Difference Between Flagella and CiliaWhat are Flagella?The whip-like appendages that come out of the surface of different kinds of cells are called flagella. Flagella are used by the cells to move their body in the aquatic environment, like water or mucus. This is the main reason flagella are mostly found in aquatic organisms because they help in their movement. The most common organism in which flagella are present are bacteria, archaea, and some eukaryotes. 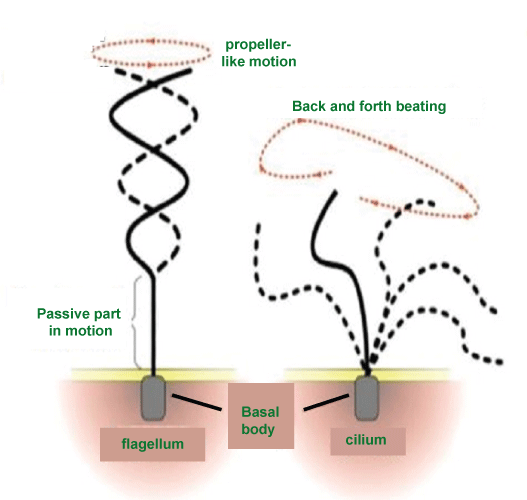
There are various types of flagella found in different organisms, and the structure of flagella mainly depends upon the type of organism and its habitat. For example, in bacteria, flagella are usually made up of long and helical protein filaments extending from the surface of the cells and rotating just like a propeller. The rotation is needed to generate the force required for the movement of the cell. A rotatory motor is present at the base of the flagellum, where the flagella attach itself. A proton gradient across the cell membrane powers the rotation and, thus, the movement of the flagella. There is a series of protein complexes present in the motor region that work together to move the flagella in different directions, that is, clockwise or counter clockwise. The movement of the flagella depends upon the direction in which the cell wants to move. The flagellar structure in archaea is more or less similar to bacterial flagella, but they have a different mechanism to power their motor for the movement of the flagella. Instead of using proton gradient for the generation of energy like bacterial flagella structure, archaea use the ATP hydrolysis mechanism to power the motor for the rotation of the flagella. On the other hand, flagella in eukaryotes have a more complex structure. Not all eukaryotic organisms have flagella. Only a few organisms belonging to the category of algae and sperm cells have flagellar structures as part of their cells. Their flagella are comparatively more complex than bacteria and archaea flagella. Flagella in eukaryotic cells is made up of a bundle of microtubules that are attached to the basal body. These microtubules work like a motor for the rotation of the flagellum. The initiation of the assembly of flagellum starts with the formation of the basal body complex. The basal body has a ring of proteins called the basal body complex which helps in the assembly of the flagellar structure. It also controls the movement of the flagella. 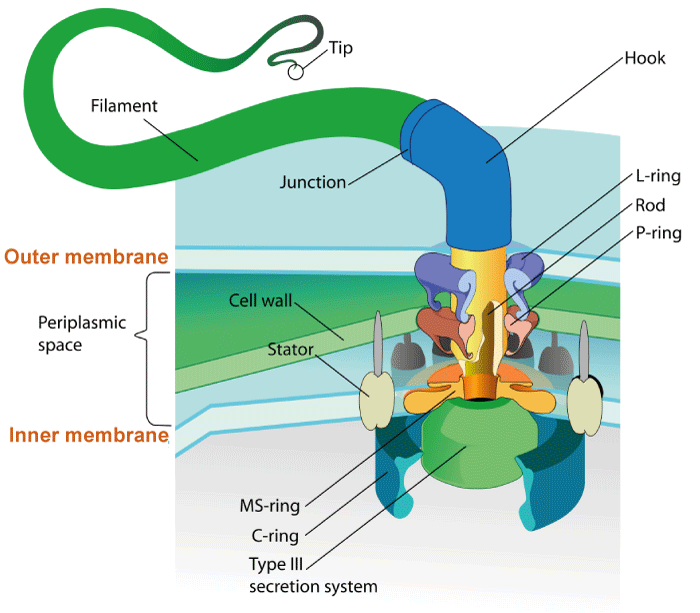
Even the movement of eukaryotic flagella is different from the movement of bacterial or archeal flagella movement. In the case of bacteria and archaea, movement is rotation-based, like a propeller. But in the case of eukaryotic flagella, the movement is a whip-like movement, also called "undulation," to propel the cell. This type of movement is generated by the activity of microtubules when they slide against each other. The sliding movement causes the bending and flexing of the flagella resulting in its movement. Apart from helping out the cell in movement and motility, the flagella also have other roles in the cell's life cycle. Some bacteria employ flagella in order to sense any stimulus in the environment and respond according to it. For example, flagella help the bacteria to sense the change in temperature and nutrient availability. Flagella in bacteria also helps the bacterial cells to attach themselves on any surface and thus carry out a lot of important functions, like the formation of biofilms and causing bacterial infections. Different functions of eukaryotic flagella include:
The research and development department has also recognized the importance of studying the role of flagella in biology and biotechnology. Flagellar studies help in understanding the unique mechanisms of cellular movements in different organisms. The studies also help in identifying and developing new technologies for microscale propulsion, such as nanomachines and microbots. Although the importance of flagella is widely known, science stills lack comprehensive information on the flagellar mechanistic. The studies and research on the structure, function, and evolution of flagella are continuously going on for their better understanding. The studies on flagella till now have already given new insights into the working and role of flagella in cell movement, and it is quite likely that future studies will bring further insights into other functions of flagella, apart from facilitating movement and attachment. What are Cilia?The slender, hair-like structures found on the surface of the cells are called cilia. Cilia are found throughout the body and are made up of microtubules. Microtubules are the long, thin-like fibers that make the structural framework of the eukaryotic system. The basal body helps in anchoring the cilia to the cell membrane. The basal body is a specialized structure in eukaryotic cells that serve as an attachment point for cilia and also supports the cilia. 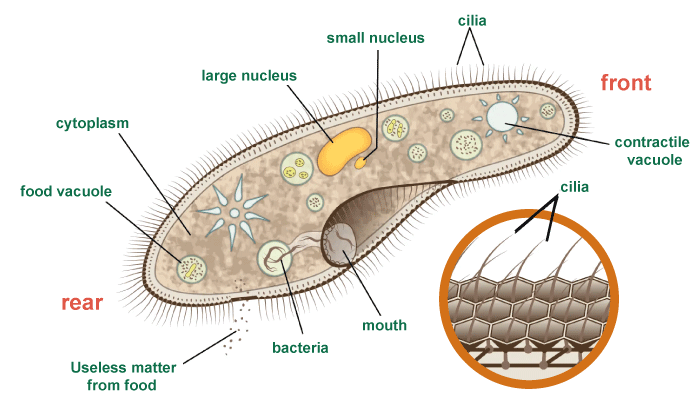
There are two main types of cilia:
Motile cilia They are usually found in cells surrounding the respiratory and reproductive tract. They are also found in the cell of the central nervous system. As the name suggests, they help in generating movements in the cells (motility). They are also involved in clearing mucus and other substances out of the body. Non-motile cilia The main function of non-motile cilia is sensory perception, like the retina in the eyes and the olfactory epithelium in the nose. Where are Cilia Found?Cilia are found on the surface of the cells in the human body. They have varied forms of structures and functions depending on the type of cells and the location of the cells. For example, cilia found in the respiratory tract help in moving mucus and other particles out of the lungs in the airways. It helps in removing the mucus from the body through a cough or end up being swallowed. On the other hand, the cilia found in the reproductive tract help the sperm move toward the egg. In the case of the central nervous system, cilia help in regulating the flow of cerebrospinal fluid. Cilia are also present in the inner ear, where they work in sensory perception and balance. In the eyes, cilia are found in retinal photoreceptor cells, where they in regulating the amount of light entering the eye. Cilia are also found in the kidneys, where they help in the regulation of blood pressure and fluid balance. Function of CiliaThe major functions of cilia are:
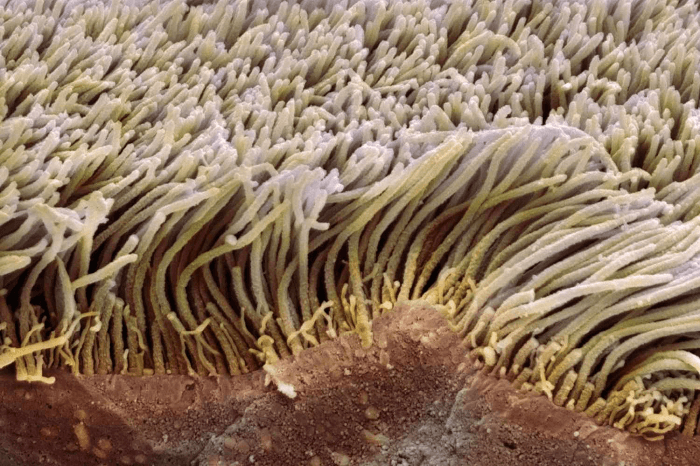
ConclusionIn summary, it can be said that although cilia and flagella show many similarities in terms of function and structure, they are also different from each other in many ways. For example, cilia are present in numerous numbers and often cover the entire surface. Cilia are also shorter and work together as a single unit to produce coordinated movements. On the other hand, flagella are usually present in specific numbers. They are typically present in pairs or singly. They help cells in locomotion and are usually present in cells like sperm cells. Difference Between Cilia and Flagella
Next TopicDifference Between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









