Difference Between Pvt Ltd and LtdPvt LtdA Pvt Ltd, or limited private organization, is an organizational structure in which the obligation of the organization's investors is limited to how much their speculation is. This implies that investors are just answerable for the obligations and liabilities of the organization up to the sum they have contributed, and their resources are not in danger. 
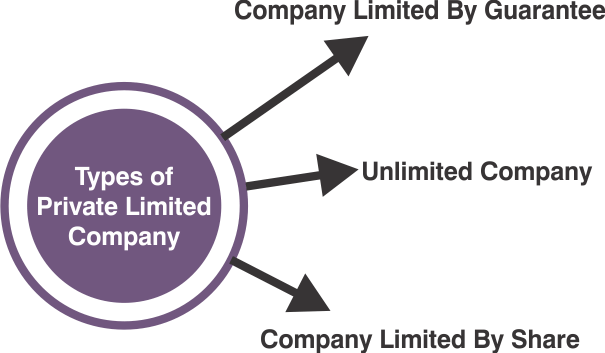
In Pvt Ltd, the business is considered a distinct legal personality from its owners and can contract, possess property, and bring or defend legal actions in its name. Pvt Ltd companies are required to have at least one directors and two shareholders, and they are also required to file annual financial statements with the regulatory authority in their jurisdiction. Small and medium-sized businesses often use Pvt Ltd companies because they offer limited liability protection to the owners while allowing them to retain control over the company. They also have certain tax advantages and may be more attractive to investors because of their legal structure. Types of Private Limited Company
Why Startups Prefer Private Limited CompaniesPrivate Limited Company is favored design by new businesses given the dependability and learning experiences presented by this construction. Additionally, it ensures the person's independent and genuine existence. Along these lines, it has the authority to involve itself in contracts and formal processes. In addition, any changes to the Board and personnel inside a firm have no impact on its status. A separate regulatory Board, for instance Administering body, is useful for people captivated by adventure reasons. Where Board works on remuneration, the people get benefits participating in sort of Benefit. 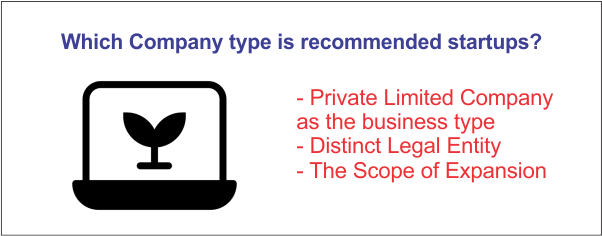
Additionally, it provides several financing options, including ESOP, private value, and more. This makes it more appropriate for outer subsidizing choices. Furthermore, in this way, it is more liked by V.C.s, Private backers, and other external financing offices than other business structures. Due to its credibility as a corporate structure, it is also relatively favored by banks and lending organizations. A private business might benefit from enrolling under the Startup India Drive of the Indian government. Tax exemptions are one of the many benefits offered by this program to recognized entrepreneurs. These factors make it the top priority for both new firms and family-run enterprises. Pvt Ltd is appropriate for product-based and growth-oriented firms, whereas service-based businesses typically use LLP. Promoters frequently encounter misconceptions and problems while thinking about forming a private limited company. Owner Defined by Share CapitalThe actual business owners are the shareholders. Share capital establishes a Private Limited Company's ownership. The capital of the firm is divided equally among the shares. Shares in the firm that the owners possess establish the ownership ratio. Such a sort of game plan in shareholding is one reason for a financial backer to be drawn towards a company type of organization. The value possession is a practical choice for them to seek after proprietorship in a business. Further, the offers can likewise be given at a premium to present more capital, facilitating the venture cycle. 
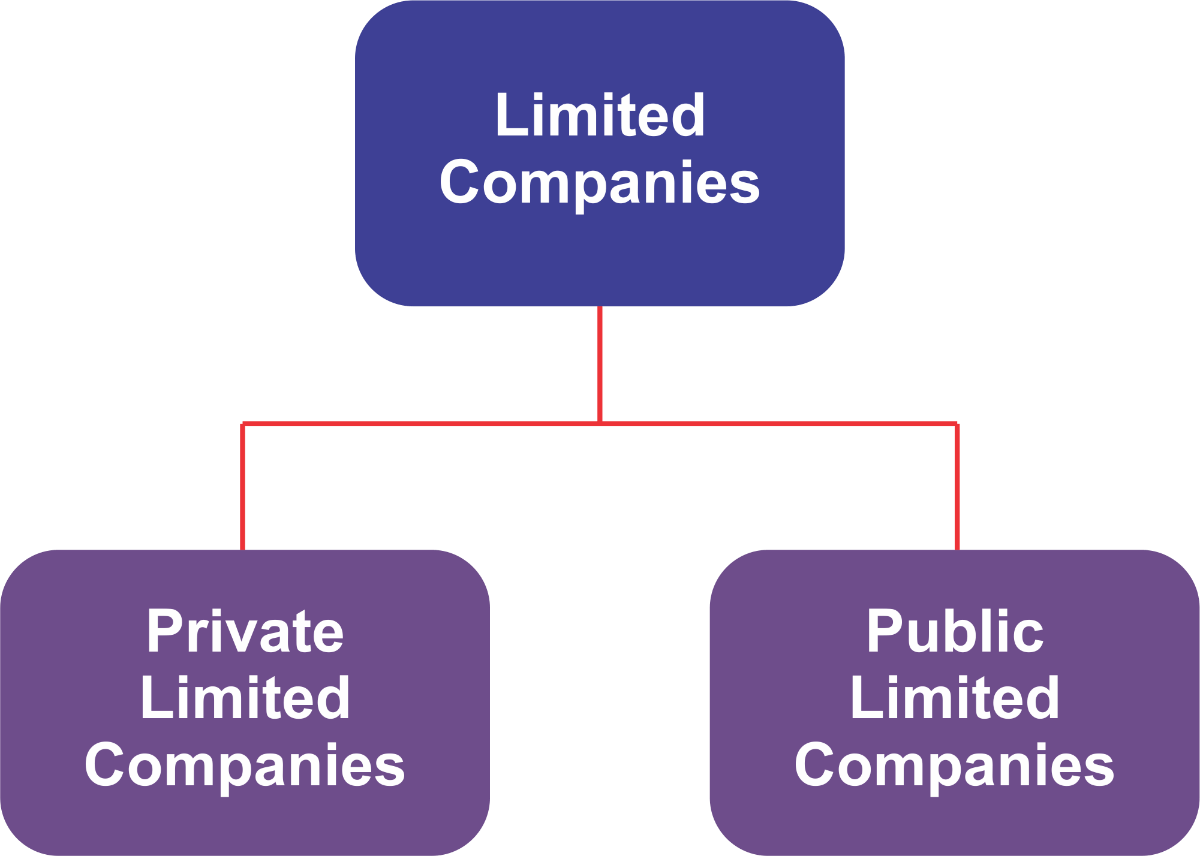
Ownership in the form of shares is easier to transfer than the capital of other forms, such as LLPs. Yet, as stated in the definition above, it is restricted. If a shareholder wants to leave the firm, he must first offer the shares to another member before selling them to a third party. Also, for the benefit of the business, the Board Members must approve the planned transfer. This limitation is in place to protect the company's private ownership. However, unlike a listed corporation, stockholders cannot publicly trade or list shares on a stock market. Ltd or LimitedA limited company's members' or subscribers' liability is constrained to the amount they have contributed or guaranteed to the business. Limited enterprises may be constrained by guarantees or by shares. Members of a corporation limited by shares are only liable for the unpaid value of their shares. The amount an owner agrees to contribute to the company's assets in the case of a winding-up constitutes the maximum amount of their liability in a company limited by guarantee. Private and public limited companies are two different categories of the former (private limited companies). A private limited company's membership is subject to legal and contractual restrictions. On the other hand, anyone could buy participates in a limited public organization. 
Limited companies can be tracked down in many nations, albeit the nitty gritty principles overseeing them change generally. It is in like manner typical for a capability to be made between the straightforwardly tradable organizations of the plc type (for example, the German Aktiengesellschaft (A.G.), Dutch and Belgian nv, English PLC, Czech a.s., Italian S.p.A., Hungarian Nyrt. additionally, the Spanish, French, Perfect, Greek and Romanian S.A.), and the "private" sorts of organizations, (for instance, the German GmbH, Dutch and Belgian bv, Portuguese Lda., English Ltd, Japanese K.K., Clean sp. z o.o., Russian ?o?, Ukrainian ??? (TOV), the Czech s.r.o., the French s.a.r.l., the Italian s.r.l., Romanian s.r.l., Hungarian kft., Macedonian ??? (DOO), Slovenian d.o.o., and Slovak s.r.o.). Types of Ltd Company
The Basics of an Ltd. Company StructureA limited company has different legal status. One or more members, often known as shareholders or owners, can join a private limited company through private sales. Directors are workers of the firm who maintain all administrative duties and tax filings, although they are not required to be shareholders. The corporation has its finances that are taxed independently from the owners. The corporation owns all gains and is responsible for paying taxes, distributing some as dividends to shareholders, and keeping the remainder for working capital. A director may only withdraw money to pay their salary, dividends, or for loans. 
When taxes are paid, the corporation is free to keep any earnings. To avoid misunderstanding, the organization's money must be maintained apart from personal ones. Public limited companies (PLCs) are additionally ordinarily utilized in the U.K. Furthermore, some Republic nations, rather than "Inc." or "Ltd.," which are the standard in the U.S. also, somewhere else. The obligatory use of the PLC condensing following the business name instantly alerts investors or anybody managing the firm that the company is public and probably enormous. Like any other significant organization, they must abide by tight regulations and disclose their financial situation so that shareholders and other interested parties may assess the stock's true value. The passing of a shareholder has no bearing on how long a PLC will exist. Key Difference Between Private Limited and Limited
Next TopicDifference between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share