.java Test it NowOutput: Parent Exception occurs rest of the code Example 5Let's see an example, to handle the exception without maintaining the order of exceptions (i.e. from most specific to most general). MultipleCatchBlock5.java Test it NowOutput: Compile-time error
Next TopicNested Try Block
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










