Difference Between Algae and FungiThe environment depends heavily on both fungi and algae. In addition to their differences, algae and fungi share many similarities. In an ecosystem, algae are major producers because they are autotrophs that use photosynthesis to make food. The method used to transform oxygen from carbon dioxide depends heavily on it. Fungi, on the contrary hand, are a significant decomposer in our ecosystem. It is essential for maintaining the ecosystem's balance. Yet, certain fungus are parasite on algae and infect plants and animals with various diseases. 
Algae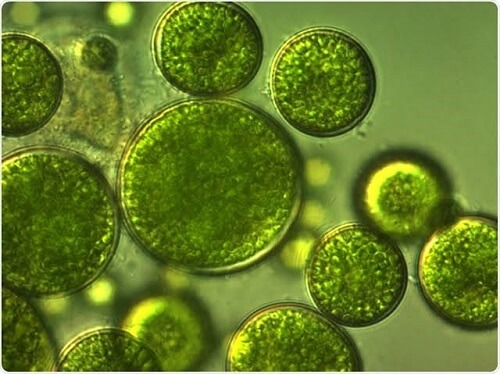
A name used to describe a group of photosynthesis eukaryotic organisms is "algae." It has a nucleus and chlorophyll, but lacks the base, stem, leaves, and many other characteristics of typical land plants. Algae are both multicellular and unicellular, such as Euglenophyta (e.g. seaweeds). Algae produce oxygen through photosynthesis. Algae can survive in a variety of settings, including moist soils, freshwater and saltwater bodies of water, as well as inside certain animals (e.g. Sloth). All algae were previously included under the kingdom Plantae due to their photosynthetic nature. Unicellular algae belonged towards the Protista Kingdom and eukaryotic algal adhere to the Plantae Kingdom. Many shapes and structures can develop as algae grow. Some algae are consumed (e.g. Agar Agar). Algae can reproduce through sexual, asexual, and vegetative means. Fragmentation happens during vegetative reproduction. Every piece grows into a thallus. Spores, primarily zoospores, carry out asexual reproduction. It generates new algae after germination and is flagellated. The fusing of gametes results in sexual reproduction. Algae's Classification and AttributesThe three main classifications of algae are:
Features of the Chlorophyceae Family
Features of the Phaeophyceae
Features of the Rhodophyceae
Fungi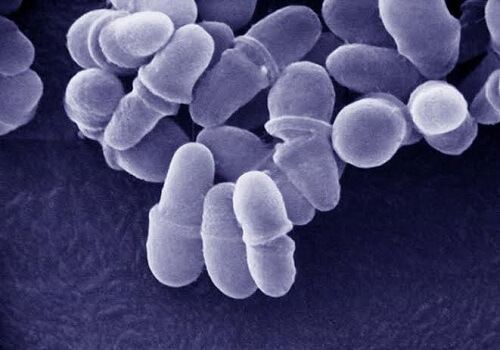
As a heterotopic creature, fungi rely on the nutrients from other alive or deceased species. It is a member of the fungi kingdom. Since there isn't any chlorophyll, there is no photosynthesis.As Eukaryotic creatures, all fungi (Multi-cellular). With the exception of yeast, all fungus have filaments. The hyphae, which resemble lengthy threads, are a feature of fungus. The collection of hyphae is known as mycelium, and it is in charge of the fungi's vegetative growth. There are three different ways that fungi reproduce: vegetatively, sexually, and asexually. Fragmentation, budding, and fission are the three methods of vegetative reproduction. By means of spores, asexual reproduction occurs. Fungi's Classification and AttributesTypically, fungi are divided into four groups that are called:
Features of the Chytridiomycota
Features of the Zygomycota
Features of the Ascomycota
Features of the Basidiomycota
Difference Between Algae and Fungi
Importance of Algae
Algae is regarded as a product with such high nutritional content that such meals also incorporate algae as a component of a salad, with pork in a fried dish, as a top on cereal, or even in fluid state as an extract in a wholesome smoothie. Yet, if we were to read about just the nutritional info regarding algae, we would learn that it already has a number of beneficial components, such as carbs, lipids, proteins, and vitamins A, B, C, and E. Algae is said to be consumed all over the world in a variety of food forms. In addition to being a relatively affordable source of protein, algae also contain a number of vital minerals like iron, potash, magnesium, calcium, manganese, and zinc.Several dairy products, including milk, ice cream, cheese, and whipped top, as well as syrup, icing, cranberry juice, and even condiments, are examples of foods that include algae. Many types of livestock animals are fed algae, particularly seaweed. For instance, Rhodymenia palmata, sometimes known as "Sheep's weed," is a product of algae that is used to feed animals like chickens and calves.Several nations, including those in northern Europe, including Sweden, Denmark, and Norwegian, as well as in Scotch, China, New Zealand, and all of North and South America, is widely known for using algae as animal feed. Importance of Fungi
Although individuals usually associate fungus with pathogenic organisms and food rot, fungi are crucial to human existence on a number of levels. Considering that they are a part of the cycling of nutrients in ecosystems, they have a substantial impact on human populations globally, as we have learned. They also participate in a range of other environmental functions. It is typical for fungi to have beneficial relationships with different types of living things. It is significant to remember that lichens, a parasitic partnership of algae and fungi, are crucial to the growth of ecosystems. Fungal linkages known as mycorrhizae develop between the soil and the stems of higher plants. The existence of fungi facilitates the uptake of soil minerals. Rhizopus, Fusarium, and other fungi are crucial in the development of the soil environment. Plant diseases include smut, rust, and bung illnesses in wheat, blight and wart disease in potatoes, blast disease in rice, rot in sugarcane, and anthracnose in cotton are caused by some fungi because they are harmful. All of the decaying organisms would start to pile up because there wouldn't be any decomposers. Consequently, no young plants would've been able to emerge in the long run because all of the minerals are chained away in the dead materials. A food chain cannot exist without plants as its base. Because of this, the ecosystem would eventually disappear, showing how crucial fungi are!
Next TopicDifference between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









