Difference Between Calcination and Roasting
Calcination & roasting are two thermochemical procedures used to treat various minerals and ores, although they are distinct in terms of their goals, circumstances, and results. Material is heated to a high temperature during calcination and roasting, but the objectives and approaches of the two processes are very different.
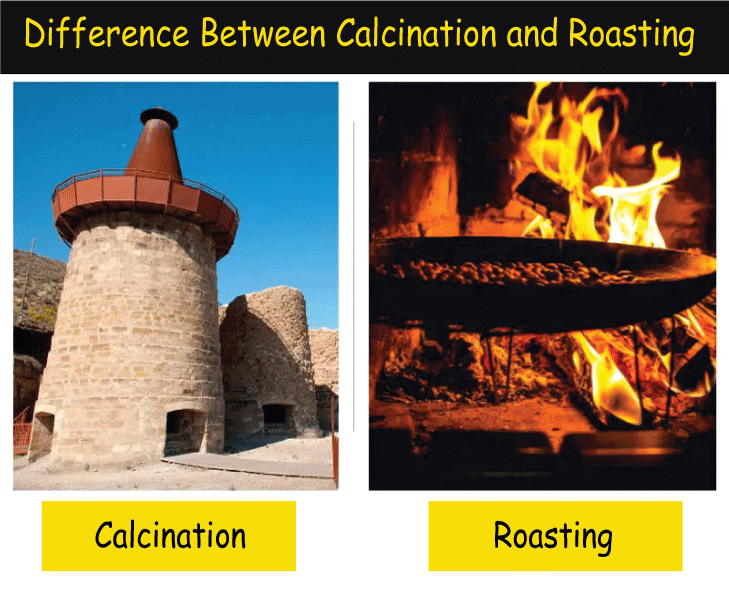
Definition of Calcination:
Calcination is the process of heating a substance to high temperatures without oxygen and air. Usually, the purpose of calcination is to evaporate any water or other volatile components from the material, leaving behind a concentrated product. Calcination is commonly used to make quicklime from limestone and plaster of Paris from gypsum.
Definition of Roasting:
Roasting is the process of heating a substance to high temperatures with air or oxygen. The purpose of roasting is often to change a substance into a more desired form, such as by eliminating impurities or initiating chemical processes that result in a beneficial outcome. Roasting is commonly used to produce the taste and aroma of coffee beans and sulfide ores, which are burned to transform the metal sulfide into metal oxide.
Based on the above information, below are some main differences between calcination and roasting-
| Calcination |
Roasting |
| Calcination is heating material without the presence of air to remove volatile components and produce a more stable result. |
Roasting is heating a material with air present to oxidize or decrease it and alter its chemical components. |
| It is typically carried out at relatively low temperatures (below 900°C). |
It often needs higher temperatures (over 900°C). |
| It is used to eliminate volatile components from the substance being processed, such as water or carbon dioxide. |
It is used to change the chemical into a more reactive state. |
| It usually occurs in an inert environment, such as nitrogen and argon. |
It occurs in the presence of oxygen or air. |
| It is frequently used for inorganic or organic materials like clay, gypsum, or limestone. |
It is frequently used for metal containing ores or other precious minerals. |
| It is frequently used to remove metals from ores, such as iron from iron ore. |
It is used to extract metals from sulfide ores, such as copper sulfide. |
| It is used in the manufacturing of cement, where limestone is calcined to form lime, which is then used to manufacture cement. |
It is used in the manufacturing of several metal products, including copper, lead, & zinc. |
| It is frequently used to reduce the size of the particles, increasing the material's surface area and making it simpler to handle. |
It can be used to reduce particle size, and its primary goal is to modify the material's chemical makeup. |
| It can be done in a variety of ways, such as rotary kilns, fluidized bed reactors, & shaft furnaces. |
It is most commonly done in a rotary kiln, although it can also be done in a fluidized bed reactor or a shaft furnace. |
| It is frequently used as a pre-roasting procedure to eliminate impurities and increase the material's reactivity. |
It can produce toxic gases, like sulfur dioxide, which must be adequately controlled to prevent environmental harm. |
| It is a pretty easy technique that doesn't need any specialized equipment. |
It is a more complicated process that involves precise control of temperature, airflow, and other variables. |
| Depending on the application, calcination can be done in an oxidizing, reducing, or inert gas environment. |
It is often done in oxidizing circumstances to guarantee that the appropriate chemical reactions occur. |
| It could require less time because it doesn't contain any chemical process. |
It takes time because chemical processes need time to occur. |
| It may cause a decrease in the surface area of the material being treated. |
It may increase surface area owing to the production of cracks and pores. |
| It may be done on a smaller scale in laboratory ovens. |
Its roasting is usually done on a greater scale in furnaces or kilns. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, although both calcination and roasting entail the application of heat to materials, they are separate processes with different goals. Calcination removes volatile chemicals, whereas roasting transforms a material into a more attractive form. In order to select the best procedure for a specific material or application, it is crucial to comprehend the differences between these two methods.
|

 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now









