Difference between Multiplexer and DemultiplexerIn digital electronics, multiplexers (MUX) and demultiplexers (DEMUX) are fundamental building blocks used in many circuits. While both of them operate on the principle of data transmission, they have different functions and applications. In this article, we will discuss the significant differences between multiplexers and demultiplexers. 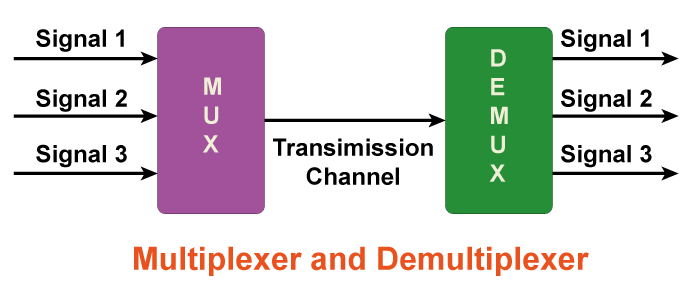
What is a Multiplexer?A multiplexer is a digital circuit that allows the selection of one out of several input signals and transmits it on a single output line. It is commonly abbreviated as MUX. It can have 'n' input lines, where 'n' can be any number. The number of output lines in a MUX is always equal to the logarithm of the number of input lines, rounded to the next higher integer value. The working of a multiplexer can be understood by the analogy of a train station. Suppose we have multiple trains arriving at the station, and passengers have to be boarded via one train at a time. The train station acts as a multiplexer that has one train at a time and takes many passengers at a time while blocking all other trains. Similarly, a multiplexer takes many input signals at a time and passes them to a single output line. Multiplexers have many applications in digital systems, including data transmission, signal routing, and memory addressing. They are also used in computer networks, where they are used to combine multiple data streams into a single transmission channel. What is a Demultiplexer?A Demultiplexer, abbreviated as DEMUX, is a digital circuit that performs the reverse function of a multiplexer. It takes a single input line and transmits it to one of several output lines, depending on the selection inputs. Demultiplexers can have 'n' input lines, where 'n' can be any number. The number of input lines in a DEMUX is always equal to the logarithm of the number of output lines, rounded to the next higher integer value. The working of a Demultiplexer can be understood by the analogy of a post office. Suppose we have multiple post boxes at the post office, and letters have to be sorted and delivered to the correct post box. The post office acts as a Demultiplexer that takes all letters and sends them to the appropriate post box via a single channel. Similarly, a Demultiplexer takes an input signal and sends it to the appropriate output lines. Demultiplexers have many applications in digital systems, including memory decoding, signal routing, and communication systems. They are also used in computer networks, where they are used to split a single data stream into multiple transmission channels. Differences: Multiplexer vs. DemultiplexerLet us now simplify the major points showing the important differences between these two terms, multiplexer, and demultiplexer, with the help of the following table:
ConclusionIn conclusion, a multiplexer (MUX) and a demultiplexer (DEMUX) are two important digital components used in various applications. A MUX selects a few of several input signals and transmits them on a single output line, while a DEMUX takes a single input signal and transmits it to one of several output lines. MUXs have n input lines and log2 (n) output lines, while DEMUXs have one input line and n output lines. Both components have selection inputs, but MUXs use them to choose which input signal to transmit to the output line, and DEMUXs use them to choose which output line to transmit the input signal to. MUXs are used in data transmission, signal routing, memory addressing, and computer networks. For example, a MUX can be used to select one of several video inputs to display on a TV. DEMUXs, on the other hand, are used in memory decoding, signal routing, communication systems, and computer networks. For instance, a DEMUX can be used to distribute a digital signal to multiple devices.
Next TopicDifference between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










