Abstract Method in JavaIn object oriented programming, abstraction is defined as hiding the unnecessary details (implementation) from the user and to focus on essential details (functionality). It increases the efficiency and thus reduces complexity. In Java, abstraction can be achieved using abstract classes and methods. In this tutorial, we will learn about abstract methods and its use in Java. Abstract classA class is declared abstract using the abstract keyword. It can have zero or more abstract and non-abstract methods. We need to extend the abstract class and implement its methods. It cannot be instantiated. Syntax for abstract class:Note: An abstract class may or may not contain abstract methods.Abstract MethodA method declared using the abstract keyword within an abstract class and does not have a definition (implementation) is called an abstract method. When we need just the method declaration in a super class, it can be achieved by declaring the methods as abstracts. Abstract method is also called subclass responsibility as it doesn't have the implementation in the super class. Therefore a subclass must override it to provide the method definition. Syntax for abstract method:Here, the abstract method doesn't have a method body. It may have zero or more arguments. Points to RememberFollowing points are the important rules for abstract method in Java:
Example of Abstract Method in JavaExample 1:In the following example, we will learn how abstraction is achieved using abstract classes and abstract methods. AbstractMethodEx1.java Output: 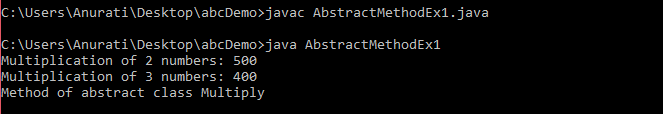
Example 2:By default, all the methods of an interface are public and abstract. An interface cannot contain concrete methods i.e. regular methods with body. AbstractMethodEx2.java Output: 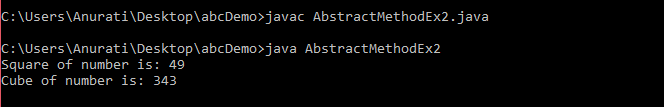
In this way, we have learned about abstract method and its implementation in Java.
Next TopicConvert Text-to-Speech in Java
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










