Single-core processor vs. Dual-core processorIt is vital to evaluate the setup of the server that matches your expectations. The spine of any computer is the variety of CPU (Central processing unit) that will fuel it, the real prototype, and the CPU category. You will add the required amount of System resources, bandwidth, and other alternatives that you utilize issue necessitates from a certain point. It will help determine the distinctions between such a single-core processor and a dual-processor client after reading this blog. If you're starting to design a stainless-steel atmosphere for your volume of work, one of the queries is either to configure a single or dual chipset. This blog should guide you toward certain making the right decisions on your long-term infrastructure requirements. Differences between CPU, core, and ThreadsBack in the day, before computer systems initiated approaching every aspect of human life, we couldn't even assume a several-core CPU. It was a fight of high CPU core data rate. The CPU could process the greater the clock boost, the quicker data. When single-core Processors were no longer appropriate, manufacturing companies began developing various core and thread processors. Soon sufficiently, we began to see different Processors servers on one chipset. But what's the distinction between the Processor, the structure, and the thread? I perused on for a brief description. What is CPU?The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is a piece of equipment responsible for conducting assignments from other computer components. Single-core CPUs have been prepared to accommodate only one sequence of commands at a period. What is Core?A Core is a substantial component of a CPU (Center processing unit). Cores operate as chipsets in a singular CPU chip. The other core the Computer system has, the more activities it can conduct concurrently. One base can accomplish one problem while other cores collaborate on projects assigned to the device. In this manner, total satisfaction is greatly enhanced as opposed to the previous single-core CPUs. Some rational processors operate as individual threads in the center. While they increase efficiency, the logical cores do not align with the visual processors. What's a CPU thread?Threads are like routes that your desktop can carry to process the information. If the Processor has six cores with double threads percenter, there are twelve pathways for the data to be stored. The biggest distinction between threads and substantial cores is that multiple threads cannot be simultaneous. At the same time, two substantial cores can execute two tasks, one core switches between threads. It is going to occur quickly so that it proves that real multi-tasking is taking place. Single Processor Server – Advantages & Statistics
Single processor software runs on a chipset with a single CPU board. It means that the maximum fundamental CPU available in the marketplace dictates the optimum fundamental per server. On the bright side, today's CPU market offers a collection of large modules that can manage substantial volume. The most effective processors pertain to the Intel® Xeon® Extensible CPU group with up to 28 cores and 56 threads. Although, Intel® Xeon® Extensible Processors are now almost entirely composed of a uniprocessor configuration. The most recent processor systems use CPUs belonging to the Intel® Xeon® E group, the predecessor to the Xeon E3 group. The most price option is the Intel® Xeon® E-2186G Processor from the recent Coffee Lake market segment. With six cores logged at 3.8 GHz (4.7 GHz Turbo Enhancement), 12 threads, and 128GB ECC RAM assistance (just after CPU update in the first half), you can execute various distinct facilities 24/7 without any problems. Intel® Xeon® E-2100 CPUs have generated immense gains in productivity, and maintainability to the one processor server's configuration. However, RAM (Random access memory) capacity constraints with one CPU setups persist one of their major flows. Use Cases for one core Processor ServersAdvanced CPU technology allows single CPU servers to accommodate the substantial volume. It is predominantly focused on the CPU method; it supports the servers and many other modules, such as Storage. Although the inconsistency between the single CPU server implementations can be considerable, it is important to categorize them into some categories. It is by no implies includes the applications of servers. It's just an elevated categorization, so you can get a basic idea of utilizing one processor server. High SegmentIf the money permits a top-level one core processor server, you can generate a significant fundamental device for more rigorous tasks. Some of these application areas include several scientific experiments and relevant statistics. In addition, huge information and internet stores can operate successfully on these comprehensive data centers. You can also establish a tiny virtual environment by making a multi-purpose server using a single core. For the cr→me de la cr→me one core→processor servers, we render media storage and watch live. Those beasts with more than 20 cores can certainly manage graphics rendering for ordinary online media usage. Large servers are also suited for future scalability and elevated server structures for advanced tasks. Middle SegmentThe series of a single-core processor server in the middle section is also diversified. A server like this still doesn't divide your lender and manages to execute all of the above-mentioned conditions, but for a bigger company. In relation, middle-range devices are a better match for a reasonable density web store or a tinier online video game server. Companies can also implement the machines as collaborative servers for a proficient communication of knowledge between multiple areas. Since information can modify at a similar time at distinct locations, collaborative effort servers maintain abreast of developments and cope with proper synchronization. There are several numerous technologies for integrative servers, varying from interactive three-dimension experience to design management software. Low SegmentWith low-end single-processor entrance servers, you can create a specific web server for a small company. It involves an email system for a couple or more eligible employees. Cost-effective one core processor servers can offer your team of developer's machines that are strong enough for the research and deployment ecosystem. You can also anticipate configuring your DNS (Domain Name Server) in this section. Most advanced entrance servers support memory error-correcting code (ECC). It adjusts evolving malicious attacks, prevention, and mitigation computer breaks and keeps the system running across the clock. Dual-core Processor Server – Advantages & Statistics
The most important distinction between singular and dual-core processor routers is that the GPU has dual CPU plugs rather than one. It is accompanied by extra advantages such as many PCI routes, two distinct cache memory lies and two RAM socket lies. If the motherboard has 24 cognitive frames, 12 slot machines pertain to the primary CPU and 12 to the secondary CPU. In situations where only a single CPU (Central processing unit) node is used, the CPU cannot utilize a certain RAM stick sequence. It is rarely possible since dual-core processor systems always have both sockets in place. The Intel® Xeon® Gold Processor line-up is the most expensive alternative for dual-core processor configuration. These involve Intel® Xeon® Gold 5118 or Intel® Xeon® Gold 6130 when you required more ram disk and greater clock frequency. One thing to remember about the dual-core processor system is the requisite delay in such structures. It refers to software projects that involve similar data sets. NUMA (non-uniform memory access) is needed to express the obtainable efficiency and reduce disrupting each other effectively. It assists in allocating memory space and systems to each Processor, making frequency periods as small as possible. But, in the workforces designed for these virtual machines, this is not a matter of concern. Dual-core processor systems and uniprocessor structures are generally the best alternatives for space-restricted ecosystems. When a company needs as much computing energy as possible in a single entity, uni-socket configurations must be used to accommodate a huge number of servers in a confined space. Use Cases for dual-core Processor ServersFairly frequently, dual-core processor clustering algorithm, the top of the range processor chips. This makes them well suited for practically every product category and value proposition. Recognize that standard local business implementations will not improve from a high core score. These systems truly look great; there are rigorous uni-threaded CPU implementations, including elevated quantum applications and visualization. The same applies to machine learning techniques, pasture rendering, and comparable HPC operations where a severe CPU measurement is carried out. Structures using a massive database with multiple concurrent inquiries reap the benefits of data centers operated by dual CPUs or as many CPUs as feasible. The more units accessible, the more server activities the system can perform. Due to the increasing amount of power consumption, dual-core processor systems can even manage various database systems on a single computer. You may have observed that we've not created a categorization of the dual-core processor in different sections. The primary cause is that if you're in the industry for a dual-core CPU console, you're already close to the surface in the computer industry's high section. Even now, providers have destination deals for dual-core CPU devices where you can rent a stainless-steel computer without spending a fortune. 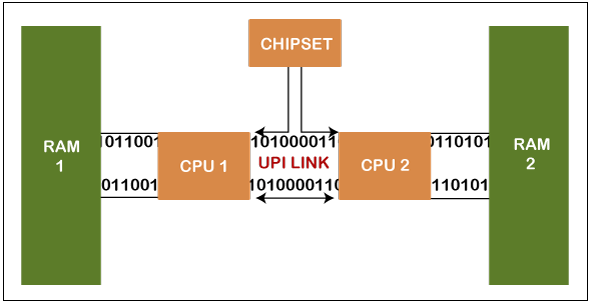
Comparison between One core and a dual-core processor
Higher core-counting computers assuredly outcast those data centers with six or eight cores and a singular Processor chip. Not everyone, nevertheless, is so simplistic. While dual-core CPU configurations are packing vast core qualifies and outshining single-core processor data centers by a massive margin, a few other evaluations have also shown only a little boost in output over one core Processor setup with similar core numbers and synchronous speeds per chip. It pertains to the conditions in which two CPUs operated on similar data at the same time. On the other side, we view significant performance enhancements in dual-core processor data centers when the work schedule is configured for configurations like these. This is certainly relevant when CPUs perform advanced multi-threaded assignments. One of them is the abstracting of assets into digital parts that work on specific things simultaneously. The speed and intensity of the chipset and the actual number are not always harmful. Dual- core processor systems support a lot more RAM than single-core processor systems do. For instance, Intel® Xeon® Gold 5118 Scalable CPUs have an optimum presumed memory capacity of 768GB. On the other side, the Xeon E-2100 CPU path comes equipped with 128GB of RAM after the Graphics adapter has been updated. Cascade Lake Xeon Scalable Processors will support Intel® Optane TM DC Continuous Memory during the first quarter of 2019 to confirm a uniprocessor server's efficiency across a single-core processor configuration. This different type of inexpensive low power memory is conveniently located between NvME, SATA, & SSD. How to choose the right server configurationThere is no wizard criterion for calculating whether you require a low percentage one core processor server or a dual-core processor demon. Several considerations play a crucial role in this judgment. It also relies on whether you'd like to sublet or purchase a computer. It is commonly more expensive to loan a server in the current economy than to establish in computing infrastructure. The explanation is the volume of effort responsible for setting up the appropriate air conditioning, strength, wiring, and everything else you'd like to execute a steady data center. Here are a few of the rules for defining the appropriate bare-metal computer for the corporation:
Next TopicDifference between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










