Ruby BlocksRuby code blocks are called closures in other programming languages. It consist of a group of codes which is always enclosed with braces or written between do..end. The braces syntax always have the higher precedence over the do..end syntax. Braces have high precedence and do has low precedence. A block is written in two ways,
Both are same and have the same functionality. To invoke a block, you need to have a function with the same name as the block. A block is always invoked with a function. Blocks can have their own arguments. syntax: Example: The below example shows the multi-line block. Output: 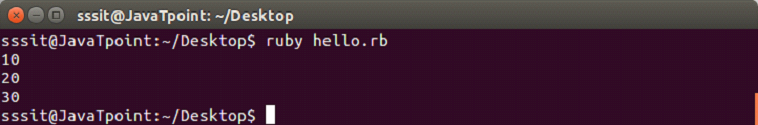 Below example shows the inline block. Output: 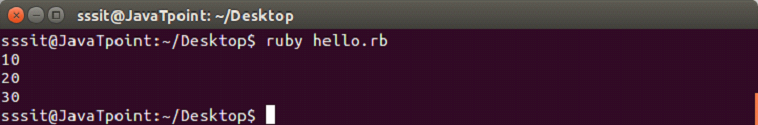 The yield statementThe yield statement is used to call a block within a method with a value. Example: Output: 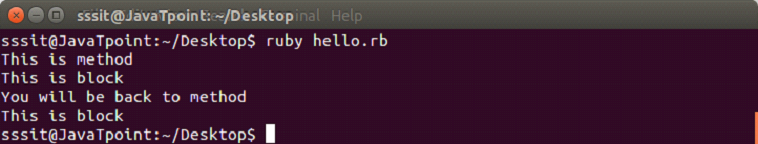 While the execution of met method, when we reach at yield line, the code inside the block is executed. When block execution finishes, code for met method continues. Passing parameters with yield statement One or more than one parameter can be passed with the yield statement. Example: Output: 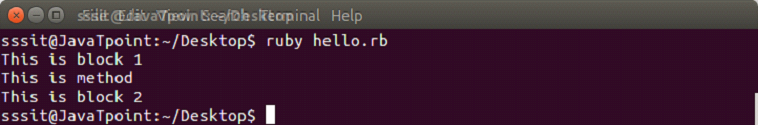 Block VariablesWe can use same variable outside and inside a block parameter. Let's see the following example. Example: Output: 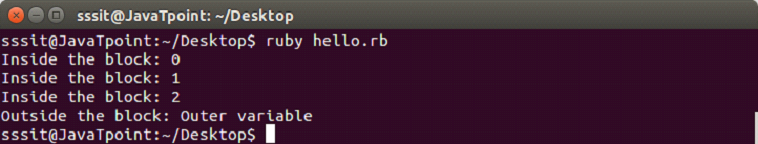 In this example, we are using same variable inside the block as the block parameter x and outside the block as a variable x. BEGIN and END blockRuby BEGIN and END block is used to declare that file is being loaded and file has been loaded respectively. Example: Output: 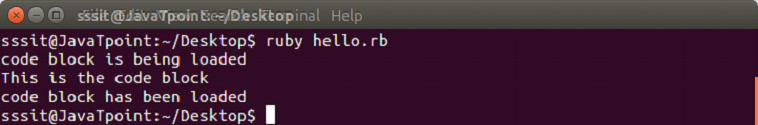 Ampersand parameter (&block)The &block is a way to pass a reference (instead of a local variable) to the block to a method. Here, block word after the & is just a name for the reference, any other name can be used instead of this. Example: Output: 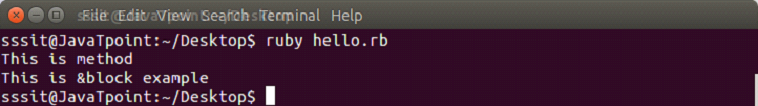 Here, the block variable inside method met is a reference to the block. It is executed with the call mehtod. The call method is same as yield method. Initializing objects with default valuesRuby has an initializer called yield(self). Here, self is the object being initialized. Example: Output: 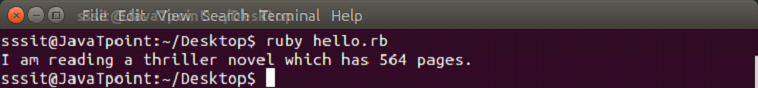
Next TopicRuby modules
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









