Immutable String in JavaA String is an unavoidable type of variable while writing any application program. String references are used to store various attributes like username, password, etc. In Java, String objects are immutable. Immutable simply means unmodifiable or unchangeable. Once String object is created its data or state can't be changed but a new String object is created. Let's try to understand the concept of immutability by the example given below: Testimmutablestring.java Test it NowOutput: Sachin Now it can be understood by the diagram given below. Here Sachin is not changed but a new object is created with Sachin Tendulkar. That is why String is known as immutable. 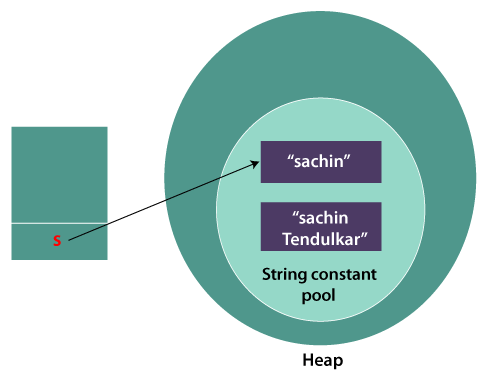
As you can see in the above figure that two objects are created but s reference variable still refers to "Sachin" not to "Sachin Tendulkar". But if we explicitly assign it to the reference variable, it will refer to "Sachin Tendulkar" object. For example: Testimmutablestring1.java Test it NowOutput: Sachin Tendulkar In such a case, s points to the "Sachin Tendulkar". Please notice that still Sachin object is not modified. Why String objects are immutable in Java?As Java uses the concept of String literal. Suppose there are 5 reference variables, all refer to one object "Sachin". If one reference variable changes the value of the object, it will be affected by all the reference variables. That is why String objects are immutable in Java. Following are some features of String which makes String objects immutable. 1. ClassLoader: A ClassLoader in Java uses a String object as an argument. Consider, if the String object is modifiable, the value might be changed and the class that is supposed to be loaded might be different. To avoid this kind of misinterpretation, String is immutable. 2. Thread Safe: As the String object is immutable we don't have to take care of the synchronization that is required while sharing an object across multiple threads. 3. Security: As we have seen in class loading, immutable String objects avoid further errors by loading the correct class. This leads to making the application program more secure. Consider an example of banking software. The username and password cannot be modified by any intruder because String objects are immutable. This can make the application program more secure. 4. Heap Space: The immutability of String helps to minimize the usage in the heap memory. When we try to declare a new String object, the JVM checks whether the value already exists in the String pool or not. If it exists, the same value is assigned to the new object. This feature allows Java to use the heap space efficiently. Why String class is Final in Java?The reason behind the String class being final is because no one can override the methods of the String class. So that it can provide the same features to the new String objects as well as to the old ones.
Next TopicString Comparison in java
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









