Difference Between Private and Public CompanyOne of the most significant and well-known types of business organization is a firm. A voluntary group of people with the same aim who agree to pool their resources and work together to accomplish the stated objectives can be characterized as it. It can be referred to as an artificial person made by the legal system with a unique legal personality and signature, known as the common seal. It is effectively an artificial person because it doesn't depend on the individuals that run, control, and support its company for its existence. There are primarily two types of businesses: 
Public CompanyAs defined by the Companies Act of 2013, a public business solicits investment money from the general public. Shares are allocated when applications are solicited via the release of a prospectus. Such businesses permit shareholders to transfer their shares without hassle. A public company's shares are listed on stock exchanges, where brokers help facilitate all transactions. The following traits of a public firm are also present.
A corporation that allows shareholders to claim the business's assets and income is known as a public company or publicly traded company. These traders acquire ownership through the unrestricted exchange of shares on the stock market. Shares of stocks that are freely exchanged on a stock exchange or in over-the-counter markets are used to organize ownership of these businesses. A corporation must list in the exchange if it is over a particular size in some nations. A public business must meet the requirements listed below:
Private CompanyContrary to a public corporation, a private firm trades its securities privately or over the counter. It does not make its securities available to the general public for subscription through stock exchanges. Additionally, these businesses could limit their members' ability to transfer shares. At some point throughout its existence, a private corporation may convert to a public company. Comparatively to a private corporation, going public would give a company access to various funding opportunities. When a private company goes public, all of its previously privately held securities are now owned by the general public and may be placed on the stock exchange. The following traits of a private corporation are also present:
A private corporation is a business that has private ownership. These businesses do not conduct their initial public offerings, although they can still issue stocks and have shareholders. It is challenging to estimate their value. There are four categories of private firms. These include C corporations, sole proprietorships, S corporations, and limited liability companies (LLCs) (C-corps). Some of its stockholders can purchase its stock privately. A small group of stockholders creates these businesses with financial or social goals. Due to their lack of access to the stock market, these businesses must raise money from corporate profits, lender loans, and private investments. Several businesses decide to remain private for the following reasons: Many businesses decide to remain private to escape regulatory oversight. Many businesses stay private to preserve their family ownership because they are exempt from the requirement to issue shares to the public, which prevents outside interference. Brief Comparison of Private and Public CompaniesUnsurprisingly, privately owned companies are just that privately owned. This suggests that a company's founders, management, or a group of individual investors frequently own it. An initial public offering (IPO) is when a private company sells all or a portion of its stock to the public, giving investors a stake in some of its assets and profits. 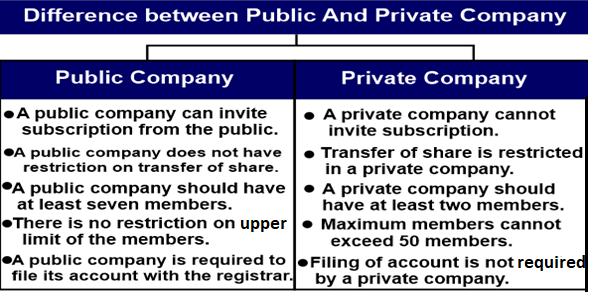
Why Public and Privately Held Companies DifferPrivate CompaniesA corporation must rely on private investment as it cannot access the public financial markets. A privately owned firm may still be allowed to sell a small number of shares without registering with the SEC under Regulation D, even though it cannot rely on doing so to earn money to fund its growth. Privately held companies may use equity shares to attract investors. Privately held companies can finance growth through earnings, venture capital investments, or bank loans. Public CompaniesA publicly traded company may take out a bond loan from investors. Conversely, stocks free up developing enterprises from having to repay bonds by allowing business founders and owners to sell off a portion of their ownership stakes in the company. Public organizations and privately held companies can both be quite large. The only thing that is different and special about them is how they get their reserves or money. Privately owned businesses receive funding from private investors and venture capitalists, and they are exempt from disclosing any organizational details or data to the general public. The general public lends a helping hand to public firms or organizations, allowing them to avoid being owned outright. These entities must go by SEC regulations. Private Company DefinitionA privately held company differs from a public institution. Shares in a privately held company cannot be traded or exchanged among members of the general public. Additionally, neither open stock trades nor public stock exchanges allow for the trading of shares of privately held companies. That doesn't mean there are no shareholders or that there are no shares in privately held companies. For privately held companies, a small group of willing financial backers control or own the shares and discreetly exchange or trade them. A privately owned company is managed like that a public organization. The key distinction is that fewer shares are typically swapped in a privately owned company, and only certain or limited individuals are entitled to the exchanged shares. 
Financial speculators looking for high-risk, high-reward enterprises are best served by funding resources or investing in privately held businesses. Privately held companies frequently borrow money from financial speculators or venture capitalists. They conduct an initial public offering (IPO) and distribute shares to the general public. If a privately held company needs additional capital to expand, it might open itself to the public or go public. With the aid of a private equity firm, a public organization can also convert to a privately owned company. Public Company DefinitionA public organization may make its own registered or enrolled securities available to the general public. An organization becomes a public organization after an IPO. A publicly traded firm can also be referred to as a public organization. Being a publicly traded firm means the company can trade on public capital markets and blatantly offer its shares to the general public. The US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) states that any organization with $10 million in assets and more than 500 supporters or subscribers must register with the SEC and abide by all announcing regulations. The investors or shareholders, senior management, and executives all own shares in a public company. An organization goes public to increase its funding for operations and expand its scope, market, and reach. Difference between Private and Public Company1. Private CompanyMeaning: A privately held company may offer a small number of eager investors its own, secretly or privately held shares. Regulations to Adhere To: Privately owned enterprises are exempt from following government regulations unless their annual revenue reaches $10 million and they have more than 500 shareholders or investors. Advantage: The main advantage of a privately traded or exchanged company is that there are no disclosure requirements and no obligations to give due respect to any investors. Size of the Company: Large organizations can also be privately held trading companies. It is erroneous to assume that a privately held corporation is a more humble or small business. Money and its Sources: There are few individual investors or financial backers for privately held businesses. A few private financial supporters claim, exchange, or trade the equity of a privately held company. Characteristics of a Private Company The qualities of a private corporation are as follows: Members: There must be a minimum of two and a maximum of 200 members in a private company. According to the legislation, even if the business fails, it will continue to exist indefinitely. 
Limited liability: These businesses have similar limitations as public companies. As a result, the stockholders will only need to sell off their services to receive payments. These businesses must add the suffix "private company" to the end of their names. It is a different legal entity from its directors and stockholders and is a separate entity. Advantages of a Private Company Private businesses have a variety of benefits, including: Tax-effective: These businesses are eligible to deduct their profits from corporate taxes. Dividends paid by private corporations to their shareholders are taxed at a reduced rate. Ease of raising capital: Because of their credibility, they may raise money by taking out loans, issuing bonds, and issuing shares. Complete ownership: When managing a business in a small group, owners gain all control, enabling complete ownership. Protection from creditors: As a result, of the restriction that prevents creditors from directly requesting payment from the owner's assets. Shareholders and directors are eventually protected because of this limitation on responsibility. 2. Public Company Meaning: A public organization can make its listed shares available to the general public. Regulations to Adhere To: The Government has a lot of regulations and detailed rules that a public organization must follow. Advantage: The main advantage of a public company is its ability to profit from the market by selling more shares. Size of the Company: Large organizations make up public corporations. Money and its Sources: The sale of the public corporation's bonds and stock is how it obtains assets or money. In stock exchanges, the equities of public companies are traded or swapped. Characteristics of a Public Company The qualities of a public firm are as follows: Paid-up capital: Establishing a public corporation requires at least a certain amount of paid capital. Suffix: A public firm must follow its name with "Limited." Prospectus: Public limited corporations are required to publish prospectuses under the Act for Public Limited Companies. Each shareholder in a public firm has a limited amount of liability. This implies that investors in a public limited business are not liable for losses bigger than their initial investments. Information Disclosure: The business must make its financial data available to the public. Advantages of Public Company These are some benefits of public companies: Public corporations issue their shares or trade their stocks in the market to raise money and capital. These businesses are required by law to provide public information about their financial standing and projected prospects. Sharing risks helps to reduce risk. They may sell shares to the general public to compensate for their losses. ConclusionA business is a grouping of people who want to carry out specific commercial activities while being legally present. The responsibility of members, the number of members, and the incorporation mode are the only factors that affect the company formed. Public Limited Companies, and Private Limited Companies are just a few of the different methods a company can incorporate. The Private and Public Companies subtypes are the most well-known.
Next TopicDifference between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










