Difference Between Colonialism and ImperialismColonialism and Imperialism are sometimes used interchangeably, yet they have distinct meanings. Although both concepts refer to economic and political dominance types, they are different in how they are carried out. Although Imperialism generally refers to extending one's authority and influence beyond one's boundaries, colonialism often refers to acquiring and keeping colonies. Colonialism: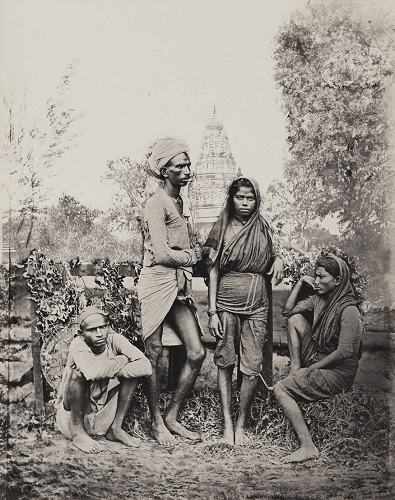
Colonialism is the process of establishing and sustaining colonies, usually by military conquest and colonization. Colonial powers construct colonies and political structures in foreign countries to gain control over such areas. Exploiting colonial labor and resources for the profit of the conquering authority is a common goal of colonialism. This may entail exploiting inexpensive labor to make commodities for export and mining natural assets, including minerals, lumber, and agricultural products. Colonialism is strongly associated with European nations such as Portugal, France, Spain, and the United Kingdom, who built colonies in America, Africa, & Asia from the 16th through the 19th century. These colonies were frequently founded via the expulsion of indigenous peoples and acts of violence. Today, the effects of colonialism may still be seen in many regions of the world in the form of social unrest, economic and political inequality, and cultural assimilation. Imperialism: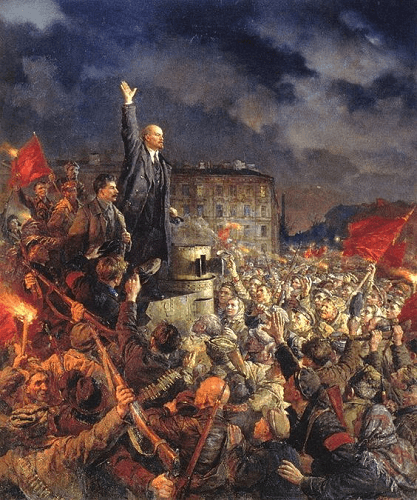
Imperialism is a broader term for the practice of extending one's influence and power beyond one's own borders. Imperial powers try to assert authority over other nations and areas through many strategies, such as military, political, and economic strength. Imperialism may manifest itself in various ways, such as geographical encroachment, economic hegemony, cultural sway, and political dominance. Effect- Imperialism and colonialism have significant and enduring repercussions. Indigenous peoples were frequently uprooted, exploited, and subjugated due to the construction of colonies, with Europeans imposing their own social, cultural, & political ideals on the colonial inhabitants. This frequently led to the loss of indigenous traditions and identities, the loss of resources and land, and the destruction of cultural practices. Based on the above information, some of the critical differences between colonialism and Imperialism are as follows:
ConclusionIn conclusion, colonialism and Imperialism are two different but linked processes. The development of actual colonies in foreign countries to exploit them is what is meant by the word "colonialism," but "imperialism" is a more general term that refers to a variety of tactics and methods for extending one's power and influence abroad. It is crucial to comprehend the contrasts between these two concepts to understand the historical and continuing economic and political dominance processes that define our world today.
Next TopicDifference Between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









