Difference between Centripetal and Centrifugal ForceCentripetal and centrifugal forces are two different types of forces. Often, students need clarification while discussing these two forces. In this article, you will learn about centripetal and centrifugal forces and their differences. What is Force?Force is a physical quantity that is a measure of the interaction between two objects. Force is a vector, meaning it has magnitude and direction. In physics, force is defined as the product of mass and acceleration, or F = ma. Many forces can act on an object, including gravitational, electromagnetic, and mechanical forces. Forces can cause objects to accelerate, change direction, or change shape. The newton (N), which corresponds to the force which is needed to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a pace of one meter per second squared, is the unit of force in the International System of Units (SI). A centripetal force is a force that is applied to an object moving along a circular path and is directed toward the path's center. It is equivalent in size to the object's weight and keeps the object moving in a circular motion. Centripetal acceleration, or the acceleration of an object toward the center of a circular route, is caused by this force, which is always perpendicular to the object's velocity. While, Centrifugal force, on the other hand, is an apparent force that is felt by an object moving in a circular path and is directed away from the center of the path. It is not a real force but a subjective sensation that an observer feels and results from the object's inertia. The magnitude of the centrifugal force is the same as the centripetal force, but it acts in the opposite direction. 1. Centripetal ForceIn Physics, centripetal force is defined as a force directed toward the center of a circular path and required to keep an object moving. This force acts perpendicular to the object's velocity and is equal in magnitude to the object's weight. The centripetal force applied on an object is pointed in the direction of the center of the object's circular movement. The acceleration of the item toward the center is caused by this force, which also maintains the object's circular motion. It is equal in magnitude to the object's weight and always perpendicular to its velocity. 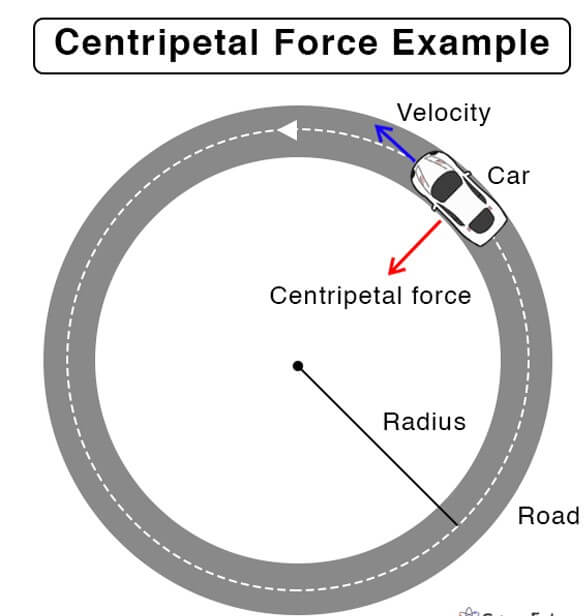
The formula for centripetal force is F = mv2/r Where: F is the centripetal force, m is the mass of the object, v is the velocity r, the radius circular path. More Details about Centripetal Force
2. Centrifugal ForceCentrifugal force is a phenomenon that appears when an object moves in a circular path. The force always acts away from the path of an object, and its strength is proportional to the object's mass and the speed at which it moves. When an object moves in a circle, it constantly changes direction, which means it is also constantly accelerating. As the force is directed away from the center of the path in the same way, its acceleration, called centrifugal acceleration, is also directed away from the path. The force that is responsible for this acceleration is called the centrifugal force. The term "centrifugal force" is often used to describe the apparent force that acts on an object moving in a circle, which seems to push it away from the center. But it is not a force but an illusion created by the object's inertia. Inertia is an intrinsic property of matter, it makes an object tend to keep moving in a straight line, and when an object is moving in a circle, it creates the illusion that a force is pushing it outwards. Thus, Centrifugal force is a pseudo-force caused by inertia; it is not real. It is the sensation that a body moving in circular path experiences, which appears to be acting away from the center of rotation. 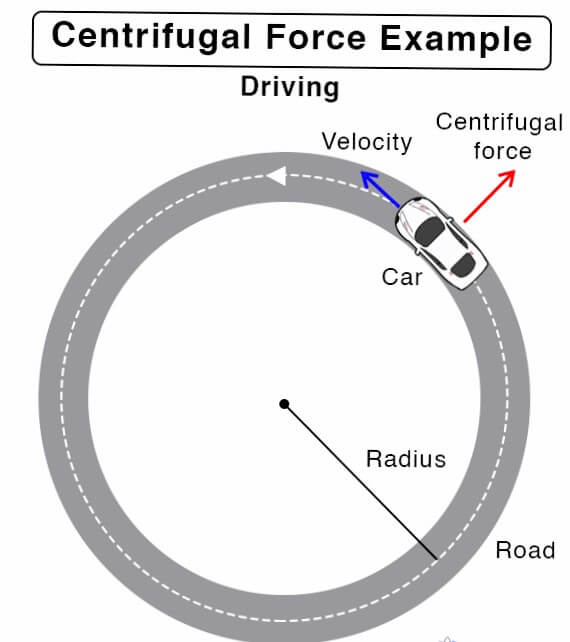
More Details about Centrifugal ForcesA centrifugal force is a "fictitious" force often used to describe the apparent force felt by an object moving in a circular path. It is important to note that a centrifugal force can also be termed as a pseudo or fake force as it is not felt usually but rather a result of an object's inertia as it moves in a circle. Here are a few points about centrifugal force:
The formula for centrifugal force is as follows: F = m * v2 / r, where m is the mass, v is the velocity, and r is the radial distance from the axis of rotation. Where: o F is the centrifugal force o m is the mass of the object o r is the distance of the object with the center of rotation This equation is only an approximation and is followed when the object is in a uniform circular motion. Also, it is important to note that centrifugal force is not a true physical force but rather an "apparent" force resulting from the object moving in a circular path. This "apparent" force acts away from the center of rotation. An alternate formula is given by Centrifugal Force = m * v2/r; here, v is the tangential velocity. Difference between Centripetal and Centrifugal ForceCentripetal force is a real force that acts toward the center of a circular path, while centrifugal force is a fictionary force that acts away from the center of a circular path. Centripetal force is responsible for changing the direction of the object's velocity. A body's inertia in a circular motion produces centrifugal force, which is not a true force. Centripetal force is required to maintain an object in a circular motion, while centrifugal force is not required for an object to continue moving in a circular path. Centripetal force is dependent on the mass and velocity of the object, as well as the radius of the circular path. In contrast, centrifugal force is not real. Centripetal force is a force acting on an object; centrifugal force is not an actual force but a sensation an observer feels in a rotating frame.
Next TopicDifference between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









