Difference Between RISC and CISC
RISC Processor
RISC stands for Reduced Instruction Set Computer Processor, a microprocessor architecture with a simple collection and highly customized set of instructions. It is built to minimize the instruction execution time by optimizing and limiting the number of instructions. It means each instruction cycle requires only one clock cycle, and each cycle contains three parameters: fetch, decode and execute. The RISC processor is also used to perform various complex instructions by combining them into simpler ones. RISC chips require several transistors, making it cheaper to design and reduce the execution time for instruction.
Examples of RISC processors are SUN's SPARC, PowerPC, Microchip PIC processors, RISC-V.
Advantages of RISC Processor
- The RISC processor's performance is better due to the simple and limited number of the instruction set.
- It requires several transistors that make it cheaper to design.
- RISC allows the instruction to use free space on a microprocessor because of its simplicity.
- RISC processor is simpler than a CISC processor because of its simple and quick design, and it can complete its work in one clock cycle.
Disadvantages of RISC Processor
- The RISC processor's performance may vary according to the code executed because subsequent instructions may depend on the previous instruction for their execution in a cycle.
- Programmers and compilers often use complex instructions.
- RISC processors require very fast memory to save various instructions that require a large collection of cache memory to respond to the instruction in a short time.
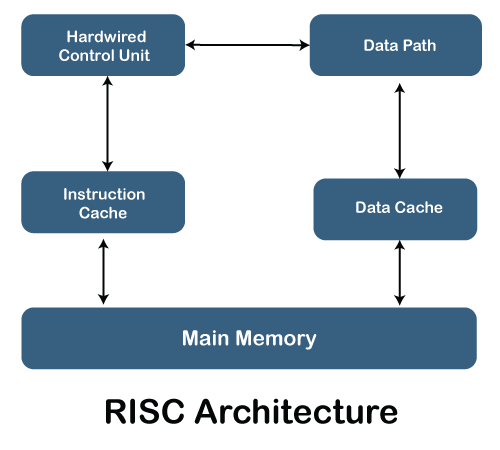
RISC Architecture
It is a highly customized set of instructions used in portable devices due to system reliability such as Apple iPod, mobiles/smartphones, Nintendo DS,
Features of RISC Processor
Some important features of RISC processors are:
- One cycle execution time: For executing each instruction in a computer, the RISC processors require one CPI (Clock per cycle). And each CPI includes the fetch, decode and execute method applied in computer instruction.
- Pipelining technique: The pipelining technique is used in the RISC processors to execute multiple parts or stages of instructions to perform more efficiently.
- A large number of registers: RISC processors are optimized with multiple registers that can be used to store instruction and quickly respond to the computer and minimize interaction with computer memory.
- It supports a simple addressing mode and fixed length of instruction for executing the pipeline.
- It uses LOAD and STORE instruction to access the memory location.
- Simple and limited instruction reduces the execution time of a process in a RISC.
CISC Processor
The CISC Stands for Complex Instruction Set Computer, developed by the Intel. It has a large collection of complex instructions that range from simple to very complex and specialized in the assembly language level, which takes a long time to execute the instructions. So, CISC approaches reducing the number of instruction on each program and ignoring the number of cycles per instruction. It emphasizes to build complex instructions directly in the hardware because the hardware is always faster than software. However, CISC chips are relatively slower as compared to RISC chips but use little instruction than RISC. Examples of CISC processors are VAX, AMD, Intel x86 and the System/360.
Characteristics of CISC Processor
Following are the main characteristics of the RISC processor:
- The length of the code is shorts, so it requires very little RAM.
- CISC or complex instructions may take longer than a single clock cycle to execute the code.
- Less instruction is needed to write an application.
- It provides easier programming in assembly language.
- Support for complex data structure and easy compilation of high-level languages.
- It is composed of fewer registers and more addressing nodes, typically 5 to 20.
- Instructions can be larger than a single word.
- It emphasizes the building of instruction on hardware because it is faster to create than the software.
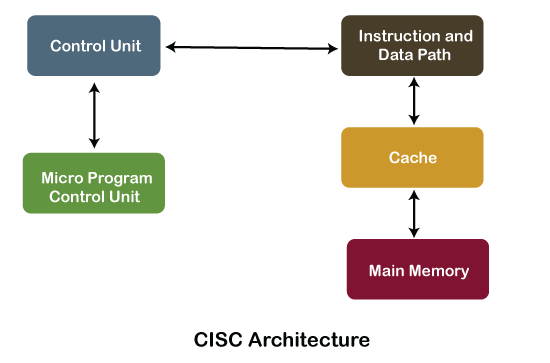
CISC Processors Architecture
The CISC architecture helps reduce program code by embedding multiple operations on each program instruction, which makes the CISC processor more complex. The CISC architecture-based computer is designed to decrease memory costs because large programs or instruction required large memory space to store the data, thus increasing the memory requirement, and a large collection of memory increases the memory cost, which makes them more expensive.
Advantages of CISC Processors
- The compiler requires little effort to translate high-level programs or statement languages into assembly or machine language in CISC processors.
- The code length is quite short, which minimizes the memory requirement.
- To store the instruction on each CISC, it requires very less RAM.
- Execution of a single instruction requires several low-level tasks.
- CISC creates a process to manage power usage that adjusts clock speed and voltage.
- It uses fewer instructions set to perform the same instruction as the RISC.
Disadvantages of CISC Processors
- CISC chips are slower than RSIC chips to execute per instruction cycle on each program.
- The performance of the machine decreases due to the slowness of the clock speed.
- Executing the pipeline in the CISC processor makes it complicated to use.
- The CISC chips require more transistors as compared to RISC design.
- In CISC it uses only 20% of existing instructions in a programming event.
Difference between the RISC and CISC Processors
| RISC |
CISC |
| It is a Reduced Instruction Set Computer. |
It is a Complex Instruction Set Computer. |
| It emphasizes on software to optimize the instruction set. |
It emphasizes on hardware to optimize the instruction set. |
| It is a hard wired unit of programming in the RISC Processor. |
Microprogramming unit in CISC Processor. |
| It requires multiple register sets to store the instruction. |
It requires a single register set to store the instruction. |
| RISC has simple decoding of instruction. |
CISC has complex decoding of instruction. |
| Uses of the pipeline are simple in RISC. |
Uses of the pipeline are difficult in CISC. |
| It uses a limited number of instruction that requires less time to execute the instructions. |
It uses a large number of instruction that requires more time to execute the instructions. |
| It uses LOAD and STORE that are independent instructions in the register-to-register a program's interaction. |
It uses LOAD and STORE instruction in the memory-to-memory interaction of a program. |
| RISC has more transistors on memory registers. |
CISC has transistors to store complex instructions. |
| The execution time of RISC is very short. |
The execution time of CISC is longer. |
| RISC architecture can be used with high-end applications like telecommunication, image processing, video processing, etc. |
CISC architecture can be used with low-end applications like home automation, security system, etc. |
| It has fixed format instruction. |
It has variable format instruction. |
| The program written for RISC architecture needs to take more space in memory. |
Program written for CISC architecture tends to take less space in memory. |
| Example of RISC: ARM, PA-RISC, Power Architecture, Alpha, AVR, ARC and the SPARC. |
Examples of CISC: VAX, Motorola 68000 family, System/360, AMD and the Intel x86 CPUs. |
|


 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










