Difference between RAM and ROM
Although RAM and ROM both are the internal memories of the computer, they are different from each other in terms of their uses, storage capacity, physical size, and more. Let us see how they differ from each other.
What is RAM:
RAM stands for Random Access Memory. It is the internal memory of the CPU in the form of a hardware device located on the motherboard of a computer. It is designed to store data, programs, and results of a program when a computer is switched on. It is the read and write memory of a computer as we can write information to it as well as read from it.
Furthermore, RAM is a volatile memory as it can?t store data and instructions permanently. For example, when we switch on a computer, the instructions from the hard disk are stored in the RAM. These instructions include the operating system (OS) and other programs which are needed to run a computer. CPU uses these instructions to perform the tasks required to run the computer. This data is retained by the RAM as long as the computer is on, the moment you shut it down, the RAM loses the data. The reason for transferring the data to RAM is that it is easy and fast to read data from RAM as compared to reading it from the hard drive.
Different Types of RAM:
- DRAM (Dynamic Random-access memory): DRAM, or dynamic random-access memory, is the most common RAM type in computer systems nowadays. Every single bit of data is stored separately in a capacitor using an integrated circuit. But because of the nature of capacitors, the stored charge slowly drains out, requiring continuous recharging.
- SRAM (Static Random-access memory): Static Random-access memory, or SRAM, is a costly and fast kind of RAM. It does not require continual refreshing because flip-flops are used to store all the data.
- DDR SDRAM (Double data rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-access memory): DDR SDRAM is an improved version of DRAM. Transferring information on both the clock signal's growing and falling edges practically doubles the records transfer rate compared to traditional SDRAM.
DDR2, DDR3, and DDR4 are several DDR SDRAM generations, each of which gives faster speeds and better performance than the one earlier. New technology and faster data transfer speeds are introduced with each technology. The most recent DDR SDRAM version frequently used in current computers is DDR4.
What is ROM:
ROM stands for read only memory. It is a non-volatile memory that stores information permanently, even when the power is turned off. Like RAM, it is also the primary memory of a computer. It is called read only memory as the programs and data stored in it can be read but cannot be written on it.
At the time of manufacturing, the manufacturer fills the ROM with programs that can?t be altered later. So, you cannot reprogram, rewrite, or erase its data after it is manufactured. However, in some types of ROM, you can modify the stored data. Some common examples of ROM include cartridge used in video game consoles, the data stored permanently on personal computers, and other electronic devices like smartphones, tablets, TV, AC, etc.
Different Types of ROM:
- PROM (Programmable Read-Only Memory): A PROM is a type of ROM that the user or the manufacturer may customize after creating the memory chip. A special tool called a PROM programmer is used to modify it; it changes or burns fuses in the memory cells to store the necessary data. The data in PROM cannot be modified after it has been programmed.
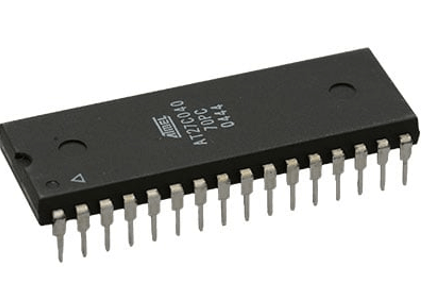
- EPROM: In contrast to PROM, EPROM can be cleaned and reprogrammed using ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Transparent windows on EPROM chips allow UV light exposure, erasing the inside data. For developing and testing firmware, EPROMs are frequently utilized.
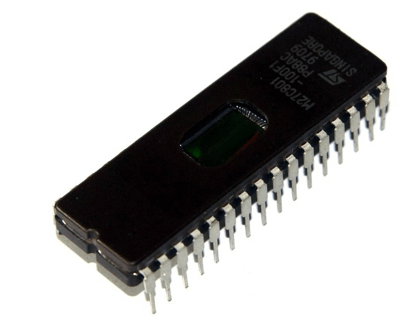
- EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory): EEPROM is an improved version of EPROM that can be erased and reprogrammed with electricity rather than UV light. EEPROM can keep its recorded data even when the power is off. It is frequently used to store small amounts of important information that is difficult to lose, such as BIOS settings that may occasionally need updating.
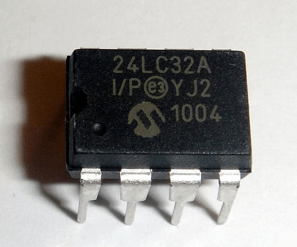
- Flash Memory: It is a kind of EEPROM that can erase or write to many memory cells simultaneously, making it quicker and more effective. It is often used in portable storage devices, including USB drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), memory cards, etc. Flash memory gives a large quantity of storage with comparatively quick access times and is non-volatile.
- Mask ROM: Mask ROM is a ROM that is programmed during the memory chip's manufacturing process. The information is kept in the memory cells forever and cannot be altered or deleted by the user. Frequently, firmware and other crucial data that should be kept the same are stored in mask ROM.

Some of the key differences between RAM and ROM are as follows:
| RAM |
ROM |
| It is a temporary memory of the computer. |
It is the permanent memory of the computer. |
| It is a read-write memory. The data can be written and read. |
It is a read only memory. The data can only be read. |
| It is a volatile memory as it temporarily stores the files as long as the computer is on and working. |
It is a non-volatile memory as it permanently stores the files even when the power is turned off, such as game cartridge and BIOS program stored in the memory of a computer, etc. |
| The storage capacity ranges from 1 to 256 GB. |
Its storage capacity ranges from 4 to 8 MB. |
| It is large in size than ROM. It comes in two different sizes for use in desktop computers and laptops. A desktop ram is around 5.5 inches in length and 1 inch in width. Whereas, the Laptop RAM is around half the length of desktop RAM. |
Its size ranges from less than an inch in length to multiple inches in length and width based on their use. It has less capacity than RAM. |
| Data stored in RAM can be retrieved and altered. |
We can only read the data stored in ROM. It cannot be altered. |
| It is faster than ROM as it is a high-speed memory. |
It is slower than the RAM. |
| The data stored in RAM is used by the CPU in real-time to run the computer. |
The data stored in ROM is used by CPU only when it is transferred to RAM. |
| It temporarily stores the files and data that the CPU needs to process the current instructions or work. |
It stores the BIOS program on the motherboard of a computer, which is needed to bootstrap the computer. |
| Examples: It is used as CPU Cache, Primary Memory in a computer. |
Examples: It is used as Firmware by micro-controllers. |
| The stored data is easy to access. |
The stored data is not as easy to access as it is in ROM. |
| It is costlier than ROM. |
It is cheaper than RAM. |
| Types: DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory), SRAM (Static Random Access Memory). |
Types: PROM (programmable read-only memory), EPROM (erasable programmable read-only memory), EEPROM( electrically erasable programmable ROM), Mask ROM. |
Characteristics of RAM
Here are some key characteristics of RAM:
- Volatility: RAM is a volatile memory that needs constant power to maintain data. The data kept in RAM is lost when the power is interrupted or shut off.
- Speed: Data may be accessed quickly, thanks to RAM. It is essential for a computer system's speedy and effective operation because it helps the CPU read and write information quickly.
- Read and Write Operations: Read and write operations are supported by RAM. It permits the reading and writing of data to and from its storage cells. The CPU can obtain and alter data using this capability as needed.
- Storage Capacity: Compared to other forms of memory, RAM generally has a bigger storage capacity.
- Temporary Storage: While the computer functions, RAM is a temporary storage location for data and program instructions. It contains the data that the processor is presently working on. The information saved in RAM is deleted whenever the power is switched off.
Characteristics of ROM
Here are some key characteristics of ROM:
- Non-Volatility: ROM is non-volatile memory, in contrast to RAM. Data is kept even when there is no constant power source. This quality makes it useful for storing crucial information and instructions that must be kept.
- Stability: As its contents cannot be readily changed or altered, ROM serves as a reliable storage medium.
- Read-Only Access: ROM is a type of memory that only enables data to be read from it, as the name suggests. The machine or user cannot alter or replace the stored information.
- Storage Capacity: When compared to RAM, ROM typically has a reduced storage capacity. It is often expressed in megabytes (MB) or kilobits (KB).
Advantages of RAM (Random Access Memory):
- RAM provides quick access times, enabling the computer's CPU to access and alter data quickly. This speed influences the system's overall responsiveness and performance.
- RAM is a volatile form of memory, requiring constant power to maintain data. Data may be quickly edited and updated in real-time, enabling quick and effective read and writes operations.
- RAM is used by the computer when it is running as temporary storage for data and program instructions. This transient character allows for flexibility and adaptability.
- RAM makes it possible for the computer to execute numerous programs at once.
- RAM is quite simple to increase in most computer systems. The system's memory capacity may be increased by adding more RAM modules.
Advantages of ROM (Read-Only Memory):
- ROM preserves its recorded data even when power is switched off or interrupted. It is useful for storing crucial firmware and instructions that shouldn't be altered or lost because of this property.
- The information saved in ROM stays intact and unaffected by unintentional alterations or software mistakes, maintaining the integrity of essential instructions and firmware.
- ROM offers long-term storage for important information, boot instructions, and firmware. This guarantees that crucial software elements needed for the system's functionality are constantly accessible.
- ROM may help to increase system security. It is more difficult for hostile assaults or software vulnerabilities to attack the system since the data in ROM is read-only and cannot be changed. As a result, it prohibits unauthorized modification or manipulation of crucial program components.
|

 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now

















