Difference Between Provision and ReserveThe terms "reserve" and "provision" are frequently used in business discussions. These words seem similar but are used for different purposes in a business setting. Both of these concepts are crucial for maintaining a company's integrity. Business experts advise saving a portion of profits as reserves for unforeseen occurrences, so businesses set aside money in reserves to cover those costs. However, this article will inform us about a few places where provisions and reserves differ from one another. 
ProvisionThe term "provision" describes an amount set aside from a company's profit to pay for possible future expenses or a possible decline in asset value. For a firm, provisions are important since they cover certain costs and payments associated with them. Provisions shouldn't be viewed as savings because they are made to cover costs associated with a possible future responsibility. The most typical kind of provision is a loan loss provision. To cover the liabilities, a bankruptcy provision has been created. These debts are not expected to be paid during an accounting period. It is shown as costs in the income statement and is included as a current obligation on the balance sheet. A provision is an amount of money placed aside to pay for possible future expenses. The phrase "possible" should be noted because these costs have not yet been incurred. Contrarily, balance sheet reserves are excess cash that a corporation sets aside to fund its upcoming initiatives. ReserveThe term "reserve" refers to a quantity or portion of earnings that a business preserves or sets aside after a fiscal year to cover future unforeseen expenses. The business is expanded using it as well. Stabilizes a company's financial position by being used for asset expansion, dividend payments, and investments. In an organization, reserves come in two different
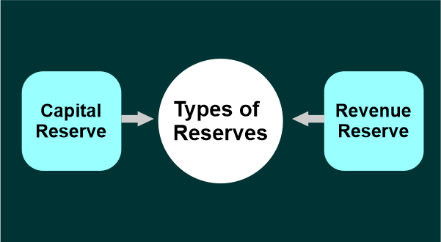
The capital reserve is converted into a capital reserve that cannot be distributed as dividends to shareholders. As a result, it cannot be funded by income from a company's primary operations. A revenue reserve is from profits earned from a company's or organization's basic operations. A profit & loss appropriation account must be formed to construct a revenue reserve. Retained profits is another name for the revenue reserve. The following are some possible uses for it.
The table below lists some of the main distinctions between Reserve and Provision.
General Guidelines for Provision Creation
Provision Requirements in Business
ConclusionA reserve is a money placed aside to cover expected loss or expense. At the same time, a provision is money appropriated from profit and accumulated profits to improve a company's financial situation.
Next TopicDifference Between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









