Difference Between Population and SamplePopulation Definition
Population, in its simplest form, is the whole of all components under investigation that have one or more characteristics, for instance, the entire population of India. In addition to referring to individuals, the word "population" can also describe objects, occasions, structures, etc. Population size is the total amount of people living in an area. For instance, if India has 100 million citizens, its population is N. Populations can be any size. The following discusses the various population types: Population Limit The population is considered finite when the total number of its components is fixed, making it feasible to count it all. A limitless population When there are too many units in a population to measure, making it impossible to see every item in the world, the population is said to be limitless. Present-day Population The term "existent population" refers to genuine people and living things. Imaginary Population The population that only exists in mind is known as the hypothetical or imaginary population. Example
Sample
By "sample," we refer to a portion of the population chosen randomly to participate in the research. The sample so chosen should be such that it represents the population in all of its features and should be free from bias in order to provide a tiny cross-section, as the sample observations are used to draw generalizations about the population. In other words, a "sample" comprises the respondents chosen from the population, and the selection of respondents is referred to as "sampling." The number of units in a sample is referred to as the sample size, while the units under investigation are known as sampling units. The majority of the time, while doing statistical testing, samples are employed when the sample size is too big to encompass the whole population being examined. Population V/S Sample
Significant Distinctions Between Sample and Population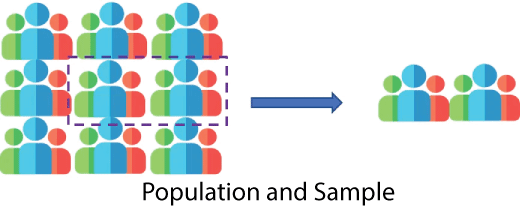
The following reasons make the distinction between population and sample clear:
ConclusionNotwithstanding the distinctions mentioned above, it is also true that the relationship between the sample and population is that the sample is taken from the population; hence, without the population, the sample might not exist. Also, the sample's primary goal is to draw as precise a statistical conclusion about the population as possible. The amount of generalization accuracy increases with the size of the sample. Population and Sample frequently asked questionsQuestion 1: What is the sample population's limitation? Answer: The sampling approach needs to be improved by using limited selection, which causes us to make incorrect inferences. When a sample selection technique is misused, bias results. Large samples that were poorly chosen may not be as dependable as relatively small samples that were carefully chosen. Question 2: How do you tell whether a set of data is population or sample? Answer: The term "population" describes the complete group of people about whom you want to make conclusions. The term "sample" refers to the population from which you will gather data. Question 3: Do samples always represent the population? Answer: Researchers and statisticians use samples to represent a population while gathering data. Samples can be useful for drawing inferences about populations that are meaningful and for representing populations. As samples are parts of populations, they are always smaller than the populations they represent.
Next TopicDifference Between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









