Difference Between Ferrous and Non-Ferrous Minerals
What are Minerals?
Minerals are inorganic elements or substances that appear naturally and have a specific chemical structure. They are necessary for maintaining life and can be found in rocks, soils, and aquatic sources. Glass, polymers, wood, and metal are just a few of the many goods made using minerals. Additionally, they play a significant role in pesticides, paints, and makeup. Minerals are created either by the cooling and crystallization of liquid rock or by the circulation of mineral-rich fluids through rocks, which leave behind deposits of minerals. Stones that have already been formed can condition and produce minerals. When groundwater passes through rocks, it may take away tiny rock fragments and place them elsewhere.

Elements like oxygen, silicon, and aluminum comprise most of the rocks' chemical makeup. These elements combine differently in each material, determining how it is made up and behaves. The chemical composition of the material is also known as this mixture. While some rocks, like diamonds, only contain one element, others, like quartz, include a variety of factors. Crystal patterns are used to categorize minerals further. The atomic structure of a material manifests itself physically as crystals. While some elements crystallize as cubes, others as hexagons or other forms. Crystals' conditions affect various characteristics, including how hard they are and whether or not they are clear or opaque.
Additionally, minerals can be divided into groups based on their hue, shine, and pattern. Color and luster are terms used to describe the color of a mineral's granules and how light bounces off it. The mineral's powder becomes streaky when rubbed against a white ceramic dish. There are many applications for minerals. They are used as construction components, glass and steel manufacture, fertilizer, and cosmetic ingredients. They are sold as goods and used to manufacture coins and jewelry. Minerals are a limited supply, and many are getting harder to find. This is because they take millions of years to form and are often mined faster than they can be replenished. In addition, many minerals are being depleted due to over-exploitation, pollution, and climate change.
Minerals are a vital resource and are essential for sustaining life. They are used in producing a wide array of products and are important components of fertilizers, cosmetics, and jewelry. As they are a finite resource, it is important to ensure that they are mined responsibly and that their use is sustainable.
What is a Ferrous Mineral?
Metallic rocks called "ferrous minerals" are made of iron and its derivatives. They are vital to the human organism and are widely distributed in the crust of the Earth. Rocks, sediments, and liquids all contain ferrous minerals in significant quantities. The two types of ferrous materials are Ferromagnetic and Paramagnetic. Paramagnetic minerals are not drawn to a magnet, whereas ferromagnetic minerals are. The Earth's bedrock is largely composed of ferrous elements. They can be discovered in igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic minerals. Hematite and magnetite contain iron and oxygen, the most prevalent metallic rocks. Since magnetite is the most attractive ferrous material, it makes electronic appliances and magnets. Iron from hematite is used to make steel and other manufacturing materials. Other prevalent ferrous rocks include siderite, limonite, goethite, magnetite, and hematite. The human body requires ferrous elements for strong bones, teeth, muscles, and other systems, so their importance cannot be overstated. Healthy blood and our body's capacity to receive and use iron depend on ferrous elements. Red blood cells, which transport oxygen to the body's tissues and functions, must contain iron to be produced. The creation of hemoglobin, which transports oxygen in the blood, also requires iron. Anemia, a disease marked by weakness and exhaustion brought on by iron shortage, can be extremely hazardous for pregnant women, young children, and the aged.
Additionally necessary for a healthy atmosphere are ferrous elements. They are employed in creating herbicides and fertilizers, as well as in water purification and waste reduction. Iron also produces cement, tarmac, pigments, and paints. Due to their magnetic qualities, ferrous minerals create batteries, turbines, and engines. The Earth's crust is rich in ferrous materials, significantly benefiting people and the ecosystem. They are required for the correct operation of the human body and are vital components of rocks, soils, and fluids. In addition, the creation of batteries, engines, motors, pigments, dyes, herbicides, and fertilizers depends on ferrous materials. By understanding the importance of these minerals, we can ensure they are available for future generations.

Types of Ferrous Mineral
Ferromagnesian and Non-Ferromagnesian rocks are the two major categories of ferrous minerals. Iron and magnesium-containing rocks are known as ferromagnesian minerals. Olivine, pyroxene, and amphibole are a few examples. Rocks that contain magnesium but not iron are known as non-ferromagnesian rocks. Magnetite, hematite, and pyrite are a few examples.
- Ferromagnesian Minerals: Silicates, which include silicon, oxygen, and other elements like iron and magnesium, are the building blocks of ferromagnesian rocks. In addition to being frequently found in metamorphic and sedimentary rocks, these minerals develop in igneous formations. Iron, magnesium, and silicon are the main elements in the ferromagnesian crystal olivine. Usually emeralds in hue, olivine has a vitreous or crystalline luster. Some basaltic lavas contain it, and meteors also contain it.
- Non-Ferromagnesian Minerals: Most non-ferromagnesian rocks do not contain iron and other elements like sulfur and oxygen. These minerals are frequently linked to hydrothermal formations and are usually found in sedimentary rocks. A non-ferromagnesian material with the elements iron and oxygen is magnetite. Magnetite typically has a shiny luster and is black or grey. Because of its magnetic qualities, it is the most magnetic of all materials and is frequently used in industry.
- Hematite is an example of a non-ferromagnesian mineral composed of iron and oxygen. Hematite is usually reddish-brown and has a dull to earthy luster. It is an important iron ore and is often used in steel production.
- Pyrite is another example of a non-ferromagnesian mineral composed of iron and sulfur. Pyrite is typically golden-yellow and has a metallic luster. It is found in sedimentary rocks and is sometimes referred to as "fool's gold" due to its resemblance to gold.
- Iron is abundant in ferrous minerals, which are also extensively used in manufacturing. The crystals olivine, pyroxene, and amphibole are examples of ferromagnesian rocks. Minerals like magnetite, hematite, and pyrite are examples of non-ferromagnesian minerals. These materials are significant for their use as iron metal and magnetic qualities.
What are Non-Ferrous Minerals?
Non-ferrous materials are those that are free of iron. These minerals are significant in several sectors, including industry, building, and energy generation. Numerous common items, including money, jewelry, and technology, contain non-ferrous minerals. Metallic and Non-Metallic minerals make up the two major divisions of non-ferrous minerals. Typically, a single metallic element, such as copper, aluminum, or nickel, makes up metallic rocks. Non-metallic materials, like sulfur, phosphorous, or carbon, comprise two or more elements. Modern society depends on non-ferrous materials. They are employed in several sectors, including industry, building, and energy generation. Everyday items like money, jewelry, and gadgets all contain non-ferrous minerals.
- Aluminum is one of the most common non-ferrous minerals. It is a lightweight metal with various uses, including in construction and automotive applications. Aluminum is also used to make cans, foil, and other containers. Aluminum is also used in the aerospace industry and is a key component of many electrical components.
- Copper is another common non-ferrous mineral. It is used in many electronics, including computer chips and wires. Copper is also used in plumbing, coins, and jewelry. Copper has high electrical and thermal conductivity, making it an important material in the electrical and telecommunications industries.
- Lead is a heavy metal and a non-ferrous mineral. It is most often used in constructing lead-acid batteries, which are used in cars and other vehicles. Lead is also used in ammunition and can be alloyed with other metals to make pipes and other products.
- Nickel is a silvery metal and a non-ferrous mineral. It is often used in alloys to make stainless steel and other metals. Nickel is also used in electroplating and earning coins. Nickel is also used in certain medical applications, such as in pacemakers.
- Tin is a soft metal and a non-ferrous mineral. It is often used in the production of cans and other containers. Tin is also used in the production of solder, and it is a key component in alloys such as bronze and pewter.
- Titanium is a strong, lightweight metal and a non-ferrous mineral. It is used in the aerospace industry, medical implants, and jewelry. Titanium also makes tennis rackets, golf clubs, and other sports equipment.
- Zinc is a non-ferrous mineral often used in galvanization, which is the process of coating steel or iron with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion. Zinc is also used in the production of brass, and it is a key component in the production of batteries.

Type of Non-Ferrous Minerals
There are two types of non-ferrous minerals metallic non-ferrous minerals and Non-metallic non-ferrous minerals.
- Metallic Non-Ferrous Minerals: Among non-ferrous solid elements, copper, aluminum, nickel, titanium, lead, zinc, and tin are the most prevalent. One of the most popular non-ferrous materials is copper. It is utilized for electrical cabling, coins, jewelry, and pipelines. Cans, car components, and airplanes are all made of aluminum. Coins and electrical gadgets use nickel, a stainless steel component. Medical devices and planes both use titanium. Batteries and radioactive protection both use lead. In addition to being used in paint and makeup, zinc is used to galvanize metals. Tin is used in food cans to cover metals like steel and copper.
- Non-Metallic Non-Ferrous Minerals: Glass, paint, rubber, and fertilizers are just a few of the goods that use non-metallic non-ferrous materials. Sulfur, phosphorous, and carbon are the three non-metallic non-ferrous elements that are most prevalent. Rubber, manure, and explosives are all made with sulfur. Paint, soap, and fertilizer all contain phosphorus. Steel, graphite, and diamond are all materials made of carbon.
Difference Between Ferrous and Non-Ferrous Minerals
Ferrous and non-ferrous minerals have several differences, including iron's presence, cost, and environmental impact.
| Ferrous Minerals |
Non-Ferrous Minerals |
| 1. Ferrous minerals are those minerals that contain iron. |
1. Whereas non-ferrous minerals are those minerals that do not contain any iron. |
| 2. Ferrous minerals are usually harder and stronger than non-ferrous minerals used in construction and manufacturing industries. Examples of ferrous minerals are hematite, magnetite, pyrite, and taconite. These minerals are commonly used to make steel and iron products and in cement production. Ferrous minerals also produce automotive parts, railroad tracks, and other transportation infrastructure. |
2. Non-ferrous minerals are softer and weaker than ferrous minerals and are often used in electronics, jewelry, and other decorative items. Common examples of non-ferrous minerals are copper, aluminum, tin, lead, and zinc. These minerals produce electrical wiring, coins, and other decorative items. Non-ferrous minerals are also used in plumbing, agriculture, and other industrial applications. |
| 3. The most significant difference between ferrous and non-ferrous minerals is that they are usually harder and stronger than non-ferrous ones, making them better suited for construction and manufacturing. |
. Non-ferrous minerals are softer and weaker, making them more suitable for electronics, jewelry, and other decorative items |
| 4. Another significant difference between ferrous and non-ferrous minerals is the cost. Due to their higher demand and availability, ferrous minerals are usually more expensive than non-ferrous minerals. |
4. Non-ferrous minerals are generally less expensive than ferrous minerals. |
| 5. The other major difference between ferrous and non-ferrous minerals is their environmental impact. Ferrous minerals often require more energy to extract and process, generating more air and water pollution than non-ferrous minerals. |
5. On the other hand, they have a much lower environmental impact. |
| 6.Ferrous minerals are important to the steel and automotive industries, as they are used to create a variety of components. Iron, for example, is used to make alloys, which are strong and lightweight materials essential to the automotive industry. Ferrous minerals are also used in construction, as they are necessary for producing concrete and other building materials. |
6. Non-ferrous minerals, however, are used in a variety of other industries. Copper, aluminum, and nickel are non-ferrous minerals in electrical components, electronics, and jewelry. Many non-ferrous minerals are also used to produce renewable energy sources such as solar cells, wind turbines, and hydroelectric systems. |
| 7. The differences between ferrous and non-ferrous minerals are in the types of minerals used and how they are extracted and processed. Ferrous minerals are typically mined from the ground, and the ore is then smelted in a furnace to remove the metal. |
7. Non-ferrous minerals are generally mined from the ground and processed using chemical or physical processes. |
| 8. Ferrous minerals are often associated with acid mine drainage, which can pollute the environment with toxic levels of iron and other metals. |
8. Non-ferrous minerals, on the other hand, are much less likely to cause environmental damage as they are not associated with acid mine drainage. |
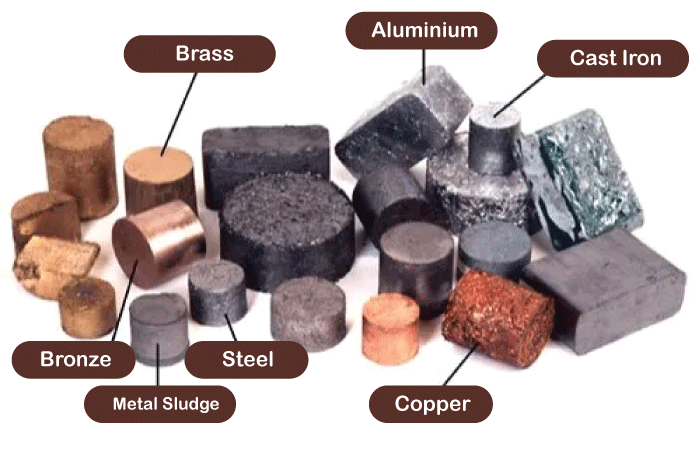

In summation, each ferrous and non-ferrous material has distinct qualities and applications. Producing metals and other components requires ferrous minerals crucial to the steel and car sectors. However, non-ferrous minerals are employed in numerous sectors, such as the jewelry, technology, and power businesses. Both kinds of minerals are significant to the global economy due to their distinctions, including the methods used for extraction and processing and their effects on the ecosystem.
|





 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










