CRUD Operations in Java
CRUD stands for Create, Read/Retrieve, Update, and Delete, which are the fundamental operations carried out on persistent storage. CRUD involves the use of standardized HTTP methods and is focused on data operations. CRUD operations are data-centric and align with the standardized utilization of HTTP methods. CRUD operations in Java refer to the fundamental operations you can perform on data in a database or data structure. These operations are necessary for maintaining and modifying data in a wide range of applications, from simple managing database systems to complex data storage systems.
These are the standard CRUD operations:
- POST: The technique is used to send data to a certain resource to be processed. On the server, a new resource is created.
- GET: The method requests data from a specified resource. It takes existing data from the server and reads or retrieves it without changing it.
- PUT: The method updates existing data on the server. It sends data to be stored at a specific resource location, replacing the resource's current content.
- DELETE: The method is used to remove data from a specified resource. The resource is removed from the server and is no longer accessible as a result.
Make a menu with the following four basic operations: Add, Search, Remove, and Show Student Details.
Explanation of each operation:
Create (C):
- When performing the "Create" procedure, new data records are added to a data storage.
- In Java, this typically involves inserting new records into a database or adding new objects to a collection or data structure.
- For databases, you can use SQL statements (e.g., INSERT INTO) or Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) frameworks like Hibernate or JPA to create records.
Read (R):
- The "Read" operation is about retrieving data from a data store.
- Java allows you to access data from a variety of sources, including external APIs, files, and databases.
- For databases, you can use SQL queries (e.g., SELECT) or Java libraries like JDBC to retrieve data.
- Reading data from files involves file I/O operations, and for external APIs, you use HTTP requests and JSON/XML parsing to fetch and parse data.
Update (U):
- To modify already-existing data records, utilize the "Update" operation.
- In Java, you can update data in a database by executing SQL statements (e.g., UPDATE) or using ORM frameworks.
- For collections or data structures, you directly update the objects by modifying their attributes.
Delete (D):
- The "Delete" procedure includes deleting data records from a data the server.
- In Java, you can delete data from a database using SQL statements (e.g., DELETE FROM) or ORM frameworks.
- For collections or data structures, you remove objects or elements from the collection.
CRUD Operations for Student Management System in Java
A Student Management System is a crucial application in educational institutions that allows efficient management of student data. The fundamental capabilities which allow for the processing of this data within a database are known as CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, and Delete). There will be four primary choices on the menu: Add, Search, Remove, and Display student information.
Files to be created:
1. StudentRecordLinkedList.java:
StudentRecordLinkedList.java serves as the main program file. It handles user interaction through a menu-driven approach, allowing users to add, delete, update, search, and display student records. The class instantiates the StudentRecordManagement class and provides a user interface for managing student data.
2. StudentRecordManagement.java:
StudentRecordManagement.java contains the StudentRecordManagement class, which encapsulates the logic for managing student records. It includes methods to add, delete, update, search, and display student records using a LinkedList data structure. The class ensures operations like adding new records, updating existing ones, and searching for records based on user input.
3. Record.java:
Record.java defines the `Record` class, representing individual student records. It includes private instance variables for name, idNumber, and contactNumber, along with constructors, getters, setters, and a toString() method. This class encapsulates the data structure for each student record, enabling the program to store and manipulate student information effectively.
Algorithm:
Step 1: Initialize Classes and Imports
- Import necessary Java packages: Java.util.Scanner and Java.util.LinkedList.
- Define a class Record with private instance variables for name, idNumber, and contactNumber.
- Implement constructors, getters, setters, and toString() method for the Record class.
Step 2: Create StudentRecordManagement Class
- Define a class StudentRecordManagement to manage student records.
- Declare a LinkedList of Record objects.
- Implement methods within the class for add, delete, update, search, and display operations.
Step 3: Main Method Initialization
- Inside StudentRecordManagement class, create the main method.
- Instantiate StudentRecordManagement class.
- Hard code a sample student record and add it to the linked list.
Step 4: User Menu
- Implement a simple text-based menu for user interaction with options:
- Add a new student record.
- Delete a student record that already exists.
- Update the existing record of the student.
- Search for a student record.
- Display all student records.
- Exit the program.
Step 5: User Input Handling
- Use the Scanner class to handle user input for various operations.
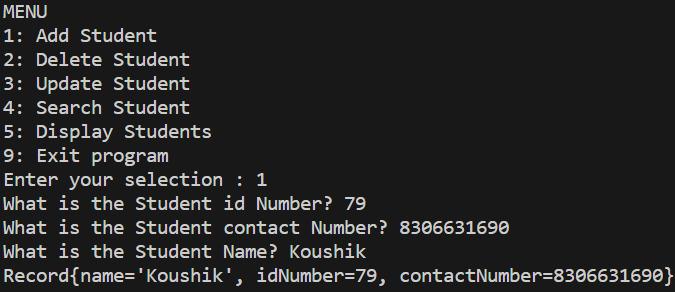
Step 6: Implement Add Operation
- Prompt user for student information (ID number, contact number, name).
- Please create a new Record object with the provided data and add it to the linked list.
Step 7: Implement Delete Operation
- Prompt the user for the ID number of the student to be deleted.
- Search the linked list for the student record with the given ID number and remove it.
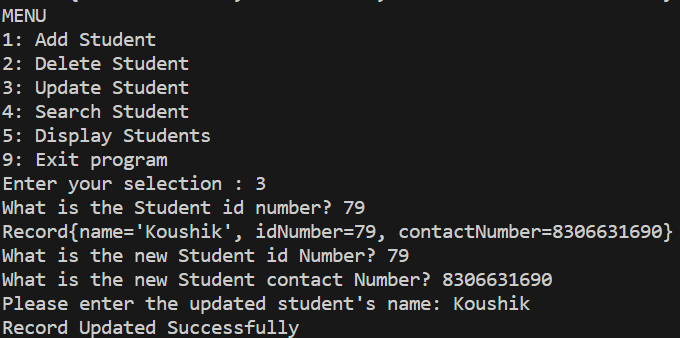
Step 8: Implement Update Operation
- Prompt the user for the ID number of the student to be updated.
- Search the linked list for the student record with the given ID number.
- Prompt users for new information and update the student record.
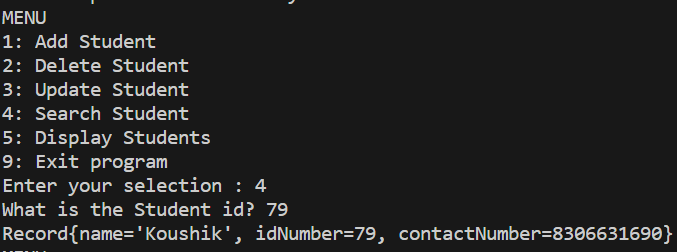
Step 9: Implement Search Operation
- Prompt the user for the ID number of the student to be searched.
- Search the linked list for the student record with the given ID number and display it if found.
Step 10: Implement Display Operation
- Iterate through the linked list and print each student record.
Implementation
Filename: StudentRecordLinkedList.java
Filename: StudentRecordManagement.java
Filename: Record.java
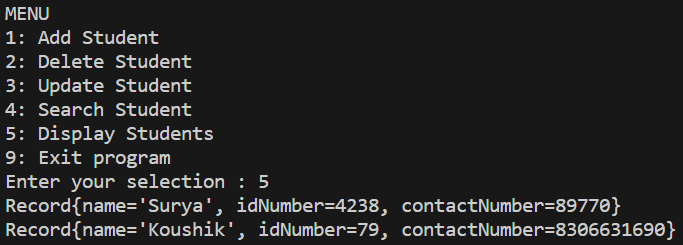
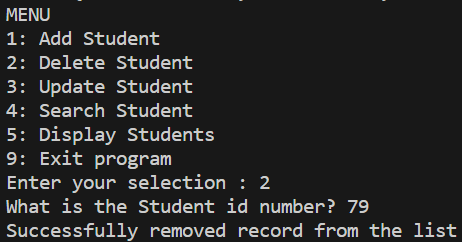
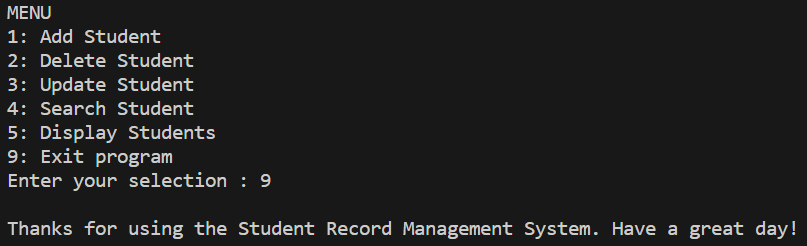
Output:
Add
Update
Search
Display
Delete
Exit
|







 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now









