Difference between Insulator and Conductor
Insulator and conductor are two different types of substances with different properties. Let us see how they differ from each other.
What is a Conductor?
A conductor is an object or kind of substance that permits charge (voltage) to pass through it. Conductors have electrical current on their surfaces, allowing current to flow. It is why they can conduct electricity. With the help of conductors, heat is also transferred from one origin to another. The substance being used and the size of a conductor determines the resistivity of a cable. The resistance of a substance is related to its bridge area. A thick copper cable, for example, has a shorter lifespan than a thin copper cable that is otherwise equal. Examples of conducting substances are metallic fluids, transistors, semiconductors, plasmas. Some non-metallic examples are carbon in the form of graphite.
The Use of Conductors in Everyday Life
- Mercury is a frequent component in thermometers that are used to measure body temperature.
- Aluminum is used in the fabrication of foils for storing food and in fry pans.
- Car radiators use conductors to transfer heat away from the engine.
- In the manufacture of automobile engines, iron is utilized to send heat.
Everything You Should Know About Conductor
- A conductor is a substance that allows electricity or heat to flow through it. Because the conductors have high conductivity, they may carry the electrical signal. The electrons flow in metal bonding cause conductance in conductors.
- The conductor's resistance increases as the temperature increases. Charged particles are free electrons in conductors.
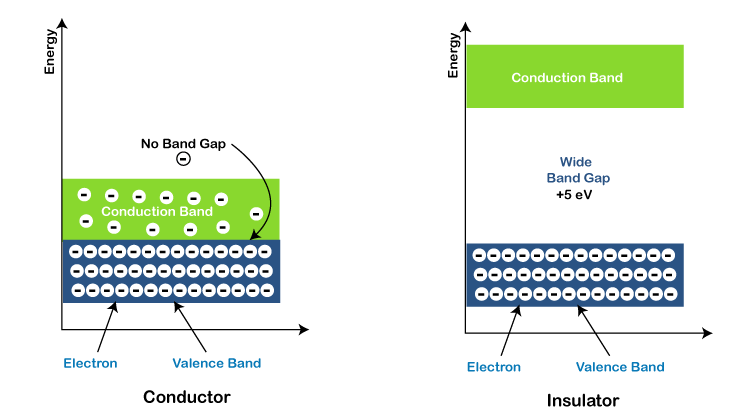
- The energy gap between some of the charge carriers of a conductor is small in circuits. Thus, the conduction condition does not need any more energy.
- The coefficient of the impedance of conductors is positive. Its resistance increases as the temperature rises.
- When supercoiled, certain specific conductors become superconductors, whereas others have finite resistance. The conductors' conduction band and the Valence band are both complete. Gold, copper, silver, aluminum, and other metals are examples.
- Metals that generate heat, such as iron, copper, and aluminum, form wires and convey electromagnetic fields.
- Metallic bonds are present in the structure of conductors. Current passes in resistance beneath electromagnetic field impact. In their composition, conductors have ionic bonding. The electromagnetic current influences the flow of current in conductors.
What is an Insulator?
An insulator, also known as a nonconductor, is a substance or item that does not enable energy or charge to pass through it. Following the definition of the electronic band, the charge flows are accelerated if the electrons are stimulated to the phases. In addition, it permits electrons to get energy and hence flow through a circuit element. If none of these states exist, the substance is an insulator.
Insulators provide support and prevent electrical conductors from making accidental contact. Porcelain and glass insulators are mostly used. Plastic will not have the same degree of flexibility as glass or porcelain, but it is still durable. Cables and wires are usually plastically insulated. Thus in massive procedures, it is utilized more.
The resistivity of an insulator is what characterizes it. The resistivity of insulators is greater than that of semiconductors or conductors. When a substance reduces the quantity of current going through it, it is also said to have good strength. Insulators are rated in the hundreds of volts range, although some are rated in the hundreds of millions of volts range and are utilized in the transmission of electricity.
Insulators Are Used In Everyday Life
- Insulators are being used in buildings to insulate them or to manage noise. Circuit boards, elevated systems, and the coating on electromagnetic, electrical cables all use electrical insulators.
- Heat insulators are often used to prevent the transmission of heat between two regions. Others are employed in the heating of homes.
Insulator: Things You Need to Know
- Insulators are the fundamental compounds that hinder heat or electrical transmission.
- They have low conductivity (10-13/m); hence electricity cannot pass through them.
- The absence of free electronic excitation causes no conductance.
- The insulator resistivity is vital; however, it decreases as the temperature increases. There are no free electrons in insulators.
- In the electronic configuration of insulators, there are eight valence electrons.
- In insulators, the valence band is vast, requiring large amounts of energy, such as lightning, to drive electrons into the charge carriers.
- An insulator's percentage of conductivity is negative, but it has a very high resistance. When the Insulator is chilled to absolute zero, the resistance rises.
- The conductivity increases as the temperature rises. Insulators have been used in networks to guard against voltage spikes and to avoid electrical shorts between wires.
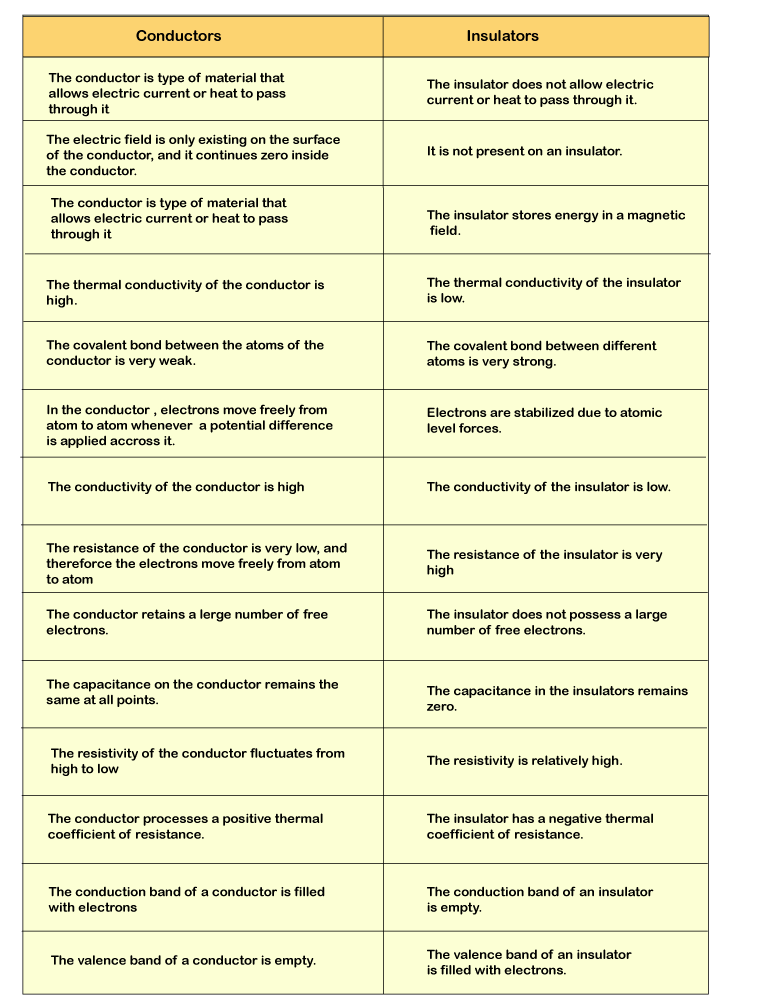
| Conductor |
Insulator |
| A conductor makes it easy to send energy, e.g., an electric motor and heat transfer. |
However, electrical charge or heat is not allowed to pass through an insulator. |
| The conduction band is vacant. |
The Insulator's valence band is filled. |
| Molecular bonds in conductors are weak. |
Massive molecular bonds are contained in an Insulator. |
| Its conductivity is high. |
The conductivity of insulators is low. |
| The conductor have little resistance. |
Insulators have very high strength, and the electrons are so bound together. |
| Electric filed is observed on the top and in the inner part of the conductor. |
There is no electrical field in the insulators, not within or on the surface. |
Furthermore, the conductivity of a substance relies on its atomic configuration. It should be noted. If the atoms cannot keep their external electrons together, a substance can show to be an excellent conductor. Because of certain electrons, heat and electrical charge travel through all the materials from one molecule to another.
The materials exhibit to be a lousy conductor or isolator if its atoms have connected electrons. Besides, conductors and insulators are crucial to us, particularly when it comes to handling electrical equipment.
|



 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










