Difference Between Acute and Chronic DiseaseAlthough the length of time for acute diseases varies based on the condition being treated and the surrounding circumstances, it is less than the length of time for chronic illnesses. The term "acute" may also be used to describe ailments in which symptoms appear suddenly and without warning. It's not always the case with acute rhinitis that a severe illness is fulminant. It frequently goes hand in hand well with the common cold. On the contrary, a "chronic" ailment is something that grows gradually and gets worse over time, while an acute condition has symptoms that emerge abruptly and get worse quickly. Numerous disorders can manifest in either an acute or chronic state. For instance, acute renal failure happens when a condition like dehydration, blood loss, or taking medications causes kidney damage. However, chronic kidney disease results in long-term illnesses like diabetes or high blood pressure and causes the kidneys to gradually deteriorate over time. 
Acute DiseasesAcute sickness is an ailment or disorder that appears suddenly, progresses quickly, and lasts very briefly. The length of time for acute diseases varies depending on the kind of sickness and its environment, although it is less than for chronic illnesses. In addition, illnesses whose fast and rapid development of symptoms fall under the category of "acute" might be mentioned. It's not always the case with acute rhinitis that a severe illness is fulminant. It frequently comes up while talking about the typical cold. However, diseases like acute respiratory ailments are often grave and have negative consequences. The fact that acute illnesses are common across a wide range of communicable diseases is, because acute illnesses are typically brought on by an infectious agent. Acute illnesses not only manifest suddenly, but they also progress more quickly than chronic illnesses. 
Every system in the body is susceptible to acute diseases or is impacted by them. However, they only have an impact on one specific system at any given time. Depending on how severe the condition is, different acute illnesses require different treatments. One of the most serious illnesses is appendicitis. Neither strep throat nor influenza require extensive medical care or hospitalization. Contrarily, even though they are urgent diseases, conditions like acute myocardial infarction (heart attack) and pneumonia demand both rapid medical care and a long-term course of therapy. Additionally, these ailments may often be treated entirely and once, without having any lasting detrimental impacts on health. Sometimes, an infection like typhoid may be brought on by a slight change in nutrition. This may result from consuming dirty water. By selecting a cleaner water source as an alternative, this may be readily avoided. Examples Of Acute DiseasesTyphoid 
Typhoid is a severe sickness brought on by an infection with the Salmonella Typhi bacteria. The illness might continue up within one month and the incubation period for the disease is anything from eight days to a month. Typhoid can be spread by consuming food or drink that has been tainted by an infected person's faeces. Diarrhea and high temperature are common symptoms that become apparent within a few days. The intensity of the symptoms may vary depending on the health of the patient's immune system, although they are not overly severe. Tests for diagnosis include Widal testing, serology, and immunoassays that can identify the presence of typhoid. By taking the right meds at the right times, as directed by the doctor, the condition can be treated. By consuming a healthy and balanced diet and maintaining a healthy and tidy environment, the condition can be prevented. Bone fracture 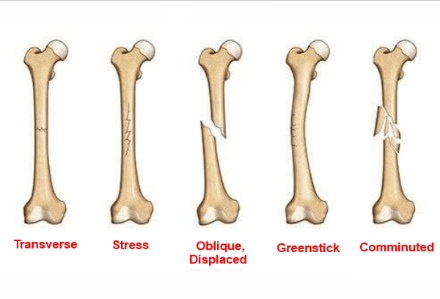
A dangerous disorder known as a bone fracture occurs when the continuity of the bones is disrupted or when cracks form inside the bone. Those with weak bones are more susceptible to bone fractures, which are usually brought on by tension or stress. Avulsion, comminuted, and hairline breaks are only a few examples of the various types of bone fractures. 90% of bone fractures result from some sort of accident. When determining the kind and degree of a bone fracture, radiographic tests of the bones can identify them. Bone healing is a common occurrence, and the best way to treat it is to create an environment that promotes the healing process naturally. Bronchitis 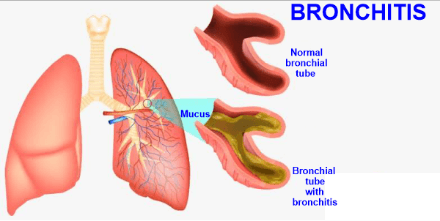
The symptoms of acute bronchitis include repeated coughing fits and mucus production that continue from a few days to a few weeks. The viruses that cause upper respiratory infections are the most common culprits. As a result, it frequently follows measles, influenza, and whooping cough, and it also occurs as a component of the common cold. Streptococcus bacteria, particularly in those with underlying chronic lung illness, can potentially cause acute bronchitis. It can also happen that chemical irritants such as poisonous gases, ammonia, strong acids, or organic solvent vapors will cause it to precipitate. The majority of acute bronchitis treatment is symptomatic, with no lasting improvement. Usually, the symptoms can be subsided with the use of expectorants, bronchodilators, and steam inhalation. A suitable antibiotic is effective in treating bacterial acute bronchitis. Chronic DiseaseA sickness that lasts longer or has long-term detrimental effects on one's health is referred to as a chronic ailment(disease). Chronic illnesses cannot be distinguished from acute illnesses by a specific period of time. Typically, they are used to contrast them with sudden diseases. But sometimes, a condition that persists for more than three months is referred to as a chronic disease. Chronic illnesses that have a high risk of leading to death since there are no treatments for them are referred to as "terminal." When chronic illnesses progress over several months or more, they generally become more challenging to treat. Numerous physiological systems and organs are affected by chronic illnesses, which don't always respond to therapy. Non-communicable diseases are the main cause of chronic diseases since they are frequently not infectious. 
Numerous of these illnesses are not brought on by an infectious disease. Most frequently, they are the outcome of unhealthy lifestyles or bad health decisions. These illnesses are brought on by long-lasting poor eating patterns and behaviors. Remissions or relapses are periods of time during which certain chronic diseases may temporarily go away. While there are many risk factors for different diseases, certain risk variables include dietary habits, way of life, and metabolic parameters. Most chronic conditions don't have a particularly high severity. But people who have chronic diseases are more likely to get deadly acute illnesses. Prevention is seen to be preferable to therapy since it is uncommon for chronic illness to respond well to treatment. This can be achieved by routinely checking for the existence of factors that predispose to issues and help in their early identification, hence reducing the likelihood of unfavorable results. According to the Centers for Disease Control, chronic illnesses account for 86% of the expenditures associated with healthcare in the United States and are the cause of 7 out of every 10 fatalities that occur each year. Examples Of Chronic DiseaseDiabetes 
This is a chronic condition is marked by elevated blood sugar or glucose levels compared to normal. There are two forms of diabetes;
Diabetes usually has no immediate symptoms and instead manifests itself gradually over time. Signs of problems due to the disease may be identified when the symptoms are obvious. The majority of diabetics are elderly adults, and the disease is frequently linked to bad eating habits. It is impossible to treat this illness. To address the condition's symptoms, there are drugs available. Cancer 
The term "cancer" refers to a group of diseases that have the propensity to spread to other organs in the human body and are long-lasting conditions brought on by unchecked cell proliferation. Smoking or usage of tobacco products, being overweight, having bad eating habits, not getting enough exercise, and alcohol consumption are some of the primary causes of cancer. Some cancers may be brought on by a person's hereditary disease or abnormality. The signs of various malignancies might include tumors, unusual bleeding, significant weight loss, and a protracted cough. They may also be caused by other factors. A biopsy, (which is when a sample of the tissue is checked for the existence of tumorous cells), is the most important test for identifying and treating cancer. Maintaining a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise is a viable choice as a preventative step against cancer, as with the majority of chronic diseases. Asthma 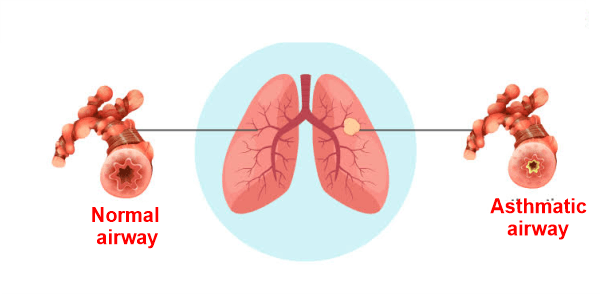
A long-lasting lung condition is asthma. Almost 1.4 million+ individuals in New York State suffer from asthma. Despite being more prevalent in children than adults, asthma may affect anybody at any age. Nearly one in thirteen school-aged children in the country suffer from asthma, and of all groups. Its prevalence is growing the fastest amongst young children and amongst those who reside in inner-city areas of cities. In this disease, the body doesn't get enough oxygen and the lungs' airways get congested and irritated, which makes breathing difficult. However, severe attacks that can be life-threatening can occur in some circumstances for asthmatics. The symptoms of Asthma frequently consist of:
Asthma has no known cure, but with the right treatment, episodes can be avoided and brought under control. To ensure that those who have asthma may lead full and active lives, New York actively collaborates with healthcare professionals, neighborhood coalitions, schools, families, and a variety of other groups. Comparing the Signs of Acute and Chronic ConditionsAcute diseases manifest fast and are accompanied by unique symptoms that necessitate immediate medical attention, or call for temporary care, and often get better quickly following treatment. Fever, a sore throat, a cough, diarrhoea, a runny nose, sneezing, headaches, and rashes are examples of acute illness symptoms. Acute disorders including pneumonia, appendicitis, heart attacks, asthma attacks, organ failure, and acute bronchitis are some examples of acute diseases with life-threatening symptoms that call for immediate medical attention. In contrast, many cases of acute illness are self-limiting and therefore will resolve on their own. Chronic diseases take longer to develop and may also cause symptom changes in mood, discomfort, and exhaustion that are not obvious to the naked eye. The majority of the time, chronic illnesses linger for more than a year and need continuing medical care or a restriction of everyday activities. The majority of chronic disorders, in contrast to acute diseases, cannot be cured and are instead managed by therapy regimens. A person should seek emergency medical treatment if they have persistent symptoms. Treatment For Acute and Chronic DiseaseIf not appropriately recognized and treated, acute and chronic illnesses can have a detrimental impact on a person's physical and mental health. Depending on the patient's acute or chronic illnesses, the course of treatment may differ. Psychiatric therapy, surgery, physical therapy, and radiation are just a few of the various therapies available for chronic disease. Doctors' prescriptions for drugs are the most popular and efficient therapies.
Serious acute illnesses require medical attention in order to be appropriately treated, much like chronic ailments. Although small acute illnesses like the flu or a cold can be treated with over-the-counter (OTC) drugs and they will eventually go away on their own, as already mentioned. However, symptoms that seem to be unimportant should still be assessed to make sure they don't get worse. ConclusionFurther investigation will undoubtedly clarify the distinction between acute and chronic illness. Consequently, an infectious agent is the most typical cause of acute illnesses. Furthermore, one of these disorders' most crucial characteristics is their abrupt onset. Some acute illnesses, such as appendicitis, the flu, and strep throat, are quite moderate in origin and of low intensity. Such illnesses definitely don't require extensive medical care. 
However, some serious illnesses, like pneumonia, may call for immediate medical care. Such disorders have a variety of symptoms that change depending on the disease's characteristics. In addition, there are no relapses at any point in the acute illness process. The lesser amount of time is the reason behind this. Chronic illnesses can linger for a very long period. An illness like this can also impair a person's freedom and health. Furthermore, as the condition advances, the severity increases. Chronic illnesses are often not brought on by infectious agents such as viruses, germs, etc. Additionally, they are largely the outcome of unhealthy lifestyles and health decisions. The signs and symptoms of chronic illnesses may overlap, for sure. Additionally, several common symptoms, such as breathlessness or weight loss, can be present in a variety of chronic conditions. Throughout the course of a chronic illness, there may also be several relapses.
Next TopicDifference between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share











