Ruby File I/ORuby I/O is a way to interact with your system. Data is sent in the form of bytes/characters. IO class is the basis for all input and output in Ruby. It may be duplexed, hence may use more than one native operating system stream. IO has a subclass as File class which allows reading and writing files in Ruby. The two classes are closely associated. IO object represent readable/writable interactions to keyboards and screens. Common modes in I/O port
IO ConsoleThe IO console provides different methods to interact with console. The class IO provides following basic methods:
Ruby opening a fileA Ruby file can be created using different methods for reading, writing or both. There are two methods to open a file in Ruby:
Difference between both the methods is that File.open method can be associated with a block while File.new method can't. Syntax: Or, Example to create a file Let's create a file in Ruby using File.open method to read or write data from files. Step 1) In file hello.rb, write the code to create a new file as shown below. Step 2) Type the following two commands in the console to view the created file. 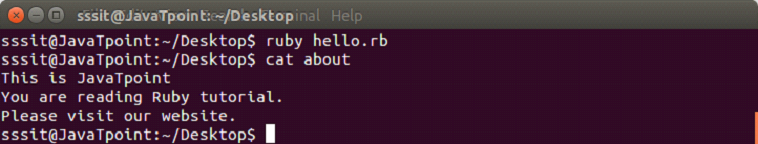
The new file is created and content is displayed in the terminal as shown above. Ruby reading a fileThere are three different methods to read a file. To return a single line, following syntax is used. Syntax: To return the whole file after the current position, following syntax is used. Syntax: To return file as an array of lines, following syntax is used. Syntax: Example to read a fileLet's create a file in Ruby using File.open method to read or write data from files. Step 1) In file hello.rb, write the code to read an already existing file as shown below. Step 2) Type the following command in the console to read the file. 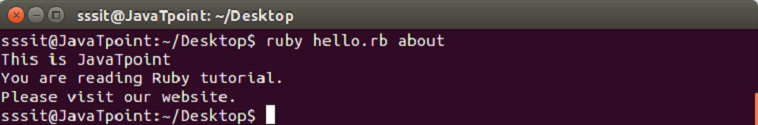
Content of about file is displayed in the console. The sysread MethodThe sysread method is also used to read the content of a file. With the help of this method you can open a file in any mode. Example: In file hello.rb, write the code to read an already existing file as shown below. Output: 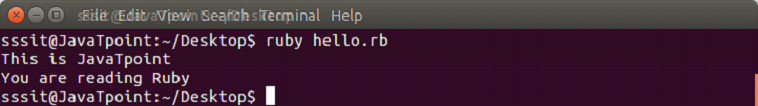
The argument 40 will print till 40 characters from the file. Ruby writing a fileWith the help of syswrite method, you can write content into a file. File needs to be opened in write mode for this method. The new content will over ride the old content in an already existing file. Example: Output: 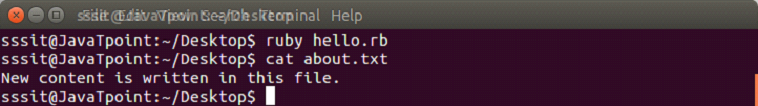
Ruby renaming and deleting a fileRuby files are renamed using rename method and deleted using delete mehtod. To rename a file, following syntax is used. Syntax: Example: Output: 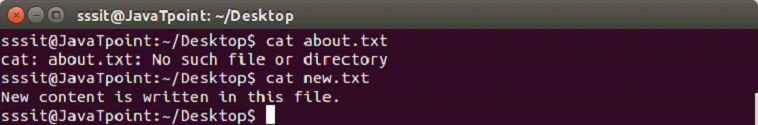
In the above output, about.txt file no longer exist as its name has been changed to new.txt file. To delete a file, following syntax is used. Syntax: Example: Output: 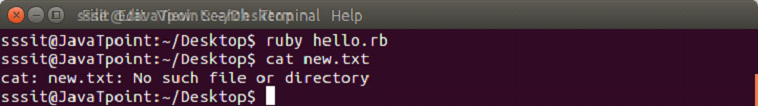
In the above output, new.txt file no longer exist as it has been deleted.
Next TopicRuby directories
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










