Solana blockchainSolana (SOL) represents a currency that was created to be comparable to and better than Ethereum. Anatoly Yakovenko, a software developer, created Solana, which is named after a tiny Southern California coastal community. Yakovenko suggested this novel cryptocurrency in 2017, Solana will go live in March 2020. Today, SOL is a well-known cryptocurrency, ranking 11th in terms of total market capitalization. What Exactly Is Solana?
Solana is a type of blockchain that resembles Ethereum so much that it's commonly known as a "Ethereum killer." The SOL token, like Ethereum, can be acquired on the majority of major exchanges. The true value of the token is in completing transactions through the Sol network, which offers distinct features.A proof-of-history consensus technique is used by the Solana blockchain. This approach defines the following block in Solana's chain using timestamps. To define each block in their chains, many early digital currencies, including Bitcoin and Litecoin, used a proof-of-work mechanism. Proof of work employs a consensus technique in which miners select what their subsequent block will be. However, this proof-of-work mechanism is sluggish and resource-intensive, requiring massive quantities of energy. This is one of the reasons Ethereum switched to a proof-of-stake method, which reduced the usage of energy by 99.9%. Proof of stake, unlike the previous proof-of-work technique, employs staking to specify the next block. The blockchain holds stalled coins as collateral until validators reach an agreement on the chain's next block. Delegated Evidence of Stake by SolanaSolana use "a combination of time-tested cryptography methods and novel approaches to address the drawbacks of crypto's first-wave solutions," as stated by Konstantin Anissimov, the chief executive officer of crypto exchange CEX.IO. The key problem Solana was seeking to tackle was Ethereum's scalability concerns, which were aided by its unique blend of proof of history and delegated proof-of-stake algorithms. Delegated proof-of-stake is an alternative to the more common proof-of-stake method. 
For those who need an overview, the proof-of-stake method is a set of transactions that uses a system of validators to generate fresh blocks in a blockchain. Solana's delegated proof-of-stake method provides consumers with various benefits. According to Christian Hazim, researcher at ETF supplier Global X, the history algorithm provides a layer of protection to the network. Solana, in essence, addresses two of the three challenges raised by Vitalik Buterin, the co-founder of Ethereum, in his cryptocurrency trilemma of scalability, security, and decentralisation. Although Buterin first asserted that Ethereum will answer all three components of the trilemma, most experts assume the network would only address two: security and decentralisation. Solana, on the other hand, aims to address two aspects of the trilemma: safety and capacity. SOL's proof of history mechanism offers the network with unrivalled security. While the Solana platform's computing speed provides for improved scalability. What distinguishes Solana?Solana offers exponentially greater speeds for transactions compared to those offered by Ethereum ( Eth ) and Cardano (ADA), at just a little of the cost, according to Anissimov, by using an innovative combination of proof of the past and delegated proof for stake. Unlike proof on work, which utilises miners to determine the next chain in the chain, or documentation of risk, which employs staked coins to define the block that follows, evidence of history defines blocks in the Solana chain using timestamps. This novel technique allows blockchain validators to vote for the timestamps of distinct blocks on the chain. This maintains the chain decentralised while also enabling for quicker, more secure calculations. How Does Solana Function?Solana employs both proof-of-history and delegate proof-of-stake protocols. According to Bryan Routledge, an assistant professor many finance at Carnegie Mellon University's Tepper School of Business, Solana is attempting to "process lots of transactions quickly. "According to Routledge, attempting to execute transactions rapidly frequently necessitates centralization. Visa, for example, requires an enormous number of computers to maintain its processing speed. Bitcoin, on the other hand, "processes transactions very slowly" in order to stay decentralised, according to Routledge. Because the fundamental goal of the technology known as blockchain is to create decentralised systems, Solana seeks to handle transactions at the speed of a major, centralised firm like Visa while retaining Bitcoin's decentralisation. Because Solana's systems have reduced environmental and monetary costs, this speed allows for greater scalability. The rapid addition of blocks to Solana's blockchain necessitates extra degrees of protection for the blockchain. Solana's proof of past algorithm come into play here. This algorithm timestamps every record in such a way that the system's security is maintained. Solana's SOL tokens were then staked and utilized as collateral to conduct network transactions. These transactions range from smart contract validation to employing Solana as a token that is not fungible (NFT) marketplace. Degenerate Ape Academy was the first significant NFT venture on the Solana marketplace for digital currencies in August 2021, over a year after Solana was created. Solana's price increased from roughly thirty dollars to seventy-five in the first week of that month. Solana reached an all-time high of approximately $260 in November 2021, at the peak of the cryptocurrency bull run. What are the distinctions between Solana and Ethereum?Both blockchains have supporters and a plethora of apps operating on them. However, Ethereum was the most widely used because it provides a more accessible and complex DApp environment. Certain distinctions between the two cannot be missed. We'll look at the distinctions among these blockchains from 10 different angles. 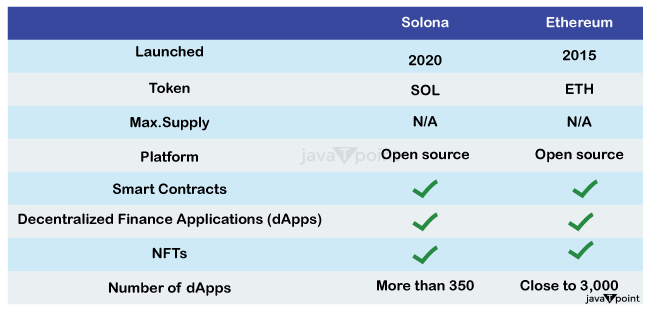
Process: Ethereum 1.0 is based on a the power needed consensus process, similar to the one employed by Bitcoin's blockchain. This implies that miners, who utilise their computer capacity to validate transactions on the blockchain and produce new blocks, defend the network. This is the very essence of a decentralised network, and it contributes to boost network security. Programming language: Smart contracts, which operate on decentralised blockchain networks, allow developers to design programmes. Every network node has its own virtual computer, which executes commands as they are recorded to the digital record. The programming languages and virtual machines supported by a smart-contract platform have an impact on smart contract security. Of obviously, a programming language is crucial since programmers who are more comfortable with it are less likely to make errors. This means that a previous virtual machine may be more reliable and have fewer mistakes than a younger one. The architecture of Solana is more complex and allows multithreading. It also runs its programmes using the Gulf Stream's transaction forwarding technique rather than mempools. Downtimes: Because Ethereum was the first customizable blockchain network, most of its problems have been ironed out. Although it might become crowded at times, it is never down since it is far more decentralised than other chains. It's one of the reasons Ethereum has failed to scale. The project's goal is for any cryptocurrency user to be able to run an Ether node on whatever hardware is available. The expense of the transaction : This is critical since many individuals despise paying transaction fees. Solana's minimal transaction costs are well-known. Solana has a lower transaction cost than Ethereum. Different blockchains manage block size differently. Some block dimensions are dictated by storage (for example, MB in Bitcoin), whereas others are defined by a gas constraint . Transaction speed: Solana is one of the quickest digital currencies to use when it relates to transaction processing. This is because of network architecture. Ethereum prioritised decentralisation, whereas Solana prioritised throughput. Size of the network: Ether is the largest platform which enables smart contracts. As reported by DeFi Llama, Ethereum's TVL (Total Worth Locked) has risen to $28.61 trillion, while Solana's TVL has remained unchanged at $276.15 million. When it pertains to TVL, the disparity among the two channels is about 200%. As a result, most financial apps choose Ethereum. Solana is only getting started with banks, and it may take some time for it to catch the full extent of Ethereum's massive network size. Market capitalization : Ethereum and Solana both include native currency that are used to pay transaction fees. These are two of the most important currencies in the whole cryptocurrency industry. As of the beginning of 2022, 1 ETH is worth $1,621, and Ethereum's market valuation is $198.4 billion, with approximately 122.3 million ETH tokens in circulation. Ether is the second most valuable cryptocurrency, after only Bitcoin. The DeFi ecosystem : Because of its age, Ethereum has a considerably wider and more diversified DeFi ecosystem that Solana. Solana, on the other hand, is making an effort to recruit more developers into its network by adopting a number of marketing methods such as hacking competitions and bug-bounty programmes. These strategies have helped to grow the number of consumers and developers since its beginnings. NFTs : Although Ethereum was not the first protocol to employ non-fungible tokens to produce NFTs that are (Non-Fungible Tokens), it became one of the most influential. Although the trade of NFTs boomed in 2021, NFTs were employed much earlier. NFTs were introduced in one of the earliest blockchain apps, CryptoKitties. It made headlines in 2017 when the software caused massive congestion on Ethereum. Solana remarkeble FeaturesLet's take a look on some of the most intriguing aspects of the distribution system known as Solana. What makes it so quick, and what distinguishes it from other cryptocurrencies. Evidence of History (PoH): When it comes to validating data blocks and records in a decentralised system, all computers have to collaborate on a time. These machines are referred to as nodes. These nodes must constantly interact in order to agree on whenever the building was produced. Furthermore, because not every nodes will have an adequate connection to the internet, the rate at which they deliver Blocks will vary. Sealevel: A word used to explain the fact that Solana validators are not required to validate just one purchase at a time. Rather, they can validate numerous smart contract codes at the same time. Scalability and Future Proof: This brings us to the issue of Solana's Scalability. According to Solana, it is not restricted by ideas or software, but by hardware. So, if processing power doubles in the future, Solana will be able to increase its efficiency. Rust programming language : Solana writes code in the Rust language for programming. This is distinct from Ethereum's usage of the Solidity programming language. Rust is a language with low levels, which implies that it requires more effort to build things, but it is far more powerful that other programming languages. One disadvantage of Rust is that users cannot just paste existing code from other blockchains into Rust. You must reconstruct and rebuild the code in Rust. Developers that intend to migrate to the Solana system will find it inconvenient. These smart contracts, however, will be stronger than Ethereum. Pipelining : Solana's activities mostly make use of Pipeline technology, which is commonly used to increase transaction speed. To handle a data input stream, the Pipeline system employs numerous consecutive phases, each with its own specialised hardware. That's how it'll appear, similar to a washing machine, only with separate dryer and washer portions. Cloudbreak : One of the most important aspects of Solana is its ability to scale, which is unique to this Cloudbreak technology. Cloudbreak is an horizontal scaling solution that uses an organised database to read and write transaction input effectively. Cloudbreak is also involved in the establishment of hardware and software links. Algorithm of Tower Tolerance for Byzantine FaultsIf : one of the nodes on the blockchain fails or is disrupted in performing its function, the Tower's Byzantine fault tolerance mechanism takes over to guarantee that it does not affect other nodes on the blockchain. Hill Tolerance for Byzantine Faults is a mechanism that allows failed nodes to continue operating despite many operational failures. Archivers : The archivers are requested to affirm that they are routinely storing the needed data by the network, which is done via archiving tiny bits of the state, and they are urged to keep away from consensus meetings. The history of the state has been erasure-coded and fractured. ConclusionUsing those protocols, systems, and technologies, Solana has evolved into a unique blockchain network with luxurious scalability, safety, and transaction speed capabilities. Solana is fantastic, with sky-high potentials that state and verify it is the ideal suit for Defi applications. It is also manageable, with limited charge alternatives and a short confirmation time, so it aids in the creation of good projects. Solana appears to have a bright career ahead of him. It is introducing more well-known digital applications to its network every day and gaining traction. We hope we managed to explain and comprehend everything about Solana, which how it operates, and its many characteristics.
Next TopicWhat Is Cardano
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










