Difference between 8085 and 8086 MicroprocessorMicroprocessors are the heart of modern computing and are responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations. Among the many microprocessors that have been developed, two of the most significant are the Intel 8085 and the Intel 8086. While both microprocessors were developed by Intel and share some similarities, there are several key differences between the two. In this article, we discuss the core differences between these two popular microprocessors. Let us first understand each in brief: 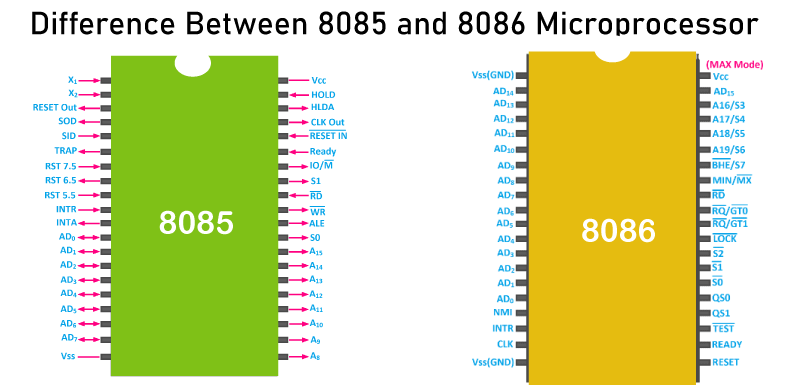
What is the 8085 Microprocessor?The 8085 microprocessor is a central processing unit (CPU) that was designed by Intel Corporation in 1976. It was an improvement over the previous 8008 and 8080 microprocessors, with more instructions executed per second for better performance. The 8085 was the first 8-bit microprocessor to have an onboard stack pointer, which made it easier to write and execute programs efficiently. The 8085 microprocessor is based on the Von Neumann architecture, which means that the memory used for both program instructions and data is stored in the same physical memory space. It has a clock speed of 3 MHz, which means that it can execute 3 million instructions per second. The 8085 microprocessor has a 16-bit address bus, which means that it can address up to 64 kilobytes of memory. It has an 8-bit data bus, which means that it can process data in 8-bit chunks. The 8085 microprocessor has a total of 246 instructions, which can be executed using a combination of the 8-bit registers and the accumulator. The 8085 microprocessor was widely used in a variety of applications, including home computers, calculators, and industrial control systems. It was particularly popular in India, where it was used in the manufacturing of a variety of electronic devices. Although the 8085 microprocessor was eventually superseded by more powerful microprocessors, it remains an important part of the history of computing and is still used in some embedded systems and retro-computing projects. What is the 8086 Microprocessor?The 8086 microprocessor is a central processing unit (CPU) developed by Intel Corporation in the late 1970s. It was the first 16-bit microprocessor and represented a significant improvement over the previous 8-bit microprocessors, such as the 8085. The 8086 microprocessor is based on the Von Neumann architecture and has a clock speed of 5 MHz, which means that it can execute up to 5 million instructions per second. The 8086 microprocessor has a 16-bit data bus and a 20-bit address bus, which means that it can access up to 1 megabyte of memory. It has a total of 29,000 transistors and was manufactured using a 3-micron process technology. One of the most important features of the 8086 microprocessor is its backward compatibility with the 8085 microprocessor. This allowed software written for the 8085 microprocessor to run on the 8086 microprocessor without any modification. The 8086 microprocessor also introduced several new instructions and addressing modes, which made it more versatile and efficient than its predecessors. The 8086 microprocessor was widely used in a variety of applications, including personal computers, industrial control systems, and embedded systems. It was particularly popular in the IBM PC and compatible computers, which helped to establish the dominance of the x86 architecture in the PC industry. Today, the 8086 microprocessor is considered a classic microprocessor and is often used in retro computing projects and educational settings. Its impact on the development of modern computing cannot be overstated, as it paved the way for more powerful and sophisticated microprocessors, such as the 80286, 80386, and 80486, which became the backbone of the modern computing industry. Differences: 8085 vs. 8086 MicroprocessorsHere's a table outlining the key differences between the 8085 and 8086 microprocessors:
ConclusionIn conclusion, the 8085 and 8086 microprocessors represent two important milestones in the development of modern computing. While both microprocessors were designed by Intel Corporation and used in a variety of applications, they differ in several key areas. The 8085 microprocessor is an 8-bit microprocessor with a clock speed of 3 MHz, while the 8086 microprocessor is a 16-bit microprocessor with a clock speed of 5 MHz. The 8086 has a larger address bus and can access up to 1 megabyte of memory, compared to the 64 kilobytes of memory that the 8085 can access. The 8086 also introduced several new instructions and addressing modes, which made it more versatile and efficient than the 8085. The 8086 was backward compatible with the 8085, which allowed software written for the 8085 to run on the 8086 without modification.
Next TopicDifference between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










