Lithium-Ion batteriesA lithium-ion battery is a type of battery used as a charging device to power electronic devices. It is considered a rechargeable battery that can be charged multiple times. It acts as a power source for the portable electronic devices commonly used in military and aerospace applications. Lithium-ion batteries have an average lifetime of around two years. It should not be confused with lithium batteries. Lithium batteries are not rechargeable, while lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable batteries. The lithium's ability to operate even in very low temperatures has increased lithium-ion batteries' popularity in various areas. History
Working of a lithium ion batteryLet's discuss the components and working of a lithium-ion battery. StructureThe structure of a lithium-ion battery is shown below: 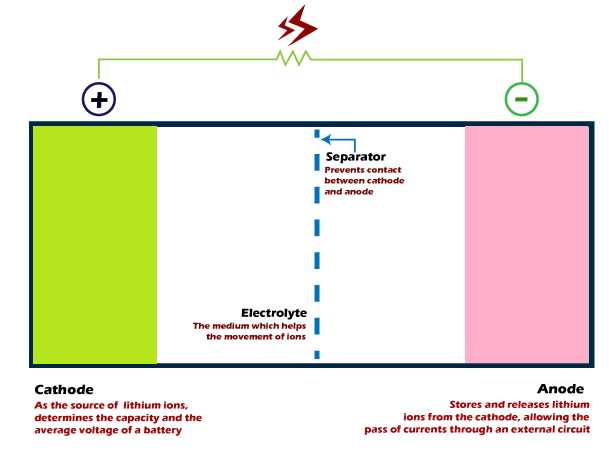
ComponentsA battery consists of three components, two electrodes, and an electrolyte. The electrodes are named cathode and anode, while the electrolyte is the solution in which the movement of charged ions takes place from one electrode to another. The cathode and anode of a battery are positive and negative. Process in a Lithium-ion batteryAs discussed, a lithium-ion battery is a rechargeable battery. It means it comprises of two processes, charging and discharging. The charging state of a battery provides electric current to the external connected circuitry. Discharging The lithium ions move from the negative electrode (anode) to the positive electrode (cathode) provides energy to the external circuit. The movement of ions takes place through the electrolyte. It is defined as the discharging state of a battery. The process loses energy because it is providing energy to the external circuit. Charging Similarly, the movement of charged ions back to the anode is defined as the battery's charging state. The charging is a process to gain back the energy. The external voltage source provides energy to the battery during the charging process. The positive electrode (cathode) provides lithium ions to the anode (negative electrode), moving through the electrolyte. The battery stores this energy from an external source. Such energy is utilized when an external circuit is connected to the battery. Again the discharging occurs when the battery supplies energy to the external circuit. The cycle goes on to recharge the battery. Thus, we can say that lithium-ion batteries can be charged multiple times. MaterialMaterial signifies the use of materials used for the construction of cathode, anode, and electrolyte. Positive Electrode The material for a positive electrode is generally a metal oxide. It includes examples such as lithium cobalt oxide, lithium manganese, etc. It means that the cathode material is the metal oxide with added lithium. It releases lithium ions during the discharging process to provide energy to the external circuit. The lithium-ion battery helps in increasing the potential difference between the cathode and anode, resulting in higher voltage. Negative Electrode The negative electrode or anode uses graphite powder as the material. The graphite powder is coated on the foil made of cooper as the electrode.
Binders Binders are the materials to hold the electrode material particles together. It contributes a very small percentage of the battery's weight. It is an essential part of a battery that provides certain benefits, such as safety enhancement and improved capacity. Electrolyte The electrolyte is a lithium salt that is used as a conductor. The ions move from one electrode to another through the electrolyte. The electrolyte's primary role in the lithium-ion battery is to act as a medium for the movement of lithium ions between the cathode and anode. WorkingLet's discuss the working of a lithium-ion battery. A chemical reaction continuously works inside a battery for its working. The battery is dead without any chemical reaction inside it. We know electricity is the flow of electrons from a negative terminal to the positive terminal. The flow of electrons comes from the element lithium present inside a battery. The lithium is present at the negative terminal or anode of the battery. It is present in between the layers of the carbon graphite. The structure of graphite keeps the lithium inside its layers. It works as a stable storage space for the lithium atoms. 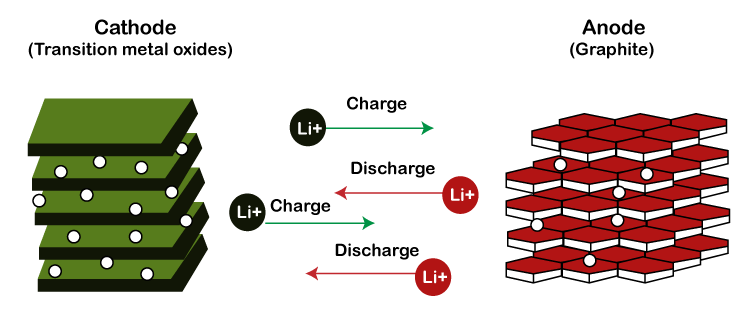
The lithium atoms give up their outer electron from their outer orbit. When it finds a path, lithium moves from the negative side to the positive side. When a lithium atoms group leaves the graphite, it causes the flow of electrons from the anode to the cathode. Similarly, the reverse process happens during recharging. The charges provide higher force to the flow of electrons in the reverse direction. The electrons from the cathode kick back the lithium ions towards the anode. The lithium atoms are forced onto the graphite and fix back into the layers of the graphite. Types of Lithium-ion BatteriesThere are various types of lithium-ion batteries, such as lithium manganese oxide, lithium cobalt battery, etc. Lithium batteries are used in most of the applications in daily life. Lithium batteries have various advantages, such as lightweight, long lifetime, and high energy density, make them a great choice. 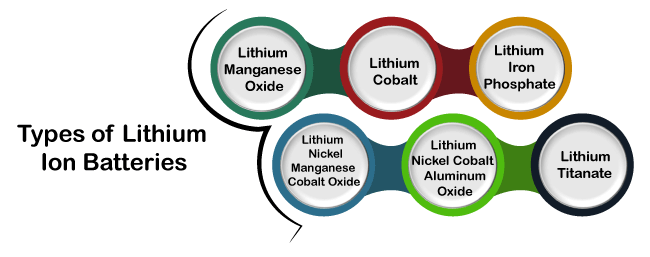
Lithium Manganese OxideThe lithium manganese oxide has manganese oxide as the material of the cathode. It has a low internal resistance, high thermal stability, better safety, and enhanced current flow. The benefit of low resistance is that it enables fast charging. Lithium CobaltThe lithium cobalt Oxide battery is used in a digital camera, computers, and mobile devices due to its high specific energy. The material at the cathode is cobalt oxide, while the material at the anode is graphite carbon. But, it has some disadvantages, such as shorter life and low thermal stability. Lithium Iron PhosphateThe lithium iron phosphate has phosphate as the cathode material. The advantage of using such batteries is good thermal stability, long life, and high current. It is proffered for applications that require proper safety and a long life span, such as electric motorcycles. Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt OxideThe combination of three (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) is considered the cathode's best material for a lithium-ion battery. The percentage contribution of the Nickel, Manganese, and Cobalt are 60, 20, and 20.Nickel has the advantage of high specific energy, while manganese has low internal resistance. Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum OxideThe primary uses of lithium nickel cobalt aluminum oxide are its use in electric powertrains. It offers high energy density and a long life span. The disadvantages of such batteries over other types of lithium-ion batteries are the low safety and high cost. Its performance is continuously monitored for the safety of the powertrains. Lithium TitanateLithium titanate battery can fast recharge. The titanate battery's primary issue is the low energy density compared to other types of lithium-ion batteries. But, the energy density is higher than the non-lithium ion batteries. The common application includes aerospace, power backups, etc. 
Advantages of Lithium-ion batteriesThe advantages of Lithium-ion batteries are listed below:
Disadvantages of Lithium ion batteriesThe disadvantages of Lithium-ion batteries are listed below:
Most shipping companies prohibit the bulk shipment of lithium-ion batteries. It is due to the risk associated with it.
The cost of lithium-ion batteries is much higher than other types of batteries, such as nickel-cadmium. It is due to its high energy density and large current handling capacity. Applications of Lithium-Ion batteries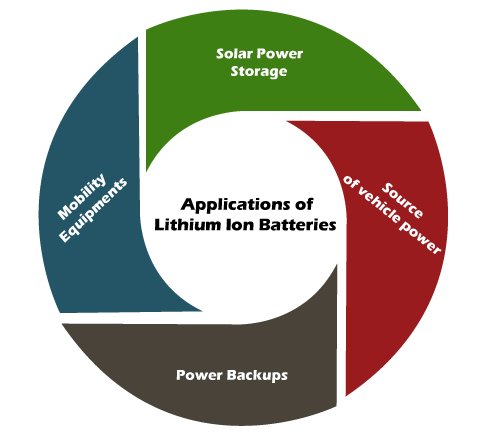
The applications of lithium-ion batteries are listed below:
Safety HazardsThere are some safety hazards to ensure the safe handling and usage of lithium-ion batteries. It is listed below:
Next TopicPID Controller
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









