Difference Between Molecule and CompoundWhat is a Molecule?Atoms that are chemically bound together form molecules. The atoms may all be from the same element or may come from various elements. A molecule can be as basic as the water (H2O) that is created when two hydrogen atoms are joined with one oxygen atom, or it can be as complicated as a protein molecule that has thousands of atoms. A molecule's characteristics and behavior are determined by its atomic composition and organization. Who Discovered Molecule?Early in the 19th century, John Dalton made the initial suggestion that molecules serve as the fundamental constituents of matter. He argued that all matter is composed of atoms and that molecules can be created when specific atoms from different elements interact in specific ratios. Based on the research of earlier scientists like Robert Boyle, Antoine Lavoisier, and Joseph Proust, this theory-known as the atomic theory of matter-is now widely accepted. Dalton was still able to put the puzzle together and come up with a thorough theory. Many characteristics of matter, including how gases behave and how chemical reactions take place, were explained by Dalton's atomic theory. Additionally, it provided the framework for the growth of contemporary chemistry and the identification of numerous novel compounds. 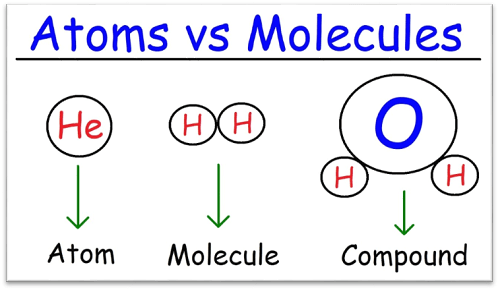
Molecule Discovery:Finding novel, synthetic, or naturally occurring compounds is known as "molecule discovery." This can be accomplished using a variety of techniques, including chemical synthesis, natural product screening, computational chemistry, and compound library screening. Finding novel molecules with certain characteristics, such as medication candidates with particular biological activities, is frequently the aim of molecular discovery. Although the process of finding molecules might be time-consuming and expensive, it is crucial to the process of finding new drugs. Keynotes on Molecule:
What is a Compound?When two or more elements are chemically mixed in a specific ratio, the result is a compound. The elements are chemically bound together and are difficult to physically separate. Compounds can be created in a lab or they can be discovered naturally in the environment. The characteristics of a compound are different from the characteristics of the constituent parts. For instance, water (H2O) is a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen, yet it differs from each of these elements alone in terms of its properties. Compounds can be divided into two groups: organic compounds and inorganic compounds. Organic substances, which are found in living things, are composed of carbon and hydrogen. Carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids are among the examples. Minerals, salts, and acids are examples of inorganic substances that do not include carbon-hydrogen bonds. It's important to keep in mind that "molecule" and "compound" are frequently used in the same sentence. No matter how many elements are present, a molecule is still defined technically as a collection of atoms that are chemically bound together. The chemical combination of two or more elements in a compound, on the other hand, follows a predetermined ratio. Discovery of Compound:Compounds were first discovered in prehistoric civilizations when people were already aware of and utilizing substances like salt, metals, and glass. Alchemists' quest to convert common metals into gold and find the Elixir of Life gave rise to the scientific study of compounds in the Middle Ages. They also contributed significantly to the science of chemistry by producing nitric acid and isolating other substances like lead and mercury. However, it wasn't until the 18th century that compounds were recognized by science as separate entities from their constituent components. The "Father of Modern Chemistry" Antoine Lavoisier's contributions set the groundwork for today's understanding of compounds. He suggested that chemical processes entail mixing or separating these elements since he understood that compounds are made up of fixed ratios of components. The law of definite proportions, which asserts that the ratio of the constituents in a compound is always the same, was developed as a result of Lavoisier's work. Scientists like John Dalton and Jöns Jacob Berzelius created the modern idea of atoms and molecules in the 19th century. They realized that compounds are created when these atoms and molecules combine chemically. New compounds are still being discovered today using a variety of techniques, including chemical synthesis, natural product screening, computational chemistry, and compound library screening. Finding new compounds with certain qualities, such as medication candidates with particular biological activities, is frequently the aim of compound discovery. Keynotes on Compounds
Unlike inorganic substances, organic substances have both carbon and hydrogen.
Difference between molecule and compound
For instance, because they are made up of only one type of element, diatomic molecules like O2, N2, and H2 are not considered to be compounding, whereas H2O is. H2O is a compound made up of two separate elements, hydrogen, and oxygen, which are chemically bonded in a constant ratio of 2:1. 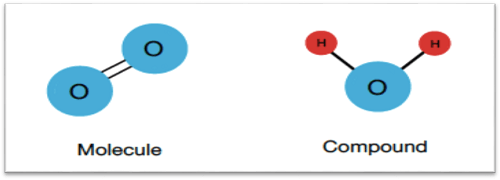
Next TopicDifference between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









