Difference Between C and PythonC LanguageA static type system helps to prevent numerous unwanted actions in the general-purpose, imperative computer programming language C, which also supports structured programming, lexical variable scope, and recursion. Operating systems, as well as other software for computers ranging from supercomputers to embedded systems that had previously been programmed in assembly language, have found ongoing use in C because it is designed to give constructs that map effectively to conventional machine instructions. 
You can use the C language on different platforms. A C program that is written by following the rules of code standards is accepted by most operating systems. The language is now available on a highly diverse spectrum of hardware, from supercomputers to embedded microcontrollers. Dennis Ritchie created C between 1969 and 1973 at Bell Labs, which was used to reimplement the Unix operating system. C compilers are now accessible for most current computer architectures and operating systems, making them one of the most commonly used programming languages. Common CompilersOperating systems and compilers have different ways of compiling a C program. Most operating systems don't have a compiler, so you'll need to install one. Some commonly used compilers are:
You may obtain a decent idea of how to get started using a couple of the most popular compilers from the documents listed below:
Original "Hello, World!" in K&R CThe original "Hello, World!" program may be found in the book "The C Programming Language" by Brian Kernighan and Dennis Ritchie, also known as "K&R." A simple hello world program in c language
Arrays in CArrays are derived data types in C, which contain the values within curly brackets and can be used to implement higher data types like Stack, and Queue. Arrays in C have a limited number of elements as restricted by their size, which can be set while defining an array. Elements in the array are stored in contiguous memory. C allows multidimensional Arrays like 2-D and 3D arrays whose elements are array. The size of an array can be determined during the run time also. The Syntax for defining arrays: type name[length]; /* Define an array of 'type' with name 'name' and length' length.' */
Setting Values in Arrays Elements of an array can be accessed by putting index value Index square brackets. Multidimensional Array The C programming language supports multidimensional arrays. A multidimensional array can be assumed as a matrix with r rows and c columns. We can create a 3-D array by giving the three values of three coordinates in the three square brackets. For example, int arr[7][6][4]; Two-Dimensional Arrays Generally, a two-dimensional array is a collection of one-dimensional arrays. We can define a two-dimensional integer array with dimensions m x n in the way shown below: 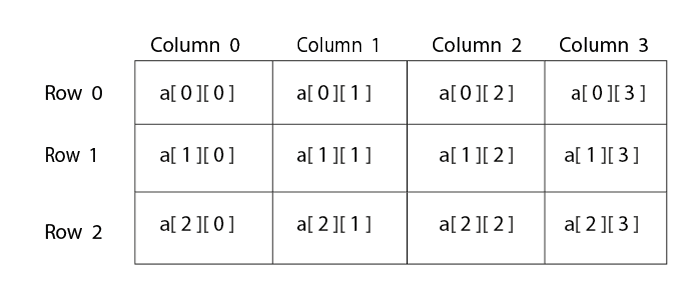
Data Types in CIn C programming, data types are declarations for variables. They determine the type and size of data associated with variables. Fundamental/Basic Data Types in C are:
Signed and Unsigned Modifiers in C The type modifiers Signed and Unsigned are used in C. Using these, you can modify how a data type stores its data:
Derived Datatypes Data types derived from the basic data types are called derived data types. For example, functions, arrays, pointers, structures, enums, etc. Iteration Statements/LoopsThere are three types of iteration statements in C language: For, While, and Do-While loops. 1. For Loop When a piece of code needs to be run a predetermined number of times, the for loop should be used. For instance, we need to call printf() n times to display the elements of an array of size n, but, by using For loop, we can easily perform this in limited execution. The Syntax of a for loop in C programming language is: Example: 2. While Loop The while loop is used when a section of code needs to run until a condition does not become false. The Syntax of a while loop in C programming language is: Example 3. Do-while Loop In this type of loop, the condition is tested after executing the statement once. If the condition is true, the statement executes one more time. Otherwise, the loops end. The Syntax of a do-while loop in C programming language is: Example Operators in CIn a programming language, an operator is a symbol that instructs the compiler or interpreter to carry out a certain task and generate the expected result. C has many powerful operators. Types of Operators in C
Example: a>b? a: c
Pointers in CA pointer is a variable that can store the address of another object or a function. The definition's meaning is unaffected by the asterisk's placement. Each pointer, however, needs its asterisk when more than one is defined simultaneously: PythonPython is a powerful, open-source, object-oriented, high-level, and popular programming language. The libraries of Python are popular in the field of Data Science, where most of the work is automated. It provides easy integration with web services and GUI (Graphical User Interface) based desktop applications. Extensively used in Data Science and for developing Machine Learning projects. It was started by Guido van Rossum in 1991 at CWI (Centrum Wiskunde Informatica) in Netherlands. 
Guido Van Rossum There are Two Primary Versions of PythonThe most recent version, Python 3.x, is still improving. Until 2020, Python 2. x, a legacy version, will only get security updates. No new functions will be added. Even though upgrading to Python 3 is becoming simpler, many projects continue to utilize Python 2. Features of Python
Hello, World Program in Python Data Types in Python 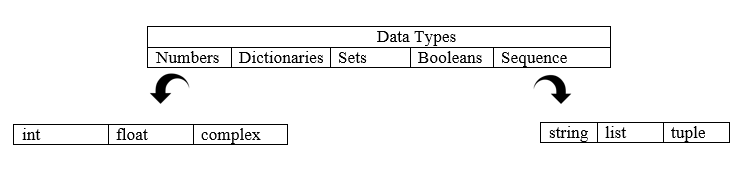
Booleans It includes a Boolean value of either True or False.
Numbers
Dictionary: An unordered collection of unique key-value pairs. a = {1: 'one,' 2: 'two'} Set: An unordered collection of unique values. a = {1, 2, 'p'} Sequence
Arrays in PythonArrays in Python are very similar to lists. The difference arises when we discuss the type of data stored in a List and array. A list can store any data; on the other hand, an array can store only a single type of data. The Syntax for defining an array: Variable_name = array(type code, [elements]) As an array is not a fundamental data type, we must import an array module to use its methods. From array import * The above line will import all methods of the array module. Another way to import an array: Import array as arr In Python, also indexes start from 0 example: Different Array Methods 1. Append ():Add a new element at the end of the array. Example: 2. Insert (): Insert an element at a particular index position. Example: 3. Extend ():This method merges two arrays. Example: 4. From list (): Using this method, we can add items from the list into an array. Example: 5. Remove (): Using this method, we can remove any element from an array. Example: 6. Pop (): Using this method, we can delete the last element of an array. Example: 7. Index (): Using this method, we can find the index of the central element. Example: 8. Reverse (): Using this method, we can reverse the sequence of elements on an array. Example: 9. Buffer_info (): This method provides the starting address of buffer memory and the number of elements in the array. Example: 10. Tostring (): Using this method, we can convert the array to a string. Example: 11. Count (): This method returns the number of times an element occurred in an array. Example: 12. Tolist(): This method can convert an array to a list. Example: Functions in PythonWhen we want to use a particular segment of code several times, we can write the code by declaring a function of it and use it anytime by just calling it. Python functions offer organized, reusable, and modular code to carry out tasks. Functions make coding faster by streamlining the process, avoiding unnecessary logic, and improving readability. Python has some useful predefined functions like print(), len(), input(), etc. You can create your functions by using the given Syntax. The Syntax for Defining a Function in Python def function_name(parameters): statement(s) Some examples of functions are given below: Function to Calculate the Factorial of a Number Function to Print Fibonacci Series OOPs (Object Oriented Programming) in PythonOOPs is a programming concept of using classes and objects for various tasks. Using OOPs, a user can create its own data type and functions that perform tasks as guided by the user. OOPs, Features
1. lasses and Objects Class is a blueprint for an object. An object is a physical or real entity that works on class data. Constructor is a special function that gets automatically called when the object of the class is created. There are mainly two types of constructors
2. Inheritance When we define a class that inherits all the properties of the parent class, this concept is called inheritance. 3. Polymorphism Polymorphism means we can perform a single task in many other ways. The same object has different behavior in different conditions. 4. Encapsulation Python provides access to all the variables and methods globally. By using encapsulation, we can restrict the variables and methods access globally by making them private or protected. 5. Abstraction By using abstraction, the user is shielded from implementation; only the highlighted set of services is provided to the user. Comparison Between C and Python
Next TopicDifference between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










