Difference between Simile and MetaphorThe English language consists of more than 100 literary devices and two of the most important are simile and metaphor. The simile is used for the comparison of objects which are somewhat similar in magnitude and words such as 'like' and 'as' are added to emphasize their similarities. 
For example- She is sly like a fox. Her heart is like gold. On the other hand, metaphors are used to directly compare two things that are not related to each other in any way. For example- You are my sunshine He is such a night owl 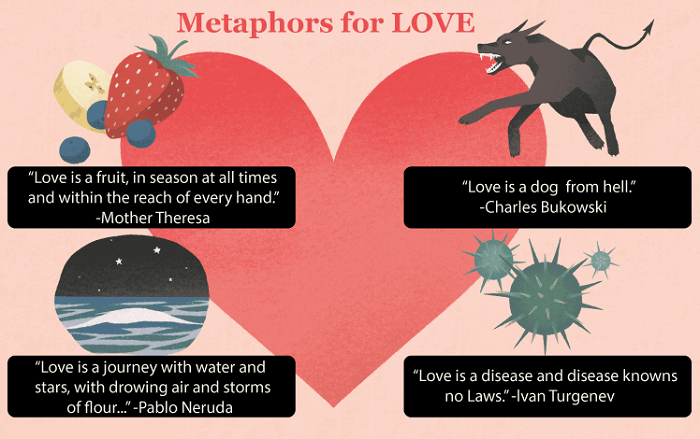
Simile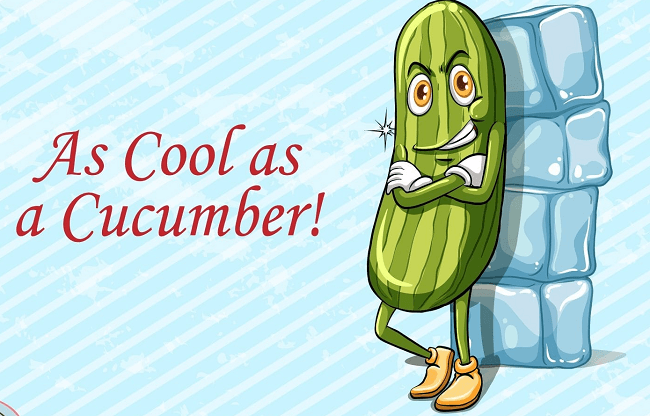
The term 'simile' had been extracted from the Latin word 'similis' which translates to similar or like which goes with its function. Many poets and literary scholars have used this since it was first discovered by Aristotle. He first use the term called 'Imago' which was then used for comparing things that are similar in some way or other. This is the component of figurative language through which one has to conjecture the traits of two things that are being compared. The noun of similar quality should be used with the adjective that matches it. For instance, in the phrase 'cool as a cucumber' the cucumber which is known for it being cool and fresh could be used to describe the calmness and patience of an individual. Uses of SimileThe similes are being used in narratives, texts, and analogies but mostly in poetries. This figure of speech makes it convenient for the readers or listeners to analyze the words and form images of two or more things that are being compared at the moment. While reading a text, the readers often come across phrases such as -"He is busy", "She is drunk", "Leena is so proud" and so on. However, the visuals are not clear and the sentences do not seem that expressive but rather floppy. Alternatively, to create accurate comparisons, articles with analogous features need to be located. The phrase "She is drunk" could be altered to "She is drunk like a fish". As the fishes live in water, they always seem 'drunk'. Therefore, the comparison fits this scenario. In addition, "Leena is so proud" could be turned to "Leena is as proud as a peacock". The sentences do not look offhand and inactive anymore. Other examples using 'as':
Using 'like'
Types of SimilesThere are two types of similes first found by Greek playwrights around the 12th century. The construction of visual representations and the surfacing of emotions is an important aspects while reading a text. So the use of similes is a valid addition to a narrative. The types of similes are: Traditional Rhetoric and Homeric similes 1. Traditional Rhetoric Similes The traditional rhetorical similes are the ones commonly used by people in their daily lives. In traditional rhetoric similes, the affirmations are followed by words such as 'like' or 'as' complete with nouns. These similes are commonly used by individuals without even realizing it. However, it is a convenient scheme to add effect, criticism, and infrequently hilarity in long chats with friends who are as good as a four-leaved clover. For example: 'As sharp as a razor', 'hard as a brick, 'proud as a young bull', 'Run like a deer, 'eyes like a hawk', 'voice like a cuckoo', 'dance like an angel' 'You resemble your mother so much', 'A dog would have been more loyal than you', and so on. 2. Homeric Similes This simile is named after the renowned playwright, Homer who is praised for writing the tragedy of 'The Illiad'. He is also known as the father of Epic poetry. The framework for using the Homeric simile is identical to that of the former simile. However, the comparison does not end in just four to five words. The sentence stretches itself to create visuals that could also be inspired by myths. These similes are also known as Epic similes as they express the detailed connection between two objects which could be completely unrelated. And it also uses most of the human imagination. For instance - Paradise Lost(Book-1) by John Milton This epic narrative is known for reviving the bible and also dramatizing it was first published in 1667. The poem had been extended to ten books and delineates the anecdote of the greatest fall of man. The entire poem is filled with the comparisons of Satan with Leviathan (the mythical sea beast), his weapons with the tallest pine trees, and his army like the beehives. The defeated army was also dispersed like "autumnal leaves" floating in the brooks. The comparisons are made by using 'like' and 'as' and the description of the similarities is quite detailed. Therefore, the use of Epic similes in this text has been glorified in history. The Illiad by Homer The mentioned text is considered to be written around the 8th century BC by the Greek dramatist, Homer. This narrative deals with the war that took place between the Trojans and the Greeks and also foregrounds the splendor of individual knights who fought in the war. The Greeks hoarding around the advisories reminded one of the swarms of bees, Achilles' comparison with the wounded lion after the death of Patroclus, and Hector resembling a snake while he prey over Achilles are instances of Homeric simile from one of the oldest text in English Literature. Metaphor
Metaphors are the comparison of things that belong to different categories altogether and the words such as 'like' and 'as' are forbidden to use. These are not direct comparisons between two objects but the action and similarity could be understood through the traits of one object associated with the name of another. For instance- The phrase by William Shakespeare: "All the world's a stage and all the men and women merely players". Now, the world and the stage are completely distinct aesthetics. However, the visuals and the unwillingness to use 'like' in the sentence gains beauty from it. Uses of MetaphorThe similes could be taken as a kind of metaphor. However, the vice versa could not be true. Now, if functional comparative sentences can be created by using the words 'like', 'resemble', 'as', and 'than', why would we need to add metaphors in our narratives? It is because writing texts and using figurative language could help to create imagery for the reader or listener which makes it easier for the comparisons or similarities that are made regarding the subjects to be obvious and easier to understand. The phrase 'Rocket Science' is commonly used for technical terms or in complex scientific matters. However, it has now become a metaphor for the contexts that are difficult to understand for the general public. Types of MetaphorsThere are six major types of metaphors are: 1. Standard metaphor The observable juxtaposition between the objects concerned in the phrase is known as a standard metaphor. These phrases could be used in our daily lives and sometimes to exaggerate matters just so the context of the speech would become clearer. For example - You have a heart of stone. Time is a thief. 2. Extended metaphor The process of framing these metaphors is the same as the standard one. However, the sentences or phrases are stretched to emphasize the collation and get the meaning out of it. Extended metaphors are commonly used by scholarly writers and poets to create a sophisticated environment for their audience. For instance-

3. Visual metaphor- These metaphors are used to receive denotation from the image, idol, or any other work of art without using direct words. Many advertisement companies and upcoming writers use the motto of "Show, don't tell" as the brain always has a hard time ignoring visual imagery than words. Mostly this metaphor is used by filmmakers and artists. For instance-
4. Implied metaphor- The differentiation of two objects, persons, or places, when one of them is not even mentioned but rather implied and the implication leads to the derivation of meaning out of the phrase. For Example -
Here the dog has not been mentioned. However, the word 'barked' represents the likeness between the girl and a dog.
5. Mixed metaphor- The use of two metaphors that are inconsistent with one another. Alternatively, they are put together as a figure of speech created through the mixing of imagery in the phrase. Most of the authors tend to avoid mixing metaphors as it further confuses the reader which is not the purpose of a metaphor. For example- "Let's bury the hatchet and let the sleeping dogs lie" 'Burying the hatchet' and 'let the sleeping dogs lie' are two entirely different phrases with different meanings. So getting the meaning out of the mentioned sentence could be quite tiresome.
6. Dead metaphor This metaphor is characterized as the figure of speech that has lost its imagery and the phrase has an entirely different meaning than the visuals this sentence creates in our minds. These metaphors are also called historical or frozen metaphors. For instance, the expression, 'hold your horses' does not have a similar interpretation which could be perceived by its words. It does not aim to hold back the horses which are trying to run away. Alternatively, it is a metaphor to calm down or be patient which could be used in our day-to-day figurative language. Other examples of the dead metaphor; The expression 'Leg of a trip' originated in the era when long voyages started sailing across the world. The term 'leg' also means to push a canoe through the tunnel by applying force on its sides and top. Nowadays, the phrase is used for long flights and trips. Also 'carbon copy' which interprets the striking similarity between two different objects and persons is the phrase that was derived due to the indistinguishable layers of writing produced when it was done by using carbon. Similarity and Comparison between Metaphor and Simile
As we have perceived that the parallelism between the metaphor and simile is that both consist of a tenor (the subject whose description has been suggested) and a vehicle (the figure of speech to which the subject is getting compared with). The differences are given below:
Next TopicDifference between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









